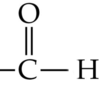Organic Chemistry Flashcards
What is a organic compound
contains carbon
What is a saturated hydrocarbon
compound containing only single bonds as as much hydrogen as possible
What is a unsaturated hydrocarbon
if there are double bonds between carbons then there is not the maximum number of hydrogens bonded to carbons
what is a multiple bond
two or more covalent bonds across an atom
displaced formula
shows every atom and every bond
structural formula
a simplified molecular formula showing the group of atoms joined to a particular carbon
skeletal formula
zig-zag line that shows the bonds between carbon atoms
molecular formula
shows the actual numbers of each atom in the molecules
empirical formula
shows the numbers of each atom in the simplest whole-number ratio
functional group
is an atom or a group of atoms in a molecules that is responsible for its chemical reactions and predictable properties
Homologous series and an example
is a family of compounds with the same functional groups, which differ in formula by CH2 from the next member Alkanes
General formula for alkanes
CnH2n+2
General formula for Alkenes
CnH2n
General formula for halogenoalkanes
CnH2n+1X
General formula for Alcohols
CnH2n+1OH
What is the number that correlates with ‘meth’
1
What is the number that correlates with ‘eth’
2
What is the number that correlates with ‘prop’
3
What is the number that correlates with ‘but’
4
What is the number that correlates with ‘pent’
5
What are the rules around locants
- When an atom and group can have different positions in a molecules, numbers and hyphens are used to show there positions - Numbers represent the carbon atom in the longest chain that the atom and group are attached to
All alkanes end in what
-ane
Name the functional group
-OH
Alcohols
Name the Fucntional group

Alkene