PCAP Flashcards
(95 cards)
State the differences between a compiled language and an interpreted language.
Compiled language:
After compilation, the program can be freely distributed without the need of the interpreter. You must have a compiler for each type of system. Faster execution. Examples: C, C++, Go.
Interpreted language:
The translation is done each time the program runs. The interpreter must be installed in all the computers to make the code run. Slower execution. Examples: PHP, Ruby, Python, Java.
How do you use binary, hexadecimal and scientific notation in Python?
Binary: 0bnnnnnnn
Hexadecimal: 0xnnnnnnn
Scientific notation: nEn, example: 3E8
Large numbers: use underscores (_) to separate big chunks of numbers
What are the three different ways you can specify a range in Python?
-
range(2,8,3): range(start, end, increment). The end does not touch
List two ways in which you can slice a sequence in Python:
-
Slice function: (,)
- Returns a slice object similar to a range function.
- You must specify the start, end and step.
lista = [i for i in range(10)]x = slice(start=None, end, step=None)sliced = lista[x]
-
Bracket slicing - Index Operator: (:)
lista = [i for i in range(10)]x = lista [start : end : step]
Calculate the module of the following operations:
4 % 6 =2.33 % 2.1 =10 % 3 =
RAr(AbArAb)
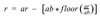
What are the different tuple methods?
Leia Meditated Meanwhile Surfers Inhaled Clever Irishmen.
len, min, max, slice, in, count, index
List two ways in which you can declare a tuple.
-
Parenthesis:
my_tuple = (1, )(s1, s2) = (1, 2)
-
No parenthesis:
my_tuple = 1, 2, 3s1, s2 = 1, 2
random Module most used functions and methods:
Strong Robocop Romanced Round Croutons Slowly
Seed, Random, Randrange, Randint, Choice, Sample
Useful methods of the datetime.date class:
-
.weekday():0: Monday -
.isoweekday(): 1: Monday (ISO) -
.isoformat():string : YYYY-MM-DD -
.replace():replaces the specified parameters. -
.strftime():readable string format.
Useful methods of the datetime.datetime class:
.today(), .now()
.strftime().strptime()
-
.fromisoformat():returns a datetime coming from a string in ISO format .isoformat()
-
.combine():combines a date and a time .replace()
Enlist all the different formatting styles that can be used with strftime:

Useful methods of the Calendar.Calendar class:
Generators:
-
.itermonthdates(year, month):datetime objects. -
.itermonthdays(year, month):int (day#). -
.itermonthdays2(year, month):tuple (day#, weekday#) -
.itermonthdays3(year, month):tuple (year#, month#, day#) -
.itermonthdays4(year, month):tuple (year#, month#, day#, weekday#)
Lists:
-
monthdatescalendar(year, month):datetime (separated in weeks). -
monthdayscalendar(year,month):int (day#) (separated in weeks). -
monthdays2calendar(year,month):tuple (day#, weekday#) (separated in weeks).
What is a Python generator?
- collections
- ⇒ Iterator()
- ⇒ Generator (yield, list-like)
- ⇒ [], (), {}, set()
- ⇒ str(), b””, bytearray(), range(), map()
- ⇒ Iterator()
-
Generator:
-
yieldstatement:
-
def gen():
x = 0
for x in range(10):
if x%2 :
yield x
- list-like:
it = (x for x in range(10) if x % 2)
(PARENTHESIS)
tkinter
How do you create the root window in an OOP program?
root = tkinter.Tk()app = Application(root)-
App:
def \_\_init\_\_(Frame):super().\_\_init\_\_()self.main = tkinter.Frame
- Pack
self.mainand this will be the master of all widgets.
tkinter
What is the process to create a RadioButton?
1. Create a variable: tkinter.BooleanVar, DoubleVar, IntVar, StringVar.
- Set a default value for it.
- Create the radiobutton:
r1 = tkinter.RadioButton(master, variable =, value=,...)
- Define the function that sets the
tkintervariable.
tkinter:
What is the process for creating a Calendar?
pip install tkcalendarimport tkcalendar.tcal = tkcalendar.Calendar(master, )-
date_temp = tcal.get_date():String
tkinter:
What is the process to create image widgets?
pip install Pillow- Imports:
import PILfrom PIL import ImageTk, Image
- Create image object:
ima = ImageTk.PhotoImage(Image.open("whatever.jpg"))ima = ImageTk.BitmapImage(Image.open("whatever.bmp"))
- Use the image:
lbl = tkinter.Label(master, image=ima)
What is the process to use gspread?
-
Google Cloud Console:
https://console.cloud.google.com/- API’s and services.
- Create Credentials ⇒ Create a service account (Key type = JSON).
- Share the Google Sheet with the client’s email.
-
Code:
-
pip:
pip install oauth2client
-
imports:
import gspreadfrom oauth2client.service_account import ServiceAccountCredentials
-
Create creds:
creds = ServiceAccountCredentials.from_json_keyfile_name("")client = gspread.authorize(creds)
-
Open a worksheet:
sheet = client.open("name")worksheet1 = sheet.worksheet("name")
-
Using gspread:
-
Get a value:
val = ws.cell(1,2)vals = ws.row_values(2)
-
Update a value:
ws.update_cell(1,2, "hello")ws.update("A1:B1", [[1, 2],[3, 4]])
-
Get a value:
-
pip:
What is the meaning of API?
Application Programming Interface
What are the basic principles of a REST API?
REpresentational State Transfer.
It has 6 constraints (LUCCCS):
-
Layered:
- Intermediate dedicated servers(security, load balancing), client does not know to which server it’s communicating.
-
Uniform Interface:
-
Resource Based:
- Server sends a representation of resources. Uniquely identified resource.
-
Self-descriptive Messages:
- Each message contains everything needed.
-
Hypermedia (HATEOAS):
- Body, request - response headers, URIS.
-
Resource Based:
-
Cacheable:
- The client caches info to decrease client-server interactions. Improves client performance.
-
Client server architecture:
- Server: data storage. Client: UI. HTTP requests, client portability, client-server independence.
-
Code on demand (optional)
- Server returns code to the client (Javascript, Java applets).
-
Statelessness:
- Each client request should have the creds, so no session keeps open by the server.
What does OAuth stand for?
Open Authorization
(HTTP requests)
What types of OAuth grants exist?
-
Resource owner password credentials:
- Resource owner supplies creds.
- Unsafe.
-
Client credentials:
- Resources are owned by the client itself.
-
Authorization code:
- Most commonly used.
- Auth server issues an auth code, then access token - refresh token.
- Resource owner credentials, never shared.
-
Implicit:
- No Oauth code is issued, only access tokens.
How do you use map()?
- Transform a set of items without the need for iteration in one single expression:
- map_object = map (callable, iterable)
-
Callable (function):
- Class constructors: Class()
- User defined function.
- Built-in function.
-
lambdafunctions.
-
Example:
mapa = map(lambda x,y: x-y, [5,5,5],[1,3,5])>> 4 2 0
How do you use a lambda function? What are they useful for?
lambda arguments(n, *): expression(just 1, no statements)- Wherever a regular function object is allowed (
lambda: syntactic sugar, anonymous function). - Functional paradigm, often used with
map(), filter(), reduce().






