Pediatric rashes Flashcards
Milia

Molluscum contagiosum

Cradle cap?
Seborrheic dermatitis affecting primarily the scalp.

Hemangioma
Natural hx: May present as patch of telangiectasias at birth. Proliferation: age 0-1, bright red raised nodule. Involution: Age 1-9. Deeper red/violet, regression in size.
Management: Observation. Topical beta blocker (eg propranolol) for ulcerated or cosmetically sensitive areas (eg face)
Complications: ulceration/scarring; vision impairment if near eye; Life-threatening if near airway.

Stork bites
aka angel kisses

fifth disease
Erythema infectiosum:
“Slapped cheek first”
Then lacy/reticular rash on trunk, extremities. Exacerbated by heat

Mongolian spot
dermal melanocytosis

seborrheic dermatitis
Yellow/scaling (cradle cap if seen just in scalp)
Red/greasy plaques on rest of body = nonitchy.
Can affect genital area.
Self limiting
Types of diaper rash
Variant 1:
spares creases. Tx = zinc oxide
Variant 2 - candidal type
Beefy red, papular, + satellite lesion. Involves creases.
Tx = antifungal
infantile eczema/atopic dermatitis
Risk factors: low humidity; relatives w/ eczema, allergies, asthma
Clinical features: In babies - itchy red scaly crusted lesions on extensor surfaces, trunk, cheek, scalp. Spares diaper area
In older kids - lichenified plaques in flexor surfaces - eg antecubital
Universally pruritic, but babies cannot scratch so become agitated.
Tx = aggressive moisturization +/- steroid ointment
Complications: Eczema herpeticum; cellulitis/abscess; discomfort interfering w/ daily activities/sleep
Pathogenesis: epidermal dysfunction due to improper synthesis of stratum corneum components

intertrigo
Moisture trapped in skin folds causes irritation (eg neck, axilla –> intertriginous areas)
Causes irritation
Can be worsened by infection w/ bacteria, yeast.
Tx: keep area dry - vigilant towel trying after bathing baby. May need to give antifungal meds.

congenital nevomelanocytic nevi
pigmented plaques, often w/hair.
have an increased rate of transformation to melanoma (risk increases with size)

cafe au lait spots
If >6 spots >5 cm in diameter, r/o NFM, Mccune Albright

coxsackie
Painful vesicles in posterior pharynx.
May cause dehydration b/c kid won’t drink due to pain.
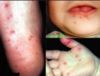
impetigo
honey crusted lesion.
Stap, Strep

Henoch Schonlein purpura
Non-blanching.
IgA vasculitis
Abdominal pain - may have arthralgia, renal involvement. Can cause intussusception.

Eczema herpeticum
Potential complication of severe atopic dermatitis. Superinfection w/ herpes simplex virus can cause vesicular eruption on preexisting inflamed skin. Pts often have fever and pain.
Erythroderma (exfoliative dermatitis)
Erythema and scaling in >90% of body. Bright red patches coalesce and gradually peel.
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Pathogenesis: S. aureus exfoliative toxin
Clinical features: fever, irritability. Generalized erythema, blisters. Epidermal shedding (Nikolsky sign). Mucosal surfaces typically spared. May have nasopharyngeal colonization or a primary skin lesion.
Mgmt: antistaphylococcal antibiotic (nafcillin, vanc); wound care
Bullous impetigo
Localized form of Staph scalded skin syndrome also caused by exfoliative toxin-producing S aureus.
Pts appear well, with blisters confined to primary area of infection.
When ruptured, blisters have honey-colored crust.
Erysipelas
Bacterial infection (GAS) of dermis presents w/ well-demarcated, warm tender area of erythema. Overlying bullae can develop in severe cases, and pts often have constitutional symptoms (fever, chills).
Erythema multiforme
Self-limited reaction to certain infections (Eg herpes simplex) that manifests as targetoid lesions. Lesions may have central bullae, but Nikolsky sign is negative.
Scarlet fever
Erythrogenic toxin-producing strains of GAS, presents w/ fine, pink, sandpaper-like rash following episode of pharyngitis in kids. Prominent in flexural areas and often desquamates but does not cause blistering or a positive Nikolsky.
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
Extensive (>30% body surface area) skin blistering and erosion typically triggered by medication. Positive Nikolsky.


