Past Exam Questions Flashcards
(435 cards)
Where is corpora arenacea found?
Pineal gland
Which of the following responds to vibration and rapidly changing pressure?
- Free nerve endings
- Ruffini’s corpuscles
- Pacinian corpuscles
- Krause’s end bulbs
- Meissner’s corpuscle
Pacinian corpuscles
Where is glucagon secreted from?
Alpha Cells
Which cell secretes surfactant?
Type II pneumocyte
Which layer is NOT present in masticatory epithelium?
- Stratum basale
- Stratum spinosum
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratum lucidum
- Stratum corneum
Stratum lucidum
What vessel is a branch of the interlobular artery?
Afferent arteriole
Which type of neuron is multipolar?
Motor neurons
Interneurons
Which type of cartilage is found in the larynx?
Hyaline Cartilage
Elastic Cartilage
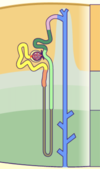
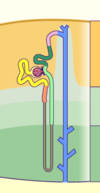
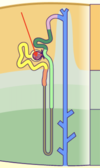
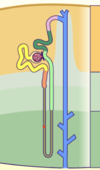
Bowman’s Capsule
When looking at the spleen, what are the invaginations of the capsule into the splenic parenchyma called?
Trabeculae
Which meninx covers the brain intimately?
Pia Mater
Which cell type is found in the adrenal medulla?
Chromaffin cells
Which of the following layers comprise the skin?
- Epidermis
- Dermis
- Hypodermis
Epidermis
Dermis
Which of the following is the inner layer of the adrenal cortex?
- Chromaffin cells
- Zona reticularis
- Zona glomerulosa
- Zona fasciculata
- None of the above
Zona reticularis
Which cell type are involved in the secretion thyroglobulin?
Follicular cells
Which of the following is an element of the central nervous system?
- Receptors
- Brachial plexus
- Sciatic nerve
- Ganglia
- Spinal cord
Spinal cord
Where do T lymphocytes gain their immunocompetence?
Thymus
Which one of the following is not found in the retina?
- Pigment epithelium
- Muller’s cells
- Huxley’s layer
- Horizontal cells
- Cones
Huxley’s layer
What type of glands are the ceruminous glands?
Apocrine sweat gland
What cell type secretes prolactin?
Lactotropic cells
What is the middle layer of the eyeball?
Uvea
What gland in the male is homologous to the greater vestibular gland in the female?
Cowper’s gland
What are the follicular cells?
Granulosa cells
Which of the following is found in the cerebellum?
- Schwann cells
- Basket cells
- Ganglion
- Neuroglia
- Satellite cells
Basket cells