Pediatric Derm Flashcards

Mongolian Spot
What are Mongolian spots
Collection of melanocytes in the dermal layer
Also known as congenital dermo-melanocytosis
What are the signs and symptoms of Mongolian spots
Flat blue or gray lesions with well-defined margins
Commonly found in the presacral region
More common dark skinned races
Often confused with bruises
Will fade with time

Erythema toxicum
What are the signs and symptoms of erythema toxicum
Small papules/pustules on an erythematous base
Usually appear after first day of life
Lesions will contain mostly eosinophils

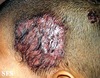
Seborrheic dermatitis
“Cradle Cap”
What are the signs and symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis
Erythematous, try, crusting lesions on the face, scalp, perineum, postauricular and intertrigenous Areas
less pruritic than eczema
What are intertrigenous ares
Area where two surfaces of skin touch or rub together
What is the treatment first of seborrheic dermatitis
Baby oil
Dandruff shampoo (Hypersensitivity to yeast)
Hydrocortisone for severe cases

Milia
What is Milia
Small inclusions cyst
Epstein’s pearls in the mouth are common
Self-limited, benign

Cutis Marmorata
What is cutis marmorata
Lacy pattern on skin
Represents is a vasomotor response to cold stress
Persistent form is seen with trisomy 21 and trisomy 18
Usually decreases with warmth to the child

Neonatal Acne
What is neonatal acne
Comedomes caused by an excess in circulating androgenic hormones
No treatment usually required

Salmon Patch

Stork Bite
What is a salmon patch
Flat vascular lesion commonly seen over the eyelids, glabella, the nucal areas, symmetric
Usually disappears time
Distinguish from Portwine stains (permanent, unilateral, more intensely colored)

Capillary Hemangioma
What is a capillary hemangioma
Macular strawberry colored lesions
Grow quickly in the first your life
99% regressed completely by age 9 with no treatment
When is treatment indicated for capillary hemangioma
Becomes Caverness (Kasabach merrit)
Is in the airway (suggested by cutaneous lessions in a beard distribution)
Threatens vision
What is kasabach merrit syndrome
Hemangioma with thrombocytopenia
Vascular tumor leads to decrease in platelets
May become cavernous

Portwine stain

Cafe Au Lait spots