Organic chemistry pt2 Flashcards
what is the functional group and homologous series of carboxylic acids?
carboxyl
-COOH
What happens when carboxylic acid comes in contact with water?
dissolves in water to form acidic solutions
they ionise and release H+ ions, however, they don’t fully ionise
- weak acids
Carboxylic acids + carbonates = ?
- CO2
- salt ( with an -anoate at the end)
- water
ethanoic acid + sodium carbonate

Carboxylic acids + alcohol (+ an acidic catalyst) =
esters +water
ethanol + ethanoic acid = and what catalyst does it use?
what type of reaction is it?
ethyl ethanoate
sulfuric acid as a catalyst
it is a reversible reaction
features of esters?
describe the boiling point and smell
- volatile compounds i.e have low boing point
- distinctive smells and are used in perfumes as well as flavourings in food
What two different types of functional groups do amino acids have?
a basic amine group, NH2
carboxyl group
COOH
Amino acids react by _____________________ to produce________-
condensation polymerisation
polypeptides
What is the chemical formula for glycine?
NCH2COOH
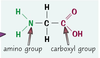
What is the condensation polymerisation reaction for glycine
(glycine + glycine)

How are proteins produced?
at least 2 different amino acids of same length are combined on the same chain
What is DNA made from?
2 polymer chains constructed from 4 different nucleotides: cytosine, guanine, adenine and thymine the two polymer chains from a double helix
what are examples of polymers of sugars?
starch and cellulose
what are sugars?
small molecules that contain carbon, oxygen and hydrogen
what are starch and cellulose made by?
plants
Why are alkenes useful for making other molecules, especially polymers
because they are unsaturated they are able to open up carbon-carbon double bond
What is addition polymerisation?
when many monomers join to form polymers - they have one product only - 100% atom economy
this involves alkenes only
What is condensation polymerisation
involves two different monomers with two functional groups, with two of the same functional groups on each monomer. When these types of monomers react they join together, usually losing small molecules such as water,
The monomers are NOT alkenes
Whats the chemical formula for polyester
* name reactants and products

General formula for carboxylic acids
CnH2nO2


