Parasitology: Protozoa Flashcards
Patient who has recently returned from a hiking trip presents with foul-smelling, fatty diarrhea.
Stool sample shows cysts (see below).
What is the organism? Proper treatment?

Giardia lamblia - a protozoan GI infection.
Spread by cysts in water - see in campers/hikers. Foul-smelling fatty diarrhea.
Diagnose with trophozoites or cysts in stool.
Treat with Metronidazole.
Think fat-rich Ghirardelli chocolates for fatty stools of Giardia.

Patient presents with bloody diarrhea and RUQ pain.
A liver abscess is discovered, and an “anchovy paste” exudate is aspirated.
Examination of the stool reveals cysts with multiple nuclei.

Entamoeba histolytica - a GI protozoan causing amebiasis.
Causes bloody diarrhea, liver abscess, RUQ pain.
Histology shows flask-shaped ulcer if submucosal abscess of colon ruptures.
Spread by cysts in water.
Diagnosed by: Serology and/or trophozoites with RBCs in cytoplasm (see below) or cysts with up to four nuclei in stool (see front of card)

How would you treat Entamoeba histolytica?
Metronidazole;
Iodoquinol for asymptomatic cyst passers.
Patient with AIDS presents with severe diarrhea.
Suspicious, you perform an acid-fast stain and find Oocytes.
Diagnosis?

Cryptosporidium - a GI protozoan
Causes severe diarrhea in AIDS. Mild disease (watery diarrhea) in immunocompetent.
Spread by Oocytes in water, shows acid-fast Oocytes on stain.
How would you treat Cryptosporidium?
Prevent infection by filtering city water supplies.
Nitazoxanide in immunocompetent hosts.
To summarize, what are the protozoa that infect the GI tract?
- Giardia lamblia* - fatty diarrhea with cysts
- Entamoeba histolytica* - bloody diarrhea; cysts with multiple nuclei; RBC inside trophozoite form
- Cryptosporidium*: AIDS severe disease, Oocytes acid-fast.
A patient with AIDs presents with fever and neurological symptoms.
MRI finds multiple ring-enhancing brain lesions
What is the infectious agent? How to diagnose?

Toxoplasma gondii
Diagnosis: Serology, biopsy will show tachyzoites (see picture)
A neonate presents with chorioretinitis, hydrocephalus and intracranial calcifications.
What is the infectious agent? How is it spread?
Toxoplasmosis gondii (the T in TORCH)
Classic triad: Chorioretinitis (inflammation of choroid and retina), hydrocephalus, and intracranial calcifications.
Spread via cysts in meat or oocytes in cat feces; cross in placenta. This is why pregnant women should avoid cats.
How would you treat Toxoplasmosis gondii?
Sulfadiazine + pyrimethamine
Patient with recent history of swimming in a freshwater lake presents with progressively worsening neuroloic symptoms.
This transitions into rapidly fatal meningoencephalitis.
How would you diagnose? Organism?
Naegleria fowleri.
Think Nalgene bottel filled with Fresh water containing Naegleria.
Diagnose by finding amoebas in spinal fluid.
Enters through cribiform plate.

What’s a potential treatment for Naegleria fowleri?
Amphotericin B has worked for a few survivors.
An immigrant from Africa presents with enarged lymph nodes, fever, somnolence, and coma.
His wife states that he suffered a painful fly bite just before coming to the United States.
What is the organism? What would be a useful diagnostic finding? Vector for causative organism?
Trypanosoma brucei - African sleeping sickness.
Recurrent fever is due to antigenic variation.
Tsetse fly is the vector.
Blood smear showing characteristic organisms (see below)

How would you treat Trypanosoma brucei?
Suramin for blood-borne disease or melarsoprol for CNS penetration.
“It sure is nice to go to sleep”; melatonin helps with sleep.
What are the protozoa causing CNS infections?
Characteristic features?
Toxoplasmosis gondii: Ring-enhancing brain lesion in HIV or congenital triad
Naegleria fowleri: Freshwater swimming, rapidly fatal meningoencephalitis
Trypanosoma brucei: Recurring fever, lymph nodes, coma, Tsetse fly bite, sub-Saharan Africa.
Patient presents with fever, headache, splenomegaly, and fatigue.
A CBC shows a normocytic anemia.
You receive a blood smear.
Why are the characteristic smear findings? Diagnosis?

Plasmodium species - protozoan that causes Malaria
Blood smear will show trophozoite ring form within RBCs (see front) and schizont containign merozoites (see below)
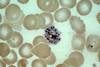
What is the vector for plasmodium?
What are the major infectious species of plasmodium, and how do you tell them apart?
Anopheles mosquito.
Plasmodium vivax/ovale: 48 hour cycle (tertian; includes fever on first day and third day). Forms dormant form (hypnozoite) in liver.
Plasmodium falciparum: Sever form, irregular fever patterns, parasitized RBCs occlute capillaries in brain (cerebral malaria), kidneys, lungs.
Plasmodium malariae: 72 hour cycle (quartan).
How do you treat malaria?
- Chloroquine, blocks Plasmodium heme polymerase. If resistant, use mefloquine or atovaquone/proguanil.
- If life threatening, use intravenous quinidine (test for G6PD deficiency)
- For vivax/ovale, add primaquine for hypnozoite (test for G6PD deficiency)
Patient from New York presents with fever and severe fatigue.
CBC shows normocytic anemia.
He reports that he loves hiking and goes every weekend.
You’re given a blood smear to examine.
Diagnosis? Risk factors/associated diseases?

Babesia - protozoan
Spread by the Ixodes tick (same as Borrelia burgdorferi of lime disease).
Diagnosis: Blood smear, ring form and Maltese cross in RBCs (arrows in front). PCR can also diagnose.
How do you treat Babesia?
Atovaquone + azithromycin.
What are the hematologic infections with protozoa?
Plasmodium species - fever, headache, anemia, mosquitos, foreign
Babesia - tick, hemolytic anemia, northeastern US, maltese cross
A patient from South America presents with fever, fatigue, and body aches.
You’re given a blood smear.
Diagnosis? Vector? Other diseases caused by this organism?

Trypanosoma cruzi - a protozoan causing Chagas disease. Found in South America.
Blood smear shows characteristic organism.
Vector: Reduviid bug (“kissing bug”) feces, deposited in a painless bite.
Chagas disease, dilated cardiomyopathy, megacolon, megaesophagus (seems to make stuff big).
How to treat Trypanosoma cruzi?
Benznidazole or nifurtimox.
A patient presents with spiking fevers. Physical exam shows hepatosplenomegaly.
CBC shows pancytopenia.
You receive a blood smear.
Diagnosis? Vector?

Leishmania donovani - protozoan causing Visceral leishmaniasis.
Vector: Sandfly
Blood smear: Macrophages containing amastigotes (see front).
How to treat leishmaniasis?
Amphotericin B, sodium stibogluconate.



