Past Q Flashcards
(269 cards)
Please list two main advantages of digital (direct) radiography over computed radiography!
A: DR improves workflow by producing higher quality images instantaneously while providing 2 to 3 times more dose efficiency than CR.
Additionally :
- X-ray photons are directly converted to a digital signal
- Time and productivity savings (= reduces the long processing conventional radiography to seconds)
- Images are instantly stored and ready to view on the computer
- In some cases patient is exposed to significantly reduced radiation doses
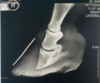
Which radiographic projection is shown on this image?

A: D45L-PlMO (dorsolateral plantar medial oblique)
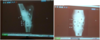
Which radiographic projection is shown on this image?

LM (in a 5-10degree tilt)
Which radiographic projection is shown on this image?

DPI (on a 5-10 degree tilt)
Which radiographic projection is shown on this image?

D45L-PIMO

Which radiographic projection is shown on this image?

PI45L-DMO
Which radiographic projection is shown on this image?

Flexed LM
(Highlight plantar aspect of trochlear ridges of tallus)
Which radiographic projection is shown on this image?

SKYLINE
or Plantarprox-Plaantardist
(Highlight tuber calcanei & Sustentacullum talli)
How do we administrate phenylbutazaone as premedication in horses?
A : Only IV
What kind of narcotic system is appropriate for equine anaesthesia?
Closed circle
Which drug is suitable for raising mean arterial blood pressure (ABP) intraoperatively?
Dobutamine
It can happen in case of an accidental intraarterial injection of alpha-2 receptor agonist?
Collapse
What sign could indicate that the horse is anaesthetised superficially?
Increase blood pressure
How do we administer phenylbutazone as a premedication in horses?
IV
The most common complication after anaesthesia of a horse with laryngeal hemiplegia?
Laryngospasm
What is true for a half limb cast, when you are using light casting as a cast material?
Quick application possible, no fluid permeability, it is light
What is the most important point to keep in mind, while you are placing a high bandage on the front limb?
Protect the accessory carpal bone against pressure sore
What kind of fluid should be used for joint lavage?
Sterile, isotonic infusion solution
Time-dependant antimicrobials are:
Beta lactams and macrolides
Please list the three main steps of preparing a foot for radiological exam:
Remove shoes and pare the foot, brush food with wire brush, pack the sulci of the frog with play doh
What is the first step in a case of a puncture wound of the sole of the hoof by a nail?
X-ray from the two views to localise the nail, the therapy depends on the nail position and injured structures
What are the phases of wound healing in the correct order?
Acute inflammation, proliferation, resorption, remodelling
When do you have to remove skin sutures following primary wound closure in a horse?
After 12-14 days postop
List two parameters which are evaluated during a distant examination:
- Size,
- conformation,
- body condition,
- posture,
- gait,
- behaviour and demeanour,
- obvious pathological changes