Overview: Organic Chemistry Flashcards
Chemical Bonds Strong Bonds Intramolecular
Ionic Covalent (Metallic) Greater than >100kJ/mol
Chemical Bonds Intramolecular Weak Bonds
Hydrogen (10-50 kJ/mol) Van der Waals <10kJ
Electron shells Unfilled
Unfilled electron shells are unstable.
Electron shells How do atoms get filled electron shells?
Accepting / Donating Sharing
Ionic bonding
Accepting / Donating
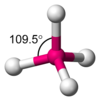
Convalent Bonding
Sharing
What is Electronegativity
Measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a molecule.
What is electronegativity dependent on?
Strength of positive charge in nucleus Distance of bonded electrons (shielding from electron shells)
Polar molecules Dipoles
Molecules with higher electronegativity draw the electrons closer to themselves and away from their neighbours.
Van der Waals forces
Attractive or repulsive forces formed by dipoles Much weaker than covalent bonds Only work at short distances.
Hydrogen Bonds Possible with dipole?
Possible with dipole where hydrogen bonds to a highly electrnegative atom.
What is a dipole?
a pair of equal and oppositely charged or magnetized poles separated by a distance.
Hydrogen Bonds Features
Relatively positive. Attracts negative atoms. Weaker than covalent bonds. Stronger than Van der Waals Vital for DNA and protein structure
Ionic Bonds Summary
Donation of electrons from one (metal) atom to another (non-metal) to form positive and negative ions which then attract.
Covalent Bonds Summary
Sharing of electron pairs (non-metals)