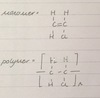Organic Chemistry Flashcards
… are long chain molecules that form lots of small … called …
the monomers are unsaturated … molecules that add together to form polymer molecules
the polymers are named after their momomer that forms, so … would be names polybutene
the polymers are types of alkanes and are therefore …. this means they are quite unreactive and so it is difficult for them to decompose or … in the environment
the persistence of plastics is a problem as it fills up … sites and can cause problems for wildlife
polymers are long chain molecules that form lots of small alkenes called monomers
the monomers are unsaturated reactive molecules that add together to form polymer molecules
the polymers are named after their momomer that forms, so butene would be names polybutene
the polymers are types of alkanes and are therefore saturated. this means they are quite unreactive and so it is difficult for them to decompose or biodegrade in the environment
the persistence of plastics is a problem as it fills up landfill sites and can cause problems for wildlife
a polymer is a chemical … made of … (called …) linked together
a polymer is a chemical compound made of many smaller, identical molecules (called monomers) linked together
after butane/ene, alkanes and alkenes take on the names of their ……..
5C =
6C =
7C =
8C =
mathematical shapes
5C = pentene/ane
6C = hexene/ane
7C = heptene/ane
8C = octene/ane
are alkanes normally reactive or unreactive?
very unreactive
are haloalkanes useful products?
yes
are hyrdocarbons found in crude oil?
yes
are isomers free to rotate?
yes
if it stays on the same carbon then it is the same
are substances with high boiling points (C20 –>) viscous or not? (in terms of crude oil)
viscous
the viscosity … as the boilingpoint gets higher
the viscoity increases as the boiling point gets higher
as fractions decrease in density and boiling point in fraction distillation, what becomes of them?
less carbon atoms
more commercially useful
as fractions increase in density and boiling point in fraction distillation, what becomes of them?
more carbon atoms
less commercially useful
As the relative molecular mass of an alkane increases which one of the following is true?
A. the boiling point and viscosity increases
B. The boiling point and the volatility increases
C. The boiling point decreases and the viscosity increases
D. The boiling point and the viscosity decreases
A
at what percentage of alcohol is yeast poisoned?
14%
Biodiesel is a fuel made by the chemical reaction of alcohol with vegetable oils such as soya bean oil. This process also produces glycerine which used in soap making. Biodiesel can be used in engines which normally would run on petroleum diesel. Biodiesel can be mixed with petroleum diesel in any proportions. Biodiesel is biodegradable and contains very little sufur. The complete combustion of smoke-type emissions that petroleum diesel. Some of the diadvanatges of biodiesel include attacking the engine hoses that were intended for a different fuel and loosening deposits wihin the engine left from previous fuels which can cause blockages.
From the given information, it is possible to conclude that biodiesel will contribute to…
A. a decrease in acid rain formtaion
B. An increase in fog formation
C. A decrease in soap production
D. A reduction in global warming
A
Biodiesel is a fuel made by the chemical reaction of alcohol with vegetable oils such as soya bean oil. This process also produces glycerine which used in soap making. Biodiesel can be used in engines which normally would run on petroleum diesel. Biodiesel can be mixed with petroleum diesel in any proportions. Biodiesel is biodegradable and contains very little sufur. The complete combustion of smoke-type emissions that petroleum diesel. Some of the diadvanatges of biodiesel include attacking the engine hoses that were intended for a different fuel and loosening deposits wihin the engine left from previous fuels which can cause blockages.
The main advantage of using biodiesel instead of petroleum diesel is that…
A. It does not cause damage to engines
B. It guaranteed the soap industry a plentiful supply of glycerine
C. It increases the amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere
D. It is a renewable fuel
D
Biodiesel is a fuel made by the chemical reaction of alcohol with vegetable oils such as soya bean oil. This process also produces glycerine which used in soap making. Biodiesel can be used in engines which normally would run on petroleum diesel. Biodiesel can be mixed with petroleum diesel in any proportions. Biodiesel is biodegradable and contains very little sufur. The complete combustion of smoke-type emissions that petroleum diesel. Some of the diadvanatges of biodiesel include attacking the engine hoses that were intended for a different fuel and loosening deposits wihin the engine left from previous fuels which can cause blockages.
Which one of the following statements about biodiesel compared with petroleum diesel is not based on scientific measursments?
A. Both fuel and its combustion products are less carcinogenic than ordinary diesel
B. For transportation, biodiesel is classes as less flamable than petroleum diesel
C. The exhaust gases from a biodiesel-fuelled engine less unburnt hydrocarbons
D. Biodiesel has a much more pleasant odour than petroleum diesel
D
butance can form two structural isomers
draw their displayed formula
which structural isomer has a higher boiling point and why?
number 1 as it has higher intermolecular force of attraction as the chain is a straight line - harder to break

By what industrial process is crude oil seperated into fractions?
A. Cracking
B. Polymerisation
C. Fractional Distillation
D. Porolysis
C
by what process are the hydrocarbons in crude oil seperated?
fractional distillation
carboxylic acid are easily made through …
oxidising alcohol
complete this diagram for the cracking of paraffin


Crude oil consists of a large number of different compounds. Explain how fractional distillation is used to produce useful compounds from crude oil. (3 marks)
Crude oil evaporated in a fractioning tower
Different hydrocarbons in the crude oil have different boiling points
Their vapour condenses at different temperatures in the tower, and are collected as either purer liquids of gases
Each fractions consist of hydrocarbons with a different number of carbon atoms and each of these has different uses
decane and octane are straight chain carbons
why are they not used in this form as fuels in the car engine?
because of their straight chain carbons they don’t burn steadily or smoothly
the straight chain compounds ignite prematurely, causing ‘knocking’, which can damage the engine
the efficiency is low
describe how crude oil was formed
formed millions of years from remains of dead organisms (dead sea creatures)
millions of yeras ago huge numbers of microscopic animals and plants, plankton, died and fell to the bottom of the sea - remains covered in mud
as the mud sediment was buried by more desiment it started to change into rock as the temperature and pressure increased - the plants and animals were ‘cooked’ by this process and slowly changed into crude oil
crude oil is less dense than the water in rocks so it will rise as a result of pressure from below and often escape altogether if the rocks are permeable
(if the rocks are impermeable, oil can’t rise through and gets trapped)