Pathology of the Female Reproductive Tract Flashcards
Vulva and Vagina
-The epithelium that covers both the vulva and vagina are the squamous epithelium. which is the same structure as the structure of the skin.
-The labia major of the vulva is covered in a modified kind of skin which as well as having the surface epidermis (stratified squamous epithelium), also has other structures like hair follicles and sweat glands.
- This is important because some of the clinical problems that happen in the vulva are the sort of problems that happen in the vulva are the sort of problem that happens in the skin.
- The vagina is also lined by stratified squamous epithelium.

Vagina at puberty
- Oestrogen secreted by the ovary stimulates maturation of squamous epithelial cells
- Glycogen is formed within mature squamous epithelial cells
- Glycogen in cells shed onto the surface is a substrate for vaginal anaerobic organisms (bacteria that live in the vagina flora ) (The Vagina is dominated by a kind of bacteria called lactobacilli). They ferment the glycogen to make lactic acid.
- Lactobacilli produce lactic acid keeping vaginal pH below 4.5.
-This acidic environment ha several consequences.
1. It helps regulate the vagina flora and prevent infection with other kinds of organism.
2. it has consequences for the development and the structure of the cervix
cervix
•Ectocervix
•Endocervix
•Transformation zone

Cervix close up Image

Ectocervix (outer cervix)
Made of stratified squamous epithelium

Endocervix: (inner cervix)
Lined by Single layer of tall, mucin producing columnar cells. They are tall because the cytoplasm produces mucin.

The endocervix has a deceptively large surface area
- Columnar epithelium lines tiny blind ending channels (‘clefts’)
- These radiate out from the endocervical canal into the surrounding stroma

More cervix..
- The ectocervix is covered by stratified squamous epithelium
- The endocervix is lined by columnar epithelium
- The junction between the two is called the ‘squamo-columnar junction
Formation of the transformation zone
- During puberty the cervix changes shape
- The lips of the cervix grow. the anterior and posterior lips of the cervix grow.
- As that happens, The distal end of the endocervix opens up, this is the bit that is close to the ectocervix.
-It changes from being a tubular shape to being a funnel shape as it flares and come down towards the vagina. when this happens, it means that the distal endocervical mucosa is exposed to the vaginal environment.
•Endocervical mucosa becomes exposed to the vaginal environment
-Initially, the stratified squamous epithelium will meet with the columna epithelium and as the cervix grows, the volume of tissue is increased and an area of what was previously columna epeptehlium has been exposed to the vaginal environment.

You can see that the endocervical canal comes down and it flares , when that flaring happens, when that change in shape happens, it means that these cells in the yellow area which start off looking like the cells of the column of the endocervix undergo a process of change.

Squamous Metaplasia
•The distal endocervical columnar epithelium is exposed to the acidic vaginal environment.
- It is not suited to this, so undergoes an adaptive change called metaplasia
- Reserve cells in this area proliferate and mature to form squamous epithelium: This process is called squamous metaplasia.
-This is a change in epithelial phenotype called metaplasia. what happens is that reserve cells which are cells that have the capacity to proliferate grow and mature to form squamous epithelium. this process where the epithelium which was glandular (columns) becomes squamous is known as squamous metaplasia.
Metaplasia
a transformation of cell type from one kind of mature differentiated cell type to another kind of mature differentiated cell type.
-It could be physiological or pathological.
The cervical transformation zone
-Going from left to right, you can see how the cells in the transformational zone go from being columna to squamous gradually by growing new cells from the bottom up .
- At first, the metaplastic squamous epithelium is thin and delicate (lots of proliferation & maturation is incomplete).
- With time, the metaplastic epithelium comes to be as strong and well formed as that on the ectocervix

body of the uterus

myometrium under higher power
Its a Bundles of smooth muscle, vasculature and nerves.
-you’ve got this cigar /oval shape nuclei forming ring bindles.

endometrium at high power
-The endometrium changes in its appearance during the course of a woman’ life/menstrual cycle.
-*Proliferative phase* (before ovulation)
-The endometrium has got 3 components;
1.Tubular glands
2.Specialised stroma; The stroma is a layer of connective tissue that varies in thickness according to hormonal influences.
3.Blood vessels that supply the stroma and the gland
-its is the coordinated proliferation and maturation of the 3 components during the course of the menstrual cycle which later the appearance of the endometrium and function.
Mitoses in glands
endometrium Secretory phase
After Ovulation, the endometrium has changed in maturation.
- The Glands become more Cork screw ins shape so their surface area is greater.
- Specialised stroma
- Blood vessels
Secretions in glands.
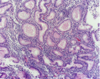
common features of neoplasia
In the female genital tract
neoplasia:
‘new growth’ – abnormal, uncoordinated and excessive cell growth.
persists following the withdrawal of stimulus and associated with genetic alterations
Nomenclature of Neoplasms
- Different neoplasms have different behaviour
- Accurate identification and naming therefore important for treating the patient
-Neoplasms are classified according to their behaviour and histogenesis
*Behaviour: Benign or Malignant
*Histogenesis: Recognising the cell of origin of the neoplasm and how it appears on the microscope.
Behaviour of Benign Neoplasms
Benign:
Remains localised and doesn’t invade surrounding tissues
Generally grow slowly
Good resemblance of parent tissue
example; Leiomyoma of the myometrium aka ‘ fibroid ’
- A benign neoplasm of smooth muscle cells of the myometrium
- Localised, does not infiltrate into soprrounding tissues
- Slow growing

Leiomyoma of the myometrium
Leiomyoma of the myometrium closely resembles parent tissue. do similar that its so difficult to distinguish between the 2 under a microscope.
Consequences of benign neoplasms
- Pressure on adjacent tissue
- Obstruction of lumen of a hollow organ.
- Hormone production that can have a wide range of effect on the body
- The potential Transformation into a malignant neoplasm
- Symptoms for the patient eg pain
Benign neoplasms,
clinical problems
Pressure on adjacent tissue
–Bladder (frequency) if to the front, Rectosigmoid (constipation) if to the back.
Obstruction to lumen of a hollow organ
–Adjacent (ureters) Blocking endocervix and obstructing menstual flow.
Hormone production
–occasionally the cervical cells can stimulate Erythropoietin producing polycythaemia.
-Transformation into a malignant neoplasm
Probably malignancy arises de novo
–Abnormal uterine bleeding, pain
Behaviour of Malignant neoplasms
- Invade into surrounding tissues
- Spread via one of 2 routes; lymphatics to lymph nodes and blood vessels to other sites (metastasis)
- Generally grow relatively quickly
- Variable resemblance to parent tissue






