Past Questions Flashcards
- How does brown snake venom affect haemostasis?
A. it damages endothelium to expose tissue factor and subendothelial collagen
B. it activates platelets
C. it activate prothrombin to form thrombin
D. it activates plasminogen to form plasmin
E. it cause inflammation which cross-links with haemostatic cascades
A. it damages endothelium to expose tissue factor and subendothelial collagen
C. it activate prothrombin to form thrombin - ADEM
- Hyperplasia of prostatic glandular epithelim in dogs occurs in response to stimulate by:
A. Oestrogen
B. Frequent sexual activity
C. Pheromones secreted by bitches in oestrus
D. Dihydrotestosterone
E. Constipation
D. Dihydrotestosterone
- Arya send a raven to tell you that every night for the last two months, her dog Nymeria wakes her up because of coughing and pacing. Nymeria seems OK during the day, but without the old vim and vigor of yestertear. You tell her that her dog has orthopnea. What underlying condition is the MOST likely?
A. bronchopneumonia
B. left heart failure
C. iron deficiency anaemia
D. pulmonary thromboembolism
E. small foreign body in the trachea
B. left heart failure
- What is cardiac tamponade? (circule one answer). (Duh)
A. Left heart failure causing right heart failure
B. Right heart failure causing left heart failure
C. Pulmonary hypertension causing left heart failure
D. Pulmonary hypertension causing right heart failure
E. Cardiac failure because of fluid distension of the pericardial sac
E. Cardiac failure because of fluid distension of the pericardial sac
- Which finding is typically associated with pulmonary infection with Mycobacterium bovis in cattle?
A. squamous metaplasia of bronchial epithelium
B. hyperplastic bronchitis
C. bronchial epithelial dysplasia
D. caseous necrosis
E. pulmonary lobular atrophy
D. caseous necrosis
- Which of the following conditions is the least likely to predispose to thrombosis?
A. brown snake bite
B. valvular stenosis
C. septic shock
D. indwelling venous catheter
E. hepatic degeneration
E. hepatic degeneration
- Choose the single best statement.
A. Occllusive aterial thrombi cause red infracts, while occlusive venous thrombi cause whute infracts
B. Occlusive arterial thrombi cause white infarcts, while occlusive venous thrombi cause red infarcts
C. Occlusive arterial thrombi and occlusive venous thrombi cause red infarcts
D. Occlusive arterial thrombi and occlusive venous thrombi cause white infracts
B. Occlusive arterial thrombi cause white infarcts, while occlusive venous thrombi cause red infarcts
- What causes lipid accumulation in hepatocytes with fatty degeneration?
A. intracellular Ca++ influx causes formation of calcium soaps
B. insufficient production of lipid transport apoproteins
C. activation of phospholispase A
D. myelin-whorl formation of damaged membrane lipids
E. insufficient oxygen for beta-oxidation of lipids
B. insufficient production of lipid transport apoproteins
- Which of the following molecules is a negative acute phase protein?
A. Fibinogen
B. C reactive protein
C. Albumin
D. Serum amyloid A
E. Complement (C3)
C. Albumin
- Causes of hyperkalaemia may include all of the following conditions EXCEPT:
A. Haemolysis in horses
B. Metabolic alkalosis
C. Bladder repture
D. Severe rhabdomyolysis
E. Hypoadrenocorticism (Addison’s disease)
B. Metabolic alkalosis
- Which of the following molecules or compunds are used in formulas to calculate serum osmolality/osmolarity?
1) sodium
2) urea
3) albumin
4) potassium
A. 1,2 and 3
B. 1, 2 and 4
C. 2 and 3
D. 3 and 4
E. 1, 2, 3, and 4
C. 2 and 3
- Which one of the following conditions is expected to cause the greatest increase in osmolal gap?
A. Renal failure
B. Diabetic hyperglycemia
C. Hypernatremia due to water deprivation
D. Acute ethylene glycol toxicity
E. Pregancy toxaemia
D. Acute ethylene glycol toxicity
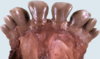
- Which one of the following could not be a cause the condition seen in this animal?
A. Cachexia caused by cancer or other systemic illness
B. Inadequate amount or poor quality of feedstuffs
C. Chronic severe gastrointestinal parasitism
D. Dental attrition
E. Inadequate secretion of growth hormone from pituitary
F. Lameness

E. Inadequate secretion of growth hormone from pituitary
- Cross section of skeletal muscle. What pathological process is depicted?
A. Atrophy
B. Involution
C. Hypoplasia
D. Degeneration
E. Apoptosis

A. Atrophy
- What caused this problem in a lamb foetus?
A. Developmental anomaly
B. Neoplastic transformation
C. Postmortem change
D. Nutritional deficiency
E. Genetic deficiency
D. Nutritional deficiency
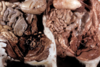
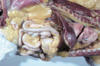
- Tissue from dogs. One of these specimens is normal. Select the correct statement about the abnormal specimen.
A. The prostate is enlarged and symmetrical
B. The prostate is small and symmetrical
C. The prostate is large and asymmetrical
D. The prostate is small and asymmetrical

A. The prostate is enlarged and symmetrical
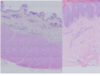
. Histologic section of lung. Select the correct diagnosis
A. Pneumonia
B. Coagulation necrosis
C. Caseousnecrosis
D. Dysplasia
E. Neoplasia

A. Pneumonia
- In cats, saddle thrombi in the distal aorta are associated with which of the following?
A Hyperlipidemia
B Mitral valve insufficiency
C Myocardial infarction
D Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
E Endocardiosis
D Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- An infarct is which of the following?
A An area of caseous necrosis
B An embolus
C An area of ischemic necrosis
D A thrombus
E An area of liquefactive necrosis
C An area of ischemic necrosis