PE - Agar recognition Flashcards
(27 cards)

Staphylococcus aureus and S. epidermidis on agar plate
S. aureus
- colonies are 1-2 mm in diameter, water- insoluble gold-coloured pigment is produced
S.epidermidis
- colonies are 1-2 mm in diameter, water-insoluble chalk-white pigment is produced

Staphylococcus aureus on blood agar plate
colonies are 2-3 mm in diameter, regular, round shaped, glittering with golden yellow pigment, which does not penetrate into the medium (lipid soluble=water-insoluble).
Around colonies, there is a strong beta-hemolytic zone

Staphylococcus epidermidis Blood-agar
colonies are 2-3 mm in diameter, regular, round shaped, water-insoluble chalk- white pigment is produced, which does not penetrate into the medium and usually no haemolysis is seen around the colonies

S. epidermidis (S) and S. saprophyticus (R) with novobiocin disc
S. epidermidis
- grows readily on simple agar medium with shaped, glittering, chalk white colonies, novobiocin sensitive (large zone of inhibition).
S. saprophyticus
- typically non- pigmented, novobiocin-resistant (no zone of inhibition).

Streptococcus pyogenes on blood agar
colonies are very tiny (0.1 mm), round shaped, colourless=no pigment is produced, strong - haemolysis is seen around the colonies, the haemolytic zone appears to be relatively large ( 1 cm in diameter) as to compared to the diameter of the colonies

Streptococcus mitis on blood and chocolate plates
Blood-agar colonies are very tiny, no pigment is produced, alpha-haemolysis is seen around the colonies
Chocolate-agar colonies are very tiny, no pigment is produced, alpha-haemolysis is seen around the colonies

Streptococcus pneumoniae on blood agar plate (optochin S) and chocolate agar plate
Blood-agar colonies are shiny and very tiny with an autolysis centre (umbilicus= Older colonies have a so called umbilicus because of autolysis), no pigment is produced, alpha-haemolysis is seen around the colonies = greyish, glitering, round shaped with a diameter of 1-2 mm
Chocolate-agar colonies are shiny and very tiny with an autolysis centre (umbilicus), no pigment is produced, alpha-haemolysis is seen around the colonies
Capsule-producing strains grow with large, mucoid appearance.

Haemophilus influenzae on chocolate agar
tiny, dewdrop-shaped colonies with nose-cold discharge- like odour.
(Since it is naturally resistant to vancomycin, in a throat culture always look for it around the vancomycin disc)


E.coli on agar plate
Esherichia coli:
- intermediate sized, glistering, iridescent, “sheen”, colourless colonies.

E. coli on EMB
intermediate sized, typical strong lactose-fermenting, glistering, iridescent colonies, those are green-black with a metallic sheen

Proteus on agar and EMB (swarming!)
wavelike swarming pattern (no individual colonies are seen, bacteria spread through the entire surface of the plate)
EMB: Proteus spp.
Do not ferment lactose and thus, produce nonpigmented, semitranslucent, transparent colonies

Pseudomonas on agar plate
Agar-plate characteristic large, oval shaped colonies, two kinds of different water- soluble pigment are produced (fluorescein - yellow, pyocyanine - blue) that add up to green and also discolour the medium (silver-grey colour), and cultures have a grape- or linden-tree-like odour
Blood-agar plate + beta- haemolysis

Klebsiella on agar plate
large, (2-3 mm in diameter), round- shaped, raised, sticky, glistering, mucous colonies (because of the capsid production)
Klebsiella on EMB plate
large (4-5 mm in diameter), mucoid, glistering, raised, deep purple coloured colonies

Salmonella on bismuth sulphite medium
Colonies of Salmonellae appear to be black because of H2S production


E. coli and Salmonella on brillant green medium
Colonies of Salmonellae appear to be colourless
Colonies of E. coli appear to be red if grown
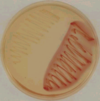
E. coli and Shigella on DC medium (deoxycholate citrate agar)
Colonies of Shigellae appear to be colourless.
Colonies of E. coli appear to be red if grown.

Faeces of patient with dysentery on DC medium (E. coli + Shigella)
- Mainly lactose non-fermenter, colourless colonies are cultivated.

Russel medium
Containing: brilliant sugar = dextrose, saccharose, lactose - Andrade indicator: decolourised fuchsine
(Acid turn in red)
Lactose + dextrose fermentation + gas production:
- red + burst (bubbles)
- (e.g. E.coli; klebsiella)
Lactose -, dextrose +, gas production:
- Butt is red, slat is not
- (e.g. proteus; salmonela)
Lactose -, dextrose fermentation:
- whole culture medium is red (no bubbles)
- (E.g. salmonela typhi; shigella)

Urease test!
NH2-CO-NH2 (ureum) –> CO2 + NH3 (ammonia)
Christensen medium: indicator (phenol red)
- urease +: purple (proteus, H.pylori, Klebsiella)
- urease -: citric yellow

Corynebacterium on Clauberg


Löffler medium

Mycobacterium tuberculosis on Löwenstein-Jensen medium
after 2-8 weeks incubation.
The colonies are rough and buff coloured (yellow bread cramps).
It is difficult to remove the growth from the medium.

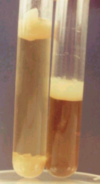
Leptospira in Korthof medium
Rabbit serum (10%) containing fluid medium in small tube.
(pH=7,2-7,6; 28-30°C, 1-2 weeks).
+: opacity, like cigarette smoke

Bacillus cereus on agar and blood agar plate
Agar large but flat, jelly- fish (medusa)- shaped colonies with number of horizontal projections (so called runways)
Blood agar large but flat, jelly-fish (medusa)-shaped colonies with number of horizontal projections (so called runways) + beta haemolysis