Ovarian Tumors of Non-Epithelial Origin and other Disorders Flashcards
Histiogenesis of Germ Cell tumors

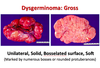
Dysgerminoma
Age?
Male Equivalent?
Young women and girls
Male equivalent is seminoma
Pathogenesis of Dysgerminoma
c-kit upregulated (diagnostic and theraputic target)
Transcription factors oct3,4, and Nanog maintain pleuripotency
Good prognosis
Gross Appearance of Dysgerminoma
Dysgerminoma Histopathology

Yolk Sac Tumor
Age?
Prognosis?
Young women <30 years of age
Good prognosis with chemotherapy
Gross appearance of Yolk sac tumor
Multiple cysts, hemorrhages

Diagnostic feature of yolk sac tumor
Increase in serum level of AFP
RICH in AFP
Yolk Sac tumor histopathology

Choriocarcinoma is identical to what?
Placental tumor
Choriocarcinoma course/timeline
Primary tumor may regress, leaving only metastasis sites
Types of epithelium involved in Choriocarcinoma
Syncytiotrophoblast
Cytotrophoblast
Choriocarcinoma gross appearance
Small hemorrhagic nidus/focus
Types of Ovarian teratomas?
Mature (benign, cystic (dermoid cyst))
Immature Teratoma
Monodermal (specialized)
Mature Teratoma
all three germ ayers
commonest germ cell tumor
Immature Teratoma
potentially malignant
Monodermal Teratoma
Struma ovarii
ovarian carcinoid
Mature Cystic Teratoma
Age?
Any age, usually younger patients
In elderly women–> might see malignant transformation (squamous cell carcinoma)
Mature Cystic Teratoma gross appearance
Mature tissues haphazardly arranged
Hair, teeth, and sebaceous glad
Mature NORMAL tissue, haphazardly arranged. Mostly, Hair, teeth and csebaceous glands. But cartilage and intestinal epithelium may also be seen.

Immature Teratoma
Age?
Prepubertal adolescents and young women
Complication of immature ovarian teratoma
Potentially malignant
Derivation of immature teratoma
immature neural tissue
Two types of monodermal (specialized) teratoma
Struma Ovarii
Ovarian Carcinoid
Complication of Struma Ovarii
thyrotoxicosis










