Papulosquamous/Desquamation Flashcards
Most successful Rx for Psoriasis?
Immune-mediating medications
What is the etiology of Psoriasis?
Hint: influences and triggers
Psoriasis is influenced by genetic & immune-mediated components.
With or Without triggers, substantial leukocyte recruitment to dermis (activated T cells that induce keratinocyte proliferation)
Ramped-up,degregulated inflammatory process with large production of various cytokines
Psoriasis is assocated with increased production of what various cytokines?
Tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF-α]
Interferon-gamma
Interleukin-12
What particular cytokine production correlates with psoriasis flare ups?
TNF-α
Psoriasis Pathophysiology:
Explain what occurs and the characteristics of why that happens?
Vascular engorgement due to telangiectasis
Altered epidermal cell cycle (hyperplasia, turnover from 23 days to 3-5 days –improper cell maturation)
Parakeratosis (cells retain nuclei in stratum granulosum)
Cells fail to relesase adequate levels of lipids
Poor adherent stratum corneum –> flaking, scaling
Name the 4 skin layers?
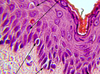
From top to bottom:
Keratin surface (cornified cells)
Stratum granulosum
Stratum Spinosum
Stratum Basale)
What’s wrong with this picture?

Hyperkeratosis w parakeratosis
loss of granular layer
Acanthosis (diffused epidermal hyperplasia)
Enlongated rete regions (hyperproliferation)
Vascular dilation
Inflammation, T-lymphocytes in the dermis & epidermis
How will a pt present w Psoriasis?
Common (2-3% of world’s pop), Chronic
Erythematous, sharply demarcated papules & rounded plaques, covered by silvery micacous scale
Variably pruritic
Koebner’s phenomenon
Exacerbated by external factors (infections, stress, meds (lithium, beta blockers, anti-malarials))
What type of Psoriasis is pictured below?

Plaque-type (discoid)
How will a pt present w Plaque-type (discoid) psoriasis?
Most common form
Stable, slowly enlarging, indolent course
Unchanged for long periods
Usually symmetrical (elbows, knees, gluteal cleft & scalp)
Needs to be tx to resolve, will spontaneously remit
What type of skin lesion is pictured below?

Inverse psoriasis
How will a pt present w Inverse Psoriasis?
Shaply demarcated plaques
May be moist & w/o scales due to their location (intertriginous regions…axilla, groin, submammary region, navel, scalp, palms, soles
What type of Psoriasis follows infection w hemolytic Streptococci, withdrawl from steroids or anti-marlarial use?
Guttate Psoriasis (eruptive psoriasis)
Name the skin disorder pictured below.

Guttate psoriasis (eruptive psoriasis)
How will a pt present w Guttate Psoriasis?
Provide the DDx
Most common in children & young adults
Acute w no h/o psoriasis
small erythematous, scaling papules
DDx = Pityriasis rosea, 2nd syphilis
Acquire med hx and recent illnesses (typically follows infection w hemolytic Strept, withdrawl from steroids, antimalarial use)
Name this skin disorder.

Pustular psoriasis
Name this skin disorder

Erythrodermic psoriasis (i.e. severe pustular)
How will a pt present w Pustular Psoriasis?
Localized to palms/soles or generalized
Painful, erythematous w pustules (excudate: inflammatory or infected if cloudy)
Variable scale depending on location
Similar in size to eczema when limited to palms/soles
How will a pt present w Erythrodermic Psoriasis?
Generlized, often recurrent, w fever 102-104 for days
Sterile pustules
intense erythema (erythrodermic)
What is the eitology of Erythrodermic psoriasis?
Local irritants
Pregnancy
Medications
Infections
Systemic glucocorticoid withdrawl may precipiate
What is the tx for pt w Erythrodermic psoriasis?
Oral retinoids for non-pregnant pts
Name the disorder pictured along w characteristics

Nail psoriasis
Characteristics include:
Punctated pitting
onycholysis
nail thickening or subungual hyperkeratosis
Helpful in non-classic presentation
Name this disorder
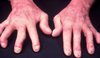
Psoriatic arthritis
How dose Psoriatic arthritis present?
10-30% pt w skin sx
Hands & feet, sometimes large joints
Stiffness, pain & progressive joint damage
Name this disorder and characteristics.

Oral psoriasis
white lesions on oral mucosa, change severity daily
Can be severe cheilosis w extension crossing vermillion border
Geographic tongue may be a form
Name this skin lesion.

Lichen Planus
Name this skin lesion.
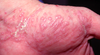
Lichen Planus
What is the distribution of Lichen Planus?
Predilection for wrists, shins, lower back, & genitalia
May affect skin, scalp, nails, & mucous membranes.






