Patient Monitoring During Anesthesia Flashcards
What are the 4 things we monitor
Circulation Oxygenation Ventilation Temperature
Systolic - diastolic pressures = ____
Pulse pressure **Not a surrogate for blood pressure
Pulse at different sites may feel different therefore you should examine the ____ at the same site
Examine the trend at the same site
Use a _____ artery such as the ____ metatarsal
Use a distal artery such as the dorsal metatarsal
Common pulse palpation sites in small animal
Labial, digital, femoral, dorsal pedal, metatarsal
Pulse palpation sites in large animals
Auricular, transverse facial, facial
Where is the esophageal stethoscope inserted
Exactly midline, dorsal to the ET tube, right along palatine raphe
The ECG does NOT indicate that ______
ECG does not indicate that the heart is contracting
What can the ECG tell you
HR and rhythm Electrolyte imbalances Chamber enlargement May provide clues about myocardial oxygenation and perfusion
P Wave is
Atrial depolarization
QRS Complex is
Ventricular depolarization
T wave is
Ventricular repolarization
Mammalian A Type: Purkinje fibers ____ the _____ only and excitation spreads via muscle fibers
Purkinje fibers excite the endocardium only
Mammalian A Type: Generates ____ to ____ current flow
Base to apex flow (Positive R Wave)

Who have mammalian A type
Humans, small animals
Mammalian B Type: Purkinje fibers _____ the ____ and most of it is excited simultaneously
Purkinje fibers penetrate the myocardium and most of the myocardium is excited simultaneously
Mammalian B Type: Generates ____ to ____ current flow
Apex to base flow (Negative R Wave)
Who have mammalian B type
Horses, ruminants, pigs
White lead goes on the
Right arm
Black lead goes on the
Left arm
Red lead goes on the
Left leg
In healthy small animals lead ___ is yielding the tallest R wave and therefore preferred
Lead 2 (white to red)
Lead 1 goes from ___ to ____
Lead 1 from white (right arm) to black (left arm)
Lead 2 goes from ____ to _____
Lead 2 goes from White (right arm) to Red (left leg)
Lead 3 goes from ____ to _____
Lead 3 goes from Black (left arm) to Red (left leg)
Where is the white lead place on the horse
Right jugular furrow or withers
Where is the black lead placed on a horse
Cardiac apex region
Where is the red lead place on a horse
Anywhere else
Which lead is preferred for horses
Lead 1 - White to Black (whithers/jugular to cardiac apex)
On the horse lead 1 has a ___ R wave
Negative
What two substances can you use for electrode contact
ECG gel or saline
***NOT ALCOHOL
What are the two common arrhythmias seen under anesthesia
Sinus bradycardia/tachycardia
AV blocks (1st and 2nd)
What is this, what caused it and how can it be prevented

V Tach in a dog with pheochromocytoma
Prevented with phenoxybenzamine pretreatment
What does V Tach do to blood pressure
Blood pressure plummets when HR is high
What is the goal when treating ventricular arrhythmias
Improve hemodynamics and prevent sudden death
What is the first line of treatment for ventricular arrythmias
Lidocaine IV
Treatment of arrythmias should be done when there is
underlying heart disease – there is risk of sudden death
You should consider treating Ventricular arrythmias when
There is severe systemic disease
With moderate systemic disease or trauma, ventricular arrythmias should only be treated when
hemodynamics are affected
BP going from Central to Peripheral the systolic becomes
Higher
BP going from Central to Peripheral the diastolic becomes
Lower
BP going from Central to Peripheral the Mean
Remains similar
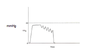
Highes point on the BP curve, represents afterload for the left ventricle
Systolic Pressure

Average BP over a full cycle, determinant of tissure perfusion
Mean pressure

Lowest point of the BP curve, determinant of myocardial perfusion
Diastolic pressure