Orofacial fungal infections Flashcards
Chronic use of broad spectrum antibiotics and corticosteroid use can lead to what?
Erythematous candiaisis
What can a patient consume to help manage Pseudomembranous candidiasis?
Live active yoghurt
What is the mechanism of action for echinocandins antifungal agents?
Inhibition of β1,3 D-glucan synthesis
What condition is this?

Chronic hyperplastic candidosis (candidal leukoplakia)
(white erythematous raised lesions which do NOT rub off)
What is the mechanism of action for polyene antifungal agents?
Disruption of fungal cell membrane
What condition is this?

CHRONIC ERYTHEMATOUS CANDIDOSIS
(DENTURE STOMATITIS)
What topical agents can be given to the patient to manage Pseudomembranous candidiasis? (3)
Cholorhexidine mouth wash
Nystatin suspension
Miconazole oral gel
Where does Erythematous candidosis commonly occur?
Commonly occurs on dorsum of tongue and palate
Clinically what can you see in this image?

Hyperplastic white areas
What are the newton classifications for denture stomatitis?
Type 1 - pinpoint inflammation
Type 2 - Diffuse inflammation in denture area
Type 3 - Granular inflammation

Give some examples of azole anti fungal agents (3)
Fluconazole
Miconazole
Ketoconazole
What are the types of acute candidosis?
Pseudomembranous candidosis
Erythematous candidosis
What is a common site for erythematous candidosis?
Common on the dorsum of the tongue and palate
What is this condition?
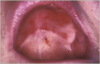
Denture stomatitis (Chronic erythematous candidosis)
What dieatry factors could lead to an increased risk of candidosis?
Deficiencies in the following;
Iron
Folate
Vitamin A
Vitamin B12
Vitamin C
What are some factors that could increase the chance of angular chelitis? (5)
Lip morphology
Xerostomia
Broad spectrum antibiotics
Diabetes
HIV
Consuming live active yogurt can help treat what condition?
Psuedomembranous candidiasis
What is the link between xerostomia and candidiasis?
Reduced salivary flushing leads to a reduction in anti fungal salivary components
What can be prescribed to manage Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis?
2-4 weeks of oral fluconazole
What is the mechanism of action for azoles antifungal agents?
Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis
What demographics have increases of candida species in the mouth? (3)
Pregnancy
Smokers
Denture wearers
What condition is this?

Median rhomboid glossitis
(you can see diamond-shaped smooth area anterior to circumvallate pappillae)
Give some examples of polyenes anti fungal agents (2)
Nystatin
Amphoterecin
What is the link between diabetes and candida?
Poorly controlled diabetics have a higher Candidal carriage




