Pathology of Breast Flashcards
Which layer is lost in cancer?

Normal Breast Tissue
The –Myoepithelial layer is lost
What type of secretion?

apocrine secretion with snouting
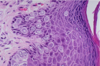
Type of Stain?

Immunoperoxidase stain with antibody to actin demonstrates the myoepithelial cell layer around the breast acinus. The myoepithelial cells are contractile and are very sensitive to oxytocin.
dx?
Common etiology?
Treatment?

Acute mastitis
Staph (MRSA)
dicloxacillin
dx?
What cells are here?
What happends if it ruptures?

Ectatic dilated ducts:
are filled with inspissated secretions and
lipid-laden macrophages.
When ruptured, a marked periductal and interstitial chronic inflammatory reaction ensues, consisting of lymphocytes, macrophages, and variable numbers of plasma cells
•Gross appearance of ill-defined nodule with hemorrhage and chalky-white areas (calcifications)
What is expected microscopically?
Fat necrosis
•necrotic adipose tissue with foamy macrophages, multinucleated giant cells and chronic inflammatory cells; often hemosiderin deposits, fibrosis and calcification
Type of necrosis in adipose tissue
What type of fibrosis?
What types of cells?
What process is occuring
Fat Necrois
- foamy macrophages, multinucleated giant cells and chronic inflammatory cells;
often hemosiderin deposits, fibrosis and calcification
Soponification
A painful erythematous subareolar mass that clinically appears to be a bacterial abscess
What difficiecy could be related to this?
Squamous metaplasia of the Lactiferous Ducts
AKA recurrent subareolar abscess, periductal mastitis, and Zuska disease
Note:
Many women have an inverted or retracted nipple, most likely as a secondary effect of the underlying inflammation
Vit A
This Results in lumpy breast, often upper outer quadrant
Is this related to cancer?

Fibrocystic changes•
Involve cystic changes and fibrosis in TDLUs
No
Clinical:
- Menstrual variation
- Pain
The following are evidence of what type of changes?
–“blue-domed”cysts
–Apocrine metaplasia
–Microcalcifications
–Adenosis
•increased number of acini per lobule

Non-proliferative fibrosis
•Adenosis with fibrosis, often with calcifications, Hyperplasia and papillomas are ___ changes
Proliferation changes
bloody nipple discharge
Intraductal Papilloma
Pre-Men. woman
•Most common benign breast tumor
Fibroadenoma
dx?

Fat Necrosis


Apocrine Metaplasia
Is there an increease risk of cancer?

Ductal epithelial hyperplasia
yes
What hormone therapy puts a pt at risk for this?
What age group is at risk?

Fibroadenoma
Estrogen therapy
20’s
How does this tumor differ from a Phyllodes Tumor

Fibroadenoma: There is less fibrosis then in the other tumor.
Pt age: 20 vs postmenapausal

BRCA-1 vs BRCA-2
BRCA-2 leads to more male breast cancers than BRCA-1
•Males typically develop ductal and not lobular cancers
BRCA-1 associated with medullary carcinoma
Aut dominant
polypoid tumor with a leaf-like pattern expands a duct
Phyllodes Tumor
This can be used as a risk marker or the developement of invasive breast cancer

Lobular carcinoma in SITU
E-Cadherin negative
dx

Comedo Ductal CIS

Noncomedo DCIS
dx
What marker can be used to differentiate ductal vs lobular?

–peau d’orange–> invasive breast cancer
IDC: + E-cadherin
ILC: -E-Cadherin