Orgo Lecture Functional Groups Flashcards
alkyl
any region of fully saturated carbon with only C–H bonds; sometimes called “aliphatic”

alkene
a C–C double bond, also called “olefins”

alkynes
a C–C triple bond

alcohol

phenol
alcohol attached to an aromatic

ether
both substituents are carbon

epoxide
three-membered cyclic ether is special type

amine
substituents can be C or H

alkyl halide
X = F, Cl, Br, I

aldehyde
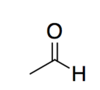
ketone

carboxylic acid (“acid”)

ester (technically carboxylic ester)
(if part of a ring, technically called a lactone

amide
N substituents can be H or C (if part of a ring, technically called a lactam)

aryl
“aromatic ring” many types, this one is a “phenyl” when it is a subsituent

acetal

hemiacetal

nitrile

nitro

guanidine
subsituents can be H or C

thiol

sulfide

sulfonate

sulfonamide
substituents can be H or C



