Outer/Middle Ear Flashcards
(15 cards)
Label the outer ear (6 structures) and what is their function?

Tragus, Antitragus, Helix, Anti-helix, Lobule, concha
Collect sound energy and channe into head

Label this picture (8 structures).

TM, Pars flaccia, Pars tensa, Umbo, Cone of light, Short handle of malleus, Manubrium (long handle), Long crus of incus.

What is the function of the TM?
Capture and transmit sound energy to the ossicles.
Label 2, 3, 4, 5 (and attachment site), 11.

Incus, Malleus, TM, Stapes, Oval Window of cochlea, Eustachian Tube
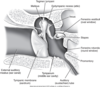
What are the functions of the ossicles?
Converts sound energy into mechanical energy and amplifies it, transferring it to oval window of cochlea
What does the eustachian tube communication to and what lines it?
Communicates btwn the middle ear and nasopharynx. Lined with resp. mucosa.
What is the function of the eustachian tube?
Allows adjustments of pressure btwn the middle ear & external environment.
Allows for ear drainage & protects middle ear from nasopharyngeal secretions & bad (pathogenic) bacteria
Is the eustachian tube open or closed normally? When does it do the other?
Closed
Opens during swallowing/yawning d/t active contraction of tensor veli palantini

Label the parts of the inner ear (7).

Labyrinth (bony and membranous), Vestibule, Semi-Circular Canals, Cochlea, CN 8

Describe the internal structure of the labyrinth.
Bony labyrinth (structure/protective function).
Filled with peirlymph (ECF, lots of Na, low in K)
Covers membranous labyrinth.
Membranous labyrinth filled with endolymph (lots of K, low in Na)
What is the function of the semi-circular canal?
Proprioception and balance
What is the function of the cochlea?
Conversion of soun energy into electrical energy. Vibrations of ossicles make endolymph move, leads to flow of K+ across negatively charged hairs of Organ of Corti. This leads to a synapse firing, which leads to CN 8 activation. The organ of corti converts the electrical energy into a nerve impulse.
What is the only vascularized endothelium in the body?
Stria vascularis (high in mitochondria)
What is the function of the stria vascularis?
Back up for the organ of Corti, helps to maintain endolymph. Its vascular supply provides nutrients to the organ of Corti while keeping the vessels at a distance minimizing the distraction of noise from blood flow
DDx for ear pain
OM (AOM, COM, OMS)
Eustachian tube issues, Neoplasm
OE (A, C), impacted cerumen, trauma, FB
Mastoidititis, Referred pain from TMJ, Wisdom teeth
Local infx, Tumor, Neuro involvment, Thyroiditis
Colds/Allergies


