PCS adhesive bridges Flashcards
bridge definition
A bridge is a dental prosthesis that is attached to the teeth in such a manner that it cannot be removed for cleaning: it spans a gap in the dentition and is an option instead of an implant restoration or a removable partial denture or no treatment
adhesive bridges
are retained by a metal wing(s) which are bonded onto minimally prepared tooth enamel
- Conservative approach
- Suits young teeth adjacent to saddle
- Cantilever design preferred where possible
- If fixed-fixed then parallelism between preparation on abutment teeth is required
- Bonding skills
- Retentive durability poorer than conventional bridges
- Prognosis better where minimal occlusal interferences exist
4 bridge retention increased by
- Maximising available bonding surface area
- Sandblasting fitting surface of wing
- Cutting groves, rests, notches and locating margins
- Incorporating rest seats to maximise bonding surface area and to direct axial forces
clinical indications for adhesive bridges (12)
- Missing teeth
- Distal extension (SDA)
- Immediate replacement
- Long term temporary (Healing)
- Unrestored abutments
- Sound abutments
- Young teeth
- Patients with time/cost/tolerance issues
- Medically compromised patients
- Space maintainers
- Post orthodontic stabilisation
- Periodontal stabilisation
11 clinical contra-indications for adhesive bridges
- Insufficient area for bonding
- Insufficient quality of bonding surfaces
- High caries rate
- Poor patient motivation and monitoring
- Long span bridges
- Discrepancy between saddle size and tooth width
- Significantly tipped or misaligned abutments
- Diastemas
- Translucent incisal edges
- Insufficient occlusal clearance
- Sports
9 advantages of adhesive bridges
- Minimal tooth preparation
- Unrestored abutments
- Immature pulps
- Small teeth
- Expediency
- No temporary required
- Ease of preparation / impression
- Time saving
- Fewer visits
- Cost
- Conservative
- Quick & simple
- Non – specialist
- Cost effective
- Convertibility
- Self diagnostic
- Increased patient acceptance
9 disadvantages for adhesive bridges
- Increased failure rate
- Partial debonds
- Aesthetics
- No space redistribution
- Metal greying out
- Short spans only
- Provisional restorations problematic
- Occlusal considerations
- Interferences of retainer on guidance
- Guidance on pontics
- No trial period possible
- Dramatic failure
- Poorer remuneration
describe restoration here

Traumatic loss of tooth 11
Anterior cantilever adhesive bridge retainers teeth 13, 12, pontic 11
Prefer only one abutment because allows better oral hygiene and less interference from divergent guidance paths (cantilevers more successfully anteriorly)
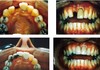
why is only one abutment tooth preferred for anterior adhesive bridges
allows better oral hygiene and less interference from divergent guidance paths (cantilevers more successfully anteriorly)

descirbe restoration here

anterior cantilever bridge
retainer 11, pontic 12
when do most failures occur
soon after placement
- Posterior more successful
- anterior Cantilever more successful
- Consequences of failure limited
5 factors affecting resin bonded bridges success
- Quality of the bonding surface
- Quality of the bonding procedure
- Design of the retainer
- Design of the pontic
- Occlusal management
5 points retainer design for adhesive bridge
rigid metal framework
- 0.5mm for lingual and approximal areas
- occlusal areas 0.1mm minimum
Maximum coverage
- Maximises surface for bonding
- Increases resistance form
Outline form
- Defined margins
- Emergence profile
Occlusal contacts
- Full coverage
- Struts
Resistance and retention
- Wrap around to counter lateral displacement - 180° Ideal
- Buccal extensions of approximal metal contacts
- Circumferential wrap
- Occlusal rests
- Grooves
- Cingulum rests
- Restricted path of insertion
5 basic points for pontic design
- Aesthetic
- Sanitary
- Domed for posterior
- Modified ridge lap for Anterior and posterior
- Wide embrasures where possible
resistance and retention designed into retainer for adhesive bridge
- Wrap around to counter lateral displacement - 180° Ideal
- Buccal extensions of approximal metal contacts
- Circumferential wrap
- Occlusal rests
- Grooves
- Cingulum rests
- Restricted path of insertion
framework design for adhesive bridge
- Determined by preparation for retainer design
- Base metal construction
- Rigidity
- Occluso-gingival height important posteriorly
- Bucco-lingual width important anteriorly
- Strength of connectors
- Short spans
- Avoid curving round arch
- Avoid locking teeth with divergent guidance paths
tooth prep with
fine diamonsds
speed increasing handpieces
polishing discs
minimal vs heavy anterior prep

occlusal registration for adhesive bridge
- Importance:
- Difficulty of adjustment pre-fit
- Danger to bond post-fit
- Anterior Guidance
- Inter-occlusal record
- Importance of opposing cast accuracy
- Facebow registration
- Opposing tooth reduction
- Laboratory made guides
minimal vs heavy posterior preparation
- Minimal
- Undercut removal only
- Limited path of insertion/withdrawal
- Heavier prep
- Clearly defined margins
- Occlusal rests
- Grooves

describe this

adhesive bridge
retainer 35, pontic 36, retainer 37



