[PATH] Bones, Joints and Soft Tissue (Part 1 BONE) [Martin] Flashcards
This image depicts what type of process?

Endochondral ossification
(in a calcaneus)
Root word association:
Osteoporosis =
Osteomalacia =
Osteopetrosis =
Osteogenesis imperfecta =
Osteitis deformans =
Osteodystrophy =
Osteoporosis = Porous; thinned out bone
Osteomalacia = Weakened, soft bone
Osteopetrosis = Peter=rock, stone bone
Osteogenesis imperfecta = Imperfect origin of bone
Osteitis deformans = Deforming bone-itis
Osteodystrophy = Bad growing bone
What are the (3) components of bone matrix?
Type I collagen
Osteoid
Mineral component
Hardness of bones is due to?
Hydroxyapatite
What are the (2) histologic forms of bone?
Woven
Lamellar
Characteristics of woven bone?
Disorganized
Produced rapidly ; fetal development and fracture repair

Characteristics of lamellar bone?
Slow production
Parallel collagen
Strong

Function of osteoblasts
Synthesize, transport and assemble matrix
*Regulates mineralization
Function of osteocytes?
Inactivate osteoblasts
Control calcium and phosphate levels
What are osteoclasts?
Function?
Multinucleated macrophages derived from circulating monocytes
Bone resorption
What type of bone is associated with:
Endochondral ossification?
Intramembranous ossification?
Endochondral ossification = Long bones
Intramembranous ossification = Flat bones
When is peak bone mass achieved?
Early adulthood
RANK
Where is it expressed?
Function?
Where is it expressed = Osteoclast precursors
Function = Breakdown
RANK-L
Where is it expressed?
Function?
Where is it expressed = Osteoblasts and marrow stromal cells
Function = Breakdown
OPG
Where is it expressed?
Function?
Where is it expressed = “Decoy” receptor made by osteoblasts that can bind RANKL and prevent it’s interaction with RANK
Function = Build
A product produced by osteocyte inhibits the WNT/Beta-catenin pathway. What is it?
Sclerostin
What are the common building circulating hormones/factors?
Estrogen
Testosterone
Vit D
What are the common breakdown circulating hormones/factors?
PTH
IL-1
Glucocorticoids
What is M-CSF?
Monocyte colony stimulating factor
Function of M-CSF?
M-CSF receptor on osteoclast precursors STIMULATES tyrosine kinase cascade that is crucial for generation of osteoclasts
What are the (3) primary developmental disorders of bone?
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteopetrosis
Mucopolysaccharidoses
What is commonly associated with developmental disorders of bone?
Transcription factor defects: specifically homeobox genes
Define:
Dysplasia
Global disorganization of bone &/or cartilage
Define:
Syndactyly/Craniosynostosis
Abnormal fusion of bones
What are wormian bones?
Extra bones within cranial sutures

What is an excellent way to determine the origin of a dwarfism pathology?
Can you give examples?
Look at the chest cavity!
Normal trunk length with achondroplasia
Small chest cavity with thanatophoric dysplasia
Achondroplasia
Gene mutation?
Presentation?
Mortality?
Gene mutation = Autosomal dominant FGFR3 gain of function
Presentation = Short extremities, normal trunk length, enlarged head, bluging forehead, depression root of nose
Mortality = NO change in longevity, intelligence or reproductive status
Thanatophoric dysplasia
Gene mutation?
Presentation?
Mortality?
Gene mutation = FGFR3 gain of function
Presentation = Small chest cavity, bell-shaped abdomen, micromelic shortening of limbs
Mortality = Die at birth or soon after
Osteogenesis imperfecta:
Which type has the best prognosis?
Worst?
Best = Type I
Worst = Type 2
Prognosis of Type II osteogenesis imperfecta?
Uniformly fatal in utero
Buzz word association for osteogenesis imperfecta type 2?
“Accordion-like” shortening of the limbs

What are the major clinical features of osteogenesis imperfecta?
Blue sclera
Skeletal fragility
Dentinogenesis imperfecta (small teeth)
Hearing impairment
Joint laxity
What is the most common type of osteogenesis imperfecta?
Type I
Also the mildest type of OI
Why is type II typically fatal?
Respiratory problems
(They have underdeveloped lungs from small thoracic cage)
What is the difference in sclera appearance b/w Type III and Type IV OI?
Type III = Blue, purple or gray tint
Type IV= White
*Remember; The order of best prognosis to worst is (1–> 4 –>3–>2) because fuck, lets make this difficult. But yeah, remember that type 4 is less severe, so the sclera are going to be normal in color.
Osteopetrosis
Aka?
(2 names)
Marble bone disease
Albers-Schonberg disease
What is the deficiency in osteopetrosis?
Carbonic anhydrase 2 (CA2)
How does osteopetrosis appear on Xray?
Buzz word association?
Erlenmeyer flask

Inheritance pattern for osteopetrosis?
Populations?
Autosomal recessive
Mediterranean and Arab race
Common clinical features of osteopetrosis?
Cranial nerve deficits:
Optic atrophy, deafness, facial paralysis
What is seen on histology with osteopetrosis?
No medullary cavity

What type of disease is mucopolysaccharidoses?
Lysosomal storage disease
What are examples of aquired bone disorders (5)?
Osteopenia/osteoporosis
Pagets
Osteomalacia/rickets
Hyperparathyroidism
Renal osteodystrophy
Define osteopenia
Define osteoporosis
Osteopenia = 1.0 - 2.5 standard deviations below the mean
Osteoporosis = At least 2.5 SD below the mean peak bone mass in young adults
If your patient has a bone mass that is less than 2.5 SD below the mean, but you still diagnose them with osteoporosis, what MUST have happened?
Atraumatic
or
Vertebral compression fractures
What population is at risk of never obtaining their full potential bone mass due to eating disorders?
Adolescent girls
(Insufficienct calcium intake during period of rapid growth restricts their peak bone mass)
What is a major hormonal influence on osteoporosis?
Menopause
(estrogen deficiency)
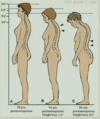
Describe the appearance of osteoporotic bone
(Right)
Loss of horizontal trabeculae

What is the method of diagnosis for osteoporosis?
DEXA-scan
Risk factors for osteoporosis?
Caucasian, light colored eyes and skin
Nutrition (too much phosphorus-soda)
Smokers
What spinal changes are associated with loss of height in osteoporosis?
Lumbar lordosis & kyphoscoliosis
Paget disease
aka?
Osteitis deformans
Paget disease
Characteristsics?
Gene?
Polyostotic (involves multiple bones)
70yo average age
Caucasians
SQSTM1 gene
Paget disease
Buzz word association with Xray appearance?
“Cotton Wool”

What is the paget disease morphology?
Mosaic pattern of lamellar bone
Jigsaw-like

What type of fractures are associated with paget disease?
Chalk stick type fractures
What are the lab values associated with paget disease?
Elevated ALK PHOSPHATASE
NORMAL = Calcium and phosphorous
Name a unique clinical feature of paget disease
Hyeprvascularity of paget disease
Warms the overlying skin
–> Can lead to high output heart failure
Rickets and osteomalacia are manifestations of?
VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY
Or it’s abnormal metabolism
What is the histology associated with hyperparathyroidism?
Train tracks

Define:
Simple fracture
Overlying skin intact
Define:
Compound fracture
Bone communicates with the skin surface
Define:
Comminuted fracture
Bone is fragmented
Define:
Displaced fracture
Ends of the bone at the fracture site are not aligned
Define:
Stress fracture
Slowly developing fracture that follows a period of increased physical activity in which bone is subjected to repetitive loads
nice.
Define:
Greenstick fracture
Extending only partially through the bone, common in infants when bones are soft
Define:
Pathologic fracture
Involving bone weakened by an underlying disease process such as a tumor
What is osteonecrosis?
Infarction of the bone and marrow
(pretty common)
What causes most cases of osteonecrosis?
Fractures
or
Corticosteroid tx
What region is typically not affected in osteonecrosis?
Why?
Cortex is not affected
Due to collateral flow
Buzz word association with osteonecrosis?
“Creeping substitution”
What is osteomyelitis?
Inflammation of the bone and marrow
Typically following infection
What are most cases of osteomyelitis caused by?
Pyogenic bacteria
&
Mycobacteria
How does pyogenic osteomyelitis typically spread in:
Kids?
Adults?
Kids = Hematogenous
Adults = Complication of open fractures, surgical procedures and diabetic infections
Most common cause of pyogenic osteomyelitis?
Staph aureus (80-90%)
Osteomyelitis:
Name the associated organism with:
Sickle cell patients
Salmonella
Osteomyelitis:
Name the associated organism with:
MAC deficiency
Neisseria
What is:
Sequestrum?
Involucrum?
Sequestrum = Dead bone following abscess
Involucrum = New bone

What is the histology associated with mycobacterial osteomyelitis?
Caseous necrosis and granulomas
What is Pott disease?
Aka Tuberculous spondylitis
Permanent compression fractures

What are the associated bone deformities seen with skeletal syphilis?
Saber shin
Saddle nose



