Pediatrics Flashcards
Heart sound that is normal in children?
etiology
best heard
sounds like
S3
etiology- Due to rapid ventricular filling
best heard - LLSB, or apex
_sounds lik_e - low pitched early diastolic
pediatric murmur characterized by vibratory, musical buzzing?
heard best?
timing?
Stills
Small aortic root/ascending aortic diameter -> high velocity flow across LVOT-ascending aorta
heard best-
- 3rd intercostal space
- LLSB
- apex
- louder in suprine position
timing- systolic ejection
name benign and malignant pediatric murmurs
benign -
S3
Peripheral pulmonary flow murmur (PPS):
Still’s murmur:
Venous hum:
Malignant: VSD
•Soft, hollow, continuous murmur, louder in diastole
heard best?
Venous hum:
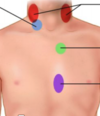
below R clavicle
pathologic murmur first noticed in newborn
heard best?
diastolic / systolic?
LLSB
Short systolic or holosystolic
where are these pediatric murmurs heard best?
S3
Peripheral pulmonary flow murmur (PPS):
Still’s murmur:
Venous hum:
Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
S3 -
LLSB,
apex
Peripheral pulmonary flow murmur (PPS):
RUSB or LUSB
Radiates to back & axilla
Still’s murmur:
3rd intercostal space
LLSB
apex
Louder in supine position
Venous hum -
below R clavicle
eliminated lying supine
Ventricular septal defect (VSD) - LLSB
pediatric murmur heard best at
RUSB or LUSB & Radiates to back & axilla
Peripheral pulmonary flow murmur (PPS):
Common benign functional murmur
•newborns & infants, Usually disappears by 1 y
venus hum Can be eliminated by
- lying supine
- changing head position
- JV compression
Peripheral pulmonary flow murmur (PPS): is caused by
turbulence from size discordance of larger main PA-smaller branch PA
stills murmur is caused by
Small aortic root/ascending aortic diameter -> high velocity flow across LVOT-ascending aorta
murmur that is Louder in supine position
Still’s murmur:
what are the murmurs?
Low-pitched, early diastolic sound
•Mid systolic ejection murmur
Short systolic or holosystolic
Vibratory/musical/buzzing SEM
Soft, hollow, continuous murmur, louder in diastole
Low-pitched, early diastolic sound - S3
•Mid systolic ejection murmur - PPS
Short systolic or holosystolic - VSD
Vibratory/musical/buzzing SEM - Stills
Soft, hollow, continuous murmur, louder in diastole - venous hum
what is the best location to hear these murmurs?
venous hum
stills

what murmur is the only one that radiates?
where does it radiate?
PPS
back & axilla
what are the 2 hip examination maneuvers?
what age are they preformed
performed up until 3m of age)
Barlows
Ortolanis
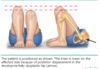
describe Barlow’s test and positive findings
- flex and ADDUCT the hips by bringing thigh near midline
- apply light pressure on knee and direct force posteriorly
positive findings:
femoral head dislocated posteriorly fro acetabulum
dislocation is palpable as head slips out of acetabulum
confirm w/ Ortolani’s test

describe Ortolanis test

- Hip evaluation important to r/o ____?
- All infants should have serial hip examinations until _____??
Developmental Dysplasia of Hip (DDH)
until they are walking
Risk factors for Developmental Dysplasia of Hip (DDH)
- F
- In utero breech position
- +FHx
hip special tests according to age
newborns
infants
older
newborns (performed up until 3m of age)
•Barlow
Ortolani maneuvers
infants
- Evaluation of hip abduction -> limited abduction: concerning
- Evaluation of symmetry of gluteal folds -> asymmetry: concerning
- Galleazzi test - used to assess for hip dislocation, specifically testing for developmental dysplasia of the hip.
older - Trendelenburg sign (weak hip abductors)
describe galleazi test and what it is udef for
infant hip exam: assess for hip dislocation, specifically testing for developmental dysplasia of the hip.