Peds Oncology Flashcards
Calculate an ANC
you need WBC, Polys, Bands
- Polys + Bands
- Multiply total by WBC
- Multiply this product by 10 = ANC
ANC > 1000 is normal
ANC < 1000 is neutropenic
List features of concerning LAD

- Persistent >4-8 weeks
- Progressive
- > 2 cm
- Generalized
- Non-tender
- Firm, rubbery, rock-hard
- Matted (several nodes connected together)
- Fixed
- Axilla, infra or supraclavicular or inquinal areas
What is the MC cancer in kids (and the MC blood cancer)?
Which cell lines are down initially?
What will you see on a peripheral blood smear?
ALL (Acute lymphoblastic leukemia)
►WBC (leukopenia)
►platelets (thrombcytopenia)
lymphoblasts seen on peripheral smear
How long is the Tx for ALL (in girls vs boys)?
Tx lasts 2 years for girls and 3 years for boys
(risk of testicular reoccurrence)
What might be some CC of someone not yet diagnosed, but who has ALL?
CC: fever (persistent or recurrent), infections, easy bruising, obvious petechial/purpuric rashes
additional Sx at presentation may include: bone pain, new onset limp or joint pain, easily fatigued

How long does it take a child with lymphoblasts in bone marrow to become symptomatic?
lag time from onset of lymphoblasts in bone marrow→ Sx/clinical presentation is less than 1 month (therefore, don’t expect weight loss as see in adult cancer presentation)

What PE findings are common with ALL?
PE: generalized LAD (including concerning areas: axiallary, supra/infraclavicular, inguinal), hepatosplenomegaly (lymphoblasts infiltrate lymph nodes, spleen and liver)
Calculate an Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC)
what defines neutropenia?
what is one consequnce (as far as wound infection goes) in someone with neutropenia?
ANC = WBC (in thousands) x (%neutrophils + %bands)
*neutropenia= ANC <500 or <1000 and still falling
**pts with neutropenia will not produce pus if sustain wound infection as have too few WBCs

List a DDx for LAD in kids.
- localized or systemic infxn (bacterial or viral)
- abscess/ lymphadenitis (would have erythema surrounding swollen nodes)
- EBV
- HIV
- cyst
- benign or malignant tumor
- systemic illness (eg JIA)
With regards to LAD, what are some of the concerning PE findings (for potential of cancer) ?
- persistent LAD (>4-8 weeks) or progressive LAD
- size >2cm
- generalized, non-tender, firm, rubbery (abscess), or rock hard or fixed nodes
- several nodes that appear to be connected together (matted)
- LAD outside cervical/ mandibular region (axiallary, supra/infraclavicular, inguinal)
- “shotty” LAD (small, pea-sized in cervical area) is not overly concerning in peds
- hepatosplenomegaly
What work-up would you do in a child with concerning LAD?
- CBC, ESR (acute-rises in 1-2 days)
- CRP (if greater than a week since onset)
- EBV titers (in young kids titer is better than monospot)
- PPD (if cough, fever, night sweats, or possible exposure→r/o TB)
- LDH + uric acid (high levels indicate high cell turnover, which indicates malignancy)
- Ultrasound helps evaluate for a cyst
What would you NOT due to work-up a child with concerning LAD?
Do NOT biopsy a node in primary care. Refer to oncology.
- risk of spreading cancer in process of Bx
- Bx indicated with:
- persistent, progressive or unusual LAD
- abnormal CXR
- systemic illness

What exam should be done on all children (regardless of CC)?
ABDOMINAL exam
ANY abdominal mass in a child is a malignancy until proven otherwise
Describe Wilm’s tumor (nephroblastoma).
A kidney cancer that is the MC abdominal malignancy found in kids (2-5yo) with an abdominal mass
Sx: none or abdominal mass/swelling/pain, fever, blood in urine
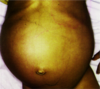
Describe a pediatric neuroblastoma.

Neuroblastoma= undifferentiated sympathetic nervous tissue
Presents in various ways →MC is at the adrenal gland (causes an abdominal mass)…could also be paraspinal, cervical or posterior mediastinal
Metastases are common (bone pain, liver/lymph node involvement, subQ nodule)
Sx: prolonged, severe watery diarrhea or catecholamine-induced HTN
Describe key signs and symptoms associated with osteosarcoma, Ewing sarcoma, retinoblastoma and rhabdomyosarcoma
osteosarcoma- long bones, peak incidence in teens, “sunburst patten on x-ray
Ewing sarcoma- pelvis or shoulder, “onion peel” pattern on x-ray
retinoblastoma- median age at presenation is ~2yo, leukocoria (white instead of “red light reflex”)
rhabdomyosarcoma- mass, hard on palpation, can occur anywhere–> MC site is head/neck, bimodal peak in young kids (2-5yo and teens)
Osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma are primary bone cancers.
What types of bone pain are especially concerning for these pathologies?
Concerning bone pain includes:
- persistent or progressive,
- occurring at night,
- associated with swelling, mass, or decreased ROM
Both rhabdomyosarcoma and retinoblastoma can affect the eye region.
Distinguish the pathology of the two.
Rhabdomyosarcoma = malignancy of skeletal muscle
Retinoblastoma is a malignancy of embryonic retinal cells
→white “red eye reflex” is sign of retinoblastoma

Understand the late effects of cancer treatment.
- Growth can be affected→ radiation for ALL, CNS tumors, head/ neck CA, so watch growth curves
- Learning problems, precocious or delayed puberty, hypothyroidism→ d/t previous cranial radiation
- Chemotherapy→ pulmonary fibrosis, fertility issues
- Second malignancies→ underlying genetic disorder with tissues in the field of previous radiation
- AML→ from various chemotherapy agents
What are some oncologic emergencies?
- tumor lysis→ releases large amounts of K+, phosphates and nucleic acids into circulation→renal damage
- very high WBCs (>50K)→ impede circulation
- neurologic symptoms→ spinal cord compression, increased intercranial pressure (spinal cord damage or brain stem herniation)
- immunocompromised→fever (≥ 101F) and/or neutropenia may mean SBI
- send to ED or directly to oncology clinic ASAP
- need full septic w/u, including bacterial and fungal cultures of chemotherapy port and empiric broad spectrum abx until cultures return


