Pathology II Lab Final Flashcards
Tissue from a cat.
Abnormal/Normal?
MDx?

Abnormal/Normal?
Abnormal
MDx?
Pyometra
Horse.
Mdx?

Mdx?
Hemangiosarcoma
Bovine
Mdx

Palatoschisis
Tissue from a male dog.
MDx?

MDx?
Sertoli Cell Tumor
Tissue from a dog.
Normal/abnormal?
MDx?

Normal/abnormal?
Abnormal
MDx?
Cystic endometrial hyperplasia
MDx

Thyroid atrophy
Edx
Condition Name

Edx - renal osteodystrophy
Common name - rubber jaw
Canine
MDx
Etiology

MDx - intestinal catarhhal enteritis
Etiology - Dipylidium caninum
Dog, MDx

Top - acute splenic infarct (red)
Bottom - chronic splenic infarct (white)
Describe what you see.
What is this likely?

Nodularity of capsular surface.
Pale, no demarcation between cortex and medulla.
Chronic case of interstitial nephritis.
Tissue from a horse.
MDx?
Pathogenesis?

MDx?
Subacute focal suppurative pneumonia
Pathogenesis?
In horses whose heads were held high by halter during shipping preventing “snorting” to expel dust and mucus which then drains down trachea.
*Unilateral - only on right side.
Cat. MDx

Diffuse, granulomatous lymphadenitis
Cyptococcosis
Tissue from a cow.
Normal/abnormal?
Mdx?

Normal/abnormal?
Abnormal, lesion
Mdx?
Granulosa cell tumor
(cystic nature with hemorrhage)
MDx?
Pathogenesis?

MDx?
Mummified fetus
Pathogenesis?
No bacterial infiltration, uterus was closed off, fetus underwent dehydration
Cow.
MDx?
Etiology?

Serous atrophy of fat.
Starvation, emaciation
Tissue from a cow.
MDx?

MDx?
Amorphos globosus
Tissues from a young horse.
MDx?
Etiology?
EDx?

MDx?
Multifocal to coalescing pyogranulomatous pneumonia
Etiology?
Rhodococcus equi
EDx?
Rhodococcal pneumonia
Canine popliteal LN aspirate. Name the disease.

Leishmaniasis
Goat.
MDx?

Lymphosarcoma
Normal/abnormal?
Tissue from a ?
Name of structure?

Normal/abnormal?
Normal!
Tissue from a ?
Horse
Name of structure?
Endometrial Cups
Dog.
Cause and associated lesion.

Canine parvovirus type 2
Lymphoid depletion (bone marrow depletion) - immunodeficiency
Tissue from a ram.
MDx?

MDx?
Epididymitis
Dog
Differentials

Melanoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Edx

Uremic pneumonitis/pneumonopathy
Dog
Mdx

Mdx - subtle coronary atherosclerosis
Hypothyroid
Dog.
Name of syndrome and cause.

Brown Dog Gut.
Intestinal lipofuscinosis. Discolouration due to ceroid deposition.
Vitamine E deficiency or PUFA can be causes
Tissue from a neonatal puppy.
Normal/abnormal?
MDx?
Etiology?

Normal/abnormal?
Abnormal
MDx?
multifocal lesions on kidney
Etiology?
Canine herpesvirus
Pig.
Name of disease?
MDx?
Etiology?

Name of disease?
Atrophic rhinitis
MDx?
Atrophic rhinitis
Etiology?
Combo of Bordetella bronchiseptica and Pasteurella multocida types A and D
Dog
MDx?

lymphadenitis
MDx

Fibrous osteodystrophy
Sinuses disappearing
Tissue from male dog.
Normal/abnormal?
MDx?

Normal/abnormal?
Abnormal
MDx?
Interstitial cells of Leydig tumor
Dog
Edx
Pathogenesis

Edx - uremic gastritis
Pathogenesis - chronic renal failure –> uremia –> Gastric mineralization
Canine
MDx

Inguinal hernia
Dog.
MDx?
Radiographic lesions?

Multiple Myeloma
Punched out lesions on radiograph
Tissue from a mare.
Etiology?
Disease name?

Etiology?
Taylorella equigenitalis
Disease name?
Cantagious Equine Metritis
-test stallions, reportable, causes infertility
Adrenal glands from a horse.
Pathological process?
Types possible?

Neoplasia
Adrenocortical adenoma
Tissue from an ovine fetus. Liver.
Normal/abnormal?
Etiology?

Normal/abnormal?
Abnormal - donut like lesions
Etiology?
Campylobacter
Cat
MDx
Etiology

MDx - granulomatous peritonitis
Etiology - Feline infectious peritonitis virus (feline coronavirus)
Cat.
Etiology?
MDx?

Platynosomum fastosum
Mdx?
Chronic proliferative and eosinophilic cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis
Ox.
MDx?
Name of Disease?

MDx: Granulomatous lymphadenitis
Name of disease: Mycobacterium bovis
Adrenal glands.
MDx?
Underlying cause?
Clinical diagnosis (disease name)?

MDx?
Adrenal cortical hyperplasia
Underlying cause?
Hyperadrenocorticism - too much ACTH from pituitary adenoma
Clinical diagnosis (disease name)?
Secondary hyperadrenocorticism
Tissue from male dog.
MDx?

Seminoma.
Equine
Mdx

Intestinal stenosis/stricture
Describe the pathogenesis of a patient with kidney disease being anemic? (eg pale mucous membranes)
Kidneys produce erythropoietin - fail to do so when in kidney failure – lack of RBCs
Tissue from a cow.
Normal/abnormal?
Mdx?
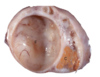
Normal/abnormal?
Abnormal, lesion
Mdx?
Follicular cyst
Dog. MDx

Dental calculus
Gingival hyperplasia
Tissue from a cow.
Normal/abnormal?
Mdx?

Normal/abnormal?
NORMAL
Mdx?
N/A
Tissue from a pig.
MDx?
Pathogenesis?

MDx?
Vulvar hyperplasia
Pathogenesis?
Hyperestrogenism - eating moldy corn
Ox. MDx

Peyer’s Patch necrosis
diffuse, severe, acute ileitis
BVDV
Tissue from a horse.
MDx?

MDx?
Laryngeal hemiplegia
Unilateral atrophy of the dorsal and lateral cricoarytenoid muscles
Cow.
Normal/abnormal?
MDx?

Normal/abnormal?
Normal is right after parturition, abnormal if a few days later
MDx?
Retained placenta
Horse.
MDx?
Name of disease?
Etiology?

MDx?
Acute suppurative lymphadenitis
Name of disease?
Strangles
Etiology?
Streptococcus equi subsp. equi
Tissue from a ram.
MDx?
Main causes?
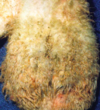
MDx?
Scrotal Dermatitis
Causes?
any infection of skin, -think Brucellosis (outward inf. of skin)
Bovine

Trichobezoars if hair
Phytobezoars if plant material
Liver from a cow.
MDx?
Cause?

Mdx?
Chronic Passive Hepatic congestion (NUTMEG LIVER)
Cause?
R-sided congestive heart failure
Species?

Llama
Dog
2 MDx

1) Siderotic plaques
2) Nodular hyperplasia
Calf.
MDx?
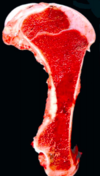
Mdx?
Normal. Hemopoietically active bone marrow in young animal.
Tissue from a cat.
MDx?

MDx?
Fibroadenomatous hyperplasia
Dog.
Etiology?

Liver Fractures
From Trauma
Dog
Mdx?

MDx?
Metastatic melanoma.
Tissue from a bull.
MDx?
Etiology?

MDx?
Balanitis
Etiology?
Bovine herpesvirus 1
Tissues from a male dog.
MDx?

Hypospadia
(incomplete fusion of urethral folds)
Tissue from a ?
Normal/Abnormal?
Name?

Tissue from a ?
Cow
Normal/Abnormal?
Normal
Name?
Normal caruncle on placenta
Tissue from a cow.
Normal/Abnormal?
MDx?

Normal/Abnormal?
Abnormal
MDx?
Piece of retained placenta
Lung tissue. Describe.

Mineralization of alveolar septae.
Canine
Mdx

Acquired Megaesophagus
(congenital would be associated with defect PRAA)
Bovine (6mo)
MDx
DDx

MDx - ulcerative stomatitis
DDx - BVD, Malignant Catarrhal Fever
Pig
Mdx?
Etiology?

Mdx - jowl abscess
Etiology - streptococcus porcinus
Cat
MDx
Etiology
Common name

MDx
Multifocal, intercostal, subpleural mineralization
Etiology
Chronic renal failure, uremia
Common name
Pleural Frosting
Tissue from a pig.
MDx?
Etiology?
Disease name?

MDx?
Massive (Panlobular) hepatic necrosis
Etiology?
Vitamin E/Selenium Deficiency
Disease name?
Hepatosis Diuretica
Dog.
MDx
Name of disease?

Necro-hemorrhagic segmental enteritis
Name of disease - canine parvovirus 2
Swine small intestine
MDx
Etiology

Mdx - proliferative ileitis
Etiology - Lawsonia intracellularis
Tissue from an equine fetus.
MDx?
Etiology?

MDx?
Multifocal necrotic hepatitis
Etiology?
Equine herpesvirus 1
Equine
MDx
Common neoplasm in non-glandular part of horse stomach?

Ulcerative gastritis
Squamous cell carcinoma
Tissue from a sheep.
MDx?
Etiology?

MDx?
Catarrhal sinusitis
Etiology?
Oestrus ovis
Llama, adult.
MDx?
Disease?

MDx?
Multifocal granulomatous osteomyelitis
Disease?
Tuberculosis
Sheep.
MDx?
Cause?
Name of Disease?

MDx?
Nasal carcinoma
Cause?
Ovine enzootic nasal tumor virus (a retrovirus)
Name of Disease?
Enzootic nasal adenocarcinoma
Tissue from a cow.
Normal/abnormal?
Differentials?
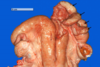
Normal/abnormal?
Abnormal
Differentials?
2 neoplasma you normally see in uterine bodies:
1) Leiomyoma
2) Lymphoma/Lymphosarcoma (BLV)
Tissue from a cat.
Floats in fixative.
Mdx?

Hepatic lipidosis

Tissue from a dog.
Normal/Abnormal?
MDx?
Pathogenesis?

Normal/Abnormal?
Abnormal
MDx?
Placental Subinvolution
Pathogenesis?
When placenta doesn’t involute - usually presents with bloody discharge - sites are bleeding –> hemoperitoneum
MDx
Pathogenesis?

MDx - coronary atherosclerosis
Pathogenesis - hypercholesterolism - cholesterol accumulates
Tissue from a cow.
Normal/abnormal?
Mdx?

Normal/abnormal?
Abnormal, lesion
Mdx?
Teratoma (all germ layers)
Tissue of a dog.
Normal/abnormal?
MDx?

Normal/abnormal?
Abnormal
MDx?
Cryptorchidism
Skin from a dog.
MDx?
Underlying endocrine abnormality?

MDx?
Calcinosis cutis
Underlying endocrine abnormality?
Cushing’s - hyperadrenocorticism
Cat. Organ.

Lower esophagus. Normal,
Tissue from a pig.
MDx?

Interstitial pneumonia.
Normal/abnormal?
Tissue from a ?
Name of structure?

Normal/abnormal?
Normal
Tissue from a ?
Cow
Name of structure?
Amniotic Plaques
Tissue from a foal
Pathogenesis?

Linear areas of hemorrhage within the tracheal mucosa.
Pathogenesis?
Iatrogenic - improper placement of nasogastric tube (down trachea instead of esophagus)
Bovine
MDx
Possible etiology?

MDx - reticular lymphoma
Tissues from a pig.
MDx?
How does the etiologic agent arrive?
What is the typical etiology?

MDx?
Embolic pneumonia
How does the etiologic agent arrive?
Hematogenous route
What is the typical etiology?
Usually bacteria, sometimes fungus
Cat
Differentials.
Disease?
Other lesions?

Differentials:
Adenomatous hyperplasia
Adenomas
Carcinoma (<5% cases)
Disease: Feline hyperthyroidism
Other lesions? fibrosis on heart, infarct in kidneys - thrombosis
Liver from rabbit.
Edx?
MDx?

Edx?
Coccidial hepatitis
Mdx?
Proliferative (hyperplastic) cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis
Dog. What is the pigment (brown on H&E) that stains blue with Prussian blue reaction (histochemical stain for iron)?

Hemosiderin
Canine
MDx

Oral papillamatosis
Tissue from a steer.
MDx?
Etiology?
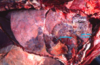
MDx?
Fibrino-hemorrhagic and necrotizing pneumonia (or bronchopneumonia)
Etiology?
Mannheimia haemolytica (Shipping Fever)
Tissue from steer that was showing severe resp. distress.
MDx?
Etiology?

MDx?
Ulcerative, fibrino-hemorrhagic and necrotizing layngotracheitis
Etiology?
Bovine Herpesvirus 1 (Same agent as: Infectious Bovine Rhinotraceitis)
Cat
Edx
Pathogenesis

Mineralization/calcification within L atrium endocardium
Edx - uremic endocarditis
Pathogenesis - uremia causes vasculitis –> endothelial damage
Tissue from a rabbit.
MDx?
Etiology?
Pathogenesis?

MDx?
Chronic suppurative pleuropneumonia
Pyothorax
Etiology?
Pasteurella multocida (“Snuffles”)
Pathogenesis?
Ruptured lung abscess leading to pyothorax, pneumothorax and atelectasis (collapse of alveolar walls)
Cat.
MDx
EDx
Etiology
Pathogenesis

MDx - Multifocal ulcerative glossitis
EDx - Uremic glossitis
Etiology - Uremia (chronic renal failure)
Pathogenesis - bacteria in oral cavity changes urea –> ammonia –> endothelial damage (necrotizing and can cause vasculitis)
Fibrin added to lesions
Canine MDx

Congenital Megaesophagus (PRAA)
Tissue from a monkey.
Normal/abnormal?
MDx?

Normal/abnormal?
Abnormal
MDx?
Endometriosis
brownish cystic structures could be anywhere in body
MDx?

Icterus
Tissue from a male dog.
MDx?

MDx?
Prostate hyperplasia
Dog.
2 MDx

2 Mdx
1) Icterus
2) Splenomegaly
Tissues from a pig.
MDx?
Disease name?
Etiology?

MDx?
Fibrino-necrotizing and hemorrhagic pneumonia confined mainly to caudal lung lobes
Disease name?
Porcine Contagious Pleuropneumonia
Etiology?
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
**Note - similar to mannheimiosis in cattle, but distribution of lesions is different
Lesion from cow.
Edx?
Mdx?
Etiology?

Edx?
Parasitic hepatitis, fluke-induced hepatitis
Mdx?
Chronic multifocal necrotizing hepatitis
Etiology?
Fascioloides magna
9 year old virgin german shepherd was admitted with continuous sanguinopurulent vaginal discharge, distended abdomen and cachexia.
MDx?

Pyometra
Cat.
Mdx?

Mdx - bilateral multifocal parathroid hyperplasia
Tissue from a ram.
MDx?
Etiology?

MDx?
Necrotizing, fibrinosuppurative epididymitis
Etiology?
Brucella ovis
Describe what you see

Uneven cortical surface. Loss of parenchyma and replacement of kidney tissue with connective tissue.
Equine.
Mdx
Etiology

MDx - multifocal ulcerative gastritis
Etiology - Gastrophilus parasite
Bovine.
Mdx
etiology

Mdx - necro-ulcerative esophagitis and glossitis
Etiology - Bovine pestivirus (BVD)
Tissue from a bovine fetus.
Normal/Abnormal?
MDx?
Etiology?
Etiology if it was in a cat?

Normal/Abnormal?
Abnormal
MDx?
Cerebellar hypoplasia
Etiology?
BDV
Etiology if it was in a cat?
Feline panleukopenia
Species?
Normal/Abnormal?
Name?

Species?
Cat/Dog
Normal/Abnormal?
Normal
Name?
Zonary Placenta
Canine - MDx

Intestinal intussusception
Canine
Mdx
Etiology

Acute segmental hemorrhagic enteritis
Etiology - canin parvovirus 2
Liver from a dog.
MDx?
Possible etiology?

MDx?
Hepatic Cirrhosis
Possible etiology? Prolonged primidone (anticonvulsant) therapy
Tissue from cat.
Mdx?
Etiology?

Mdx?
Chronic cholangitis (bile ducts very thickened)
Etiology?
Platynosomum fastosum
Tissue from a sheep.
Normal/abnormal?
Etiology?

Normal/abnormal?
Abnormal
Etiology?
Toxoplasma
Cow
Mdx?

Lymphoma (lymphosarcoma) - vertebral canal, epidural space
Cat
MDx?

Mdx: Lymphoma of cranial mediastinal LN
Thymoma possible ddx
Tissue from a cat.
MDx?

MDx?
Prolapsed uterus
Ferret
MDx
Clin path associated with this?

MDx - insulinoma
pancreatic islet cell tumor
hypoglycemia
Dog. Lymph Node.
MDx?

Acute lymphadenitis
MDx
Underlying condition?

Mdx - facial myxedema
also will see conjuncitivitis
Underlying condition - Hypothyroidism
Canine. Provide differentials.

Histiocytic sarcoma
Lymphoma
Plasma cell tumor
Mast cell tumor
Splenitis
Amyloidosis
Goat.
Etiology
MDx

Etiology - Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
MDx - diffuse granulomatous lymphadenitis (Caseous lymphadenitis)
Pig.
Name of disease
Etiology.

Swine Dysentery
Brachyspira hyodysenteriae
Tissue from a cow.
Normal/abnormal?
Mdx?
Consequences?
Predisposing Factors?

Normal/abnormal?
Abnormal
Mdx?
Uterine torsion
Consequences?
Complete block of blood supply - if fetus present it will die
Predisposing Factors?
Twinning, dystocia, trauma
Sheep.
MDx?
Etiology?

MDx: Chronic caseous lymphadenitis
Etiology: Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
Ovine
Edx

Edx - Necro-hemorrhagic coccidial enteritis
Liver from a cow.
Etiology?

Fascioloides magna
Liver fluke
Iron-porphyrin pigment from fluke
Rabbit.
Edx?
Etiology?

Edx?
Coccidial hepatitis
Etiology?
Eimeria stiedae
Tissue from a rat.
MDx?

MDx?
Mammary fibroadenoma
MDx

MDx - lymphocytic thyroiditis
Equine
Edx

Ascaridial enteritis
Catarrhal inflammation
Equine
MDx
Etiology

MDx
Gastric hyperplasis on L
Multifocal ulcerative gastritis on R
Etiology
L - Trichostrongylus
R- Gastrophilus
Normal/abnormal?
Tissue from a ?
Name of structure?

Normal/abnormal?
Normal
Tissue from a ?
Horse
Name of structure?
Cervical Star
Tissue from bovine fetus.
Etiology?

Leathery skin lesions on fetus - think fungal!
Etiology?
Aspergillus fumigatus
Placentitis also.
Collected from cat gallbladder.
Etiology?

Liver fluke - Platynosomum fastosum
What are these slides demonstrating?
Which breed of dogs is associated with familial renal disease?

Mineralization of tissues of stomach.
Shih tzu dogs.
Canine
MDx
Pathogenesis

MDx - bilateral symmetrical ulcerative glossitis
Pathogenesis - increased urea in blood ( due to renal disease) –> oral bacteria change to ammonia –> ulcers
Tissue from foal.
MDx?
Etiology?

MDx?
Multifocal to coalescing pyogranulomatous pneumonia
Etiology?
Rhodococcus equi
Tissue from a cow.
Normal/Abnormal?
MDx?

Normal/Abnormal?
Normal
MDx?
Adventitious Placentation - incidental finsing
MDx
Etiology

MDx - fibrous osteodystrophy
Etiology - renal secondary hyperparathyroidism
Osteolysis and replacement of bone with fibrous connective tissue
Dog
Edx

Uremic gastritis
Equine
MDx
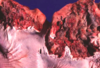
Squamous cell carcinoma * most common neoplasm of horse stomach
Tissue from a pig. A few enlarged alveolar macrophages with tachyzoites were found on histology.
MDx?
Dual etiologies?

MDx?
Interstitial fibrino-necrotizing pneumonia
Etiologies?
1) Porcine circovirus 2
2) Toxoplasma
Tissue from a cow
Normal/abnormal?
Mdx?

Normal/abnormal?
Abnormal
Mdx?
Luteal cyst
(Cystic corpus luteum)
Pig
MDx?

Diffuse severe splenic congestion
Equine.
MDx
Etiology

MDx - intestinal ulceration and perforation
Equine.
Intestine MDx

Granulomatous enteritis
Dog.
MDx?
2 Possible causes.
Pathogenesis
Posisble clinical signs.

MDx?
Ulcerative gastritis
2 Possible causes.
NSAIDs, Mast Cell Tumor (Histamine)
Pathogenesis
NSAIDs –> prostaglandin inhibitiation –> vasoconstriction –> blood flow cut off –> necrosis
Posisble clinical signs.


