Pathology Pictures Flashcards

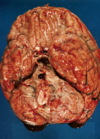
- Vasodilation
- Redness
- Pus associated with meningitis
*
What are the abnormal findings in the subarachnoid space?

- Cogested vessels
- Background of stringy exudate
- Proteinaceous exudate
- Cells - neutrophils
What are features of acute inflammation are seen in this photograph?

- Swelling
- Redness
- Pus

What are the cells lining these vessels?
What is the organisation of these cells termed?
What adhesion molecules are involved?


How will this heal?

Primary intention - the skin edges are placed in close proximity

How will this type of wound be treated, and what otehr options could be considered?

- Suture what can be sutured
- The area devoid of skin would heal by secondary intention
- Skin grafting can be done

What are the structures indicated




Where do cells that are responsible for producing new bone come from?
Pluripotent cell derived from the periosteum and bone marrow
5 months post fracture, what has happened?

Non union has occurred. The fibula and Tibia have not healed together.
Diagnosis is fibrous non-union.
What are some of the reasosn that this has occurred
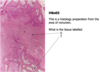
S = Fibrous connective tissue
T = Woven bone
Reasons:
- Excessive movement
- Not enough movement
- Infection
- Poor blood supply
- Poor nutrition
- Medications


Varus deforminity - bow legs.
Quadricepts muscles wasted.
On examination:
- Decreased range of movement
- osteophyte formation
- Crepitus
- Pain

This Xray is of osteoarthritis
There is:
- Loss of joint space medially
- Sclerosis of adjacent bone
- Osteophytes


The articular cartilage on both is pitted with erosion of the cartilage exposing the underlying bone on the right fermoral condyle.

Describe this femoral head



Cartilage showing:
- Loss of the typical bluish staining
- Small islands of hyperplasia of the chondrocytes on the right
- On the left the surface has become frayed which is termed fibrillation
- Bits of cartilage may dislodge from here to from ‘joint mice’

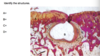


The main feature is the erosion of the bone at the periphery of the joint.
Pannus is modified synovium which is situated at the periphery of the joint.


The red material is residual pannus, it is red and inflammed.
There is erosion and damage to the underlying bone due to the overlying pannus (now removed).


It’s soft tissue pannus
A fleshy fibroinflammatory tissue which has developed from the synovium of the joint


Fleshy fronds of synovium with the darkly stained areas representing chronic inflammatory cells




Acute gout.
The greated toed MTP joint is markedly swollen with swelling also of the majority of the fore foot. The foot is red and would be hot to palpation. It would be extremely painful.

What’s this?