Path Lab Flashcards
(29 cards)
The patient had a cholecystectomy , through a tangential surgical incision. Laparoscopic surgery could not be done. Now this 58 yo woman is coughing, has a mild fever and is mildly short of breath. What does this xray suggest this patient has?

atelectasis
right lower lobe is partially collapsed, see the underlying opacity
This is a 47 yo man who presents with a high fever, a productive cough with blood tinged sputum and who appears moderate ill. He is admitted to the hospital where a blood culture grows Strep pneumoniae. His wbc is 18,000 with 85% neutrophils, 12%bands and 3% lymphs. What is your diagnosis?

the blood comes b/c the pneumonia is eroding into the blood vessel
abnormal amounts of bands–>body is pumping out too many premature neutrophils
xray shows lung infiltrate in right lower lobe b/c strep pneumo damages pneumocytes. Type 1 damage=edema; Type 2=surfactant decrease, collapsed alveoli
ACUTE PNEUMONIA
blood culture grew strep pneumo
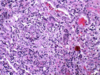
What does this histo show?

neutrophils filling the alveoli
capillaries sometimes break & you get hemorrhage in the sputum
pneumococcal pneumonia
What does this pic show?

bronchopneumonia
white surrounding the bronchioles are the neutrophils
What is pneumonia? Pneumonitis? Different forms of pneumonitis?
pneumonia–inflammation of the alveoli
pneumonitis–inflammation of the interstitium
forms of pneumonitis–>radiation pneumonitis & hypersensitivity pnemonitis
19yo UNR college student has been sick for about a week with a sore throat, non-productive cough, mild fever, runny nose and tired. But, now his cough is worse and he’s bringing up some greenish sputum “globs” as he says. He has a headache, mild fever and feels “lousy” and cannot go to class. Chest auscultation reveals bilateral wheezes.

increased interstitial markings on the left-some sort of pneumonia
because it developed gradually over a week-probably atypical pneumonia. A strep pneumonia would have come on suddenly.
Diagnosis: Community Acquired Atypical Pneumonia; think of:
Mycoplasma
Chlamydia pneumonia
Influenza A & B, RSV, human metapneumovirus, adenovirus, rhinovirus, rubeola, varicella
What is shown here?

viral pneumonia
lots of inflammation & lymphocytes in the interstitium
-could also be mycoplasma as that attracts lymphocytes as well
What does a CBC show in cases of community acquired atypical pneumonia?
increased lymphocytes
only slightly increased WBC count
This is a 78yo man who presents with a 3 day history of worsening posterior chest pain. The pain increases with inspiration and coughing. [This would classify as pleuritic chest pain] He also has had a few times of “trouble getting my breath”. He reports no fever, hemoptysis or sputum production. PE reveals tachypnea with 20 breaths/min. Pulse is 102 beats/min, forehead temp is 38 degrees and BP 138/85. EKG shows increased heart rate but no other specific changes.
- In patients with pleuritic chest pain what are some clinical possibilities? What is viral pleurisy?
- Would you want to examine this man’s legs? Why?
- What is a D-dimer test?
Possible DVT–>PE. Pleuritic chest pain felt often with pulmonary embolism. Keep in mind that usu pleuritic chest pain is caused by a virus.
D-dimer shows if clots are being broken up.
This is a 65 yo man who presents with shortness of breath with short walks. He walks his dog but this is getting difficult. He has smoked a pack of cigarettes everyday since he was 17. He always has had a chronic cough with sputum production. The cough has gotten worse. Walking up stairs is next to impossible for him because of shortness of breath. Exam reveals a prolonged expiration and auscultation reveals expiratory wheezing. His fingernails have a cyanotic appearance. What is this likeLY? What are the options when you know someone has COPD?

emphysema. note the dilated alveoli on histo.
COPD: could be chronic bronchitis, emphysema, small airway disease
•The patient is 21yo Hispanic male that arrived here in Reno, from Central Mexico, about 8 months ago. He does not feel well, has a chronic cough with sputum production. He wakes up at night in a cold sweat and sometimes he feels hot. He coughs at night and spits up green phlegm. He can hardly work at his job because he is so tired. He has lost weight and is not hungry. He was seen in this clinic a week ago. He was felt to have atypical pneumonia based on the CXR, next slide. He was given antibiotics but he is no better. He thinks he is worse.

infiltrates & spider webs are present here
these infiltrates are likely composed of macrophages of granulomatous inflammation, b/c it is likely a case of TB
What is shown here?

acid fast stain
positive red snappers
supports TB
What is shown here?

histo supports caseous necrosis, TB
giant cells found here
A patient has Rheumatoid Arthritis and is on an anti-TNF drug. They come down with a case of TB. Why?
Th1 cells-IFN
Macrophages–TNF
TNF is a warrior against TB. When it is fought for its negative inflammatory effects in RA, Crohn’s etc…patients are more susceptible to coming down with TB infection.
What is probably shown here? What type specifically?

bronchogenic carcinoma
because it is central, probably a squamous carcinoma.
What is shown here?

i think probably a squamous cell, bronchogenic carcinoma
What is shown here?

glandular differentiation
Metastatic cancers to the lung are usu of which type? Can primary tumors be of this type too?
metastatic–>usu adenocarcinomas
primary tumors can also be adeno
What is shown here? Which 2 cell types?

cytology from breast cancer patient who had mets to the lung
little cells are called lymphocytes
big cells are the malignant cells
Note: you can see this type of lymphocytosis in a pleural effusion in both TB & cancer
What does this chest xray show?

mets to the lung. Multiple hits.
55yo male is involved in a serious car accident. He sustained trauma to his chest. He also sustained some closed head injury. He is admitted to the ICU. Look at next slide. What is the red mark across his chest? It’s where his seat belt caused a contusion. He is stable for the first day but on his 2nd day of admission he begins having breathing problems.

Trauma caused acute lung injury
this led to ARDS. On a histo level: diffuse alveolar damage (DAD)
type 1 damage-edema; type 2 damage-loss of surfactant, collapsed alveoli & stiff lung
What’s this?

this shows alveolar damage (DAD)
some alveoli are distended & some are collapsed
hyaline membranes are there as well.
What is shown in this histo slide?

The upper portion shows scarring.The lower portions show open alveoli/air spaces. This histologic pattern is called “usual interstitial pneumonia”. It’s a very heterogeneous picture. Inflammation is patchy.
What is shown in this histo slide?

Here is another picture that shows “honeycombing” or honeycomb fibrosis. These are cystic spaces lined by bronchiolar-like epithelium. But notice the heterogeneous picture of fibrosis, some inflammation in the center, increased vascularity. This is called UIP
UIP: usual interstitial pneumonia