oral pic exam 2 Flashcards
how would you describe this
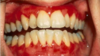
desquamative gingivits
it is a clinical term, not a ds
ONLY for erosive lichen planus not reticular
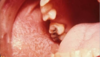
lichen planus - reticular
White striae or leukoplakia appearance
Bilateral!
Can be on other mucosal surfaces BUT buccal is the most common

lichen planus
White striae or leukoplakia appearance
Bilateral!
Can be on other mucosal surfaces BUT buccal is the most common
Commonly seen on areas that flex, like wrists, elbows etc.
They are SUPER itchy, and have a small lace like appearance to them too.

lichen planus
White striae or leukoplakia appearance
Bilateral!
Can be on other mucosal surfaces BUT buccal is the most common
Commonly seen on areas that flex, like wrists, elbows etc.
They are SUPER itchy, and have a small lace like appearance to them too.

reticular lichen planus
“classic appearance”
Bilateral asymptomatic white lesions of the buccal mucosa
Wickman striae lace-like appearance.
Plaque-like areas.
Normally not painful.
Can be in different surfaces like the alveolar mucosa and then onto the vestibular appearance involved.

Erosive form of lichen planus
Bilateral symptomatic erythematous areas with fine white radiating striae
Central ulceration
Desquamative gingivitis → ONLY ON EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS NOT THE RETICULAR ONE

Reticular lichen planus
Bilateral asymptomatic white lesions of the buccal mucosa
Wickman striae lace-like appearance.
Plaque-like areas.
Normally not painful.
Can be in different surfaces like the alveolar mucosa and then onto the vestibular appearance involved.

Reticular lichen planus
Bilateral asymptomatic white lesions of the buccal mucosa
Wickman striae lace-like appearance.
Plaque-like areas.
Normally not painful.
Can be in different surfaces like the alveolar mucosa and then onto the vestibular appearance involved.

Reticular lichen planus
Bilateral asymptomatic white lesions of the buccal mucosa
Wickman striae lace-like appearance.
Plaque-like areas.
Normally not painful.
Can be in different surfaces like the alveolar mucosa and then onto the vestibular appearance involved.
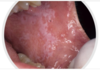
Reticular lichen planus
Bilateral asymptomatic white lesions of the buccal mucosa
Wickman striae lace-like appearance.
Plaque-like areas.
Normally not painful.
Can be in different surfaces like the alveolar mucosa and then onto the vestibular appearance involved.
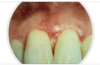
Reticular lichen planus
fine lace like apperance with some red in the background.
Bilateral asymptomatic white lesions of the buccal mucosa
Wickman striae lace-like appearance.
Plaque-like areas.
Normally not painful.
Can be in different surfaces like the alveolar mucosa and then onto the vestibular appearance involved.
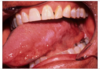
Reticular lichen planus
Here it is a plaque-like presentation of lichen planus
This is not a classic presentation.
Would still get a biopsy to confirm.
Bilateral asymptomatic white lesions of the buccal mucosa
Wickman striae lace-like appearance.
Plaque-like areas.
Normally not painful.
Can be in different surfaces like the alveolar mucosa and then onto the vestibular appearance involved.

Erosive form of lichen planus
Bilateral symptomatic erythematous areas with fine white radiating striae
Central ulceration
Desquamative gingivitis → ONLY ON EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS NOT THE RETICULAR ONE

Erosive form of lichen planus
Bilateral symptomatic erythematous areas with fine white radiating striae
Central ulceration
Desquamative gingivitis → ONLY ON EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS NOT THE RETICULAR ONE

Erosive form of lichen planus
Bilateral symptomatic erythematous areas with fine white radiating striae
Central ulceration
Desquamative gingivitis → ONLY ON EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS NOT THE RETICULAR ONE

Erosive form of lichen planus
Bilateral symptomatic erythematous areas with fine white radiating striae
Central ulceration
Desquamative gingivitis → ONLY ON EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS NOT THE RETICULAR ONE
Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces

Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces

Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces

Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces

Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces

Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces
Oral lesions come FIRST then SKIN lesions
Think second = skin
Prognosis improved it tx early
May be fatal without tx.
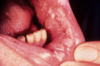
Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces
Oral lesions come FIRST then SKIN lesions
Think second = skin
Prognosis improved it tx early
May be fatal without tx.

Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces
Oral lesions come FIRST then SKIN lesions
Think second = skin
Prognosis improved it tx early
May be fatal without tx.

Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces
Oral lesions come FIRST then SKIN lesions
Think second = skin
Prognosis improved it tx early
May be fatal without tx.
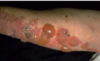
Pemphigus vulgaris
mutliple areas of ulceration because cells arent atttached really.
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells. Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces
Oral lesions come FIRST then SKIN lesions
Think second = skin
Prognosis improved it tx early
May be fatal without tx.
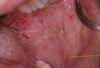
Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells. Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces
Oral lesions come FIRST then SKIN lesions
Think second = skin
Prognosis improved it tx early
May be fatal without tx.

Pemphigus vulgaris
this is painful.
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces
Oral lesions come FIRST then SKIN lesions
Think second = skin
Prognosis improved it tx early
May be fatal without tx.
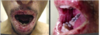
paraneoplatic pemphigus
which is associated with malignancy: lymphoma and leukemia.

Mucous membrane pemphigoid
This is a chronic, autoimmune blistering mucocutaneous ds
Autoantibodies to basement membrane antigens: Laminin 5 (epiligrin) & BP180
Subepithelial split involved.
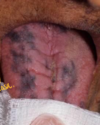
Oral lesions of mucous membrane pemphigoid: has Vesicles, bullae, and ulcerations, desquamative gingivitis and nikolsky sign
They do not respond to steroids but do respond to Cellcept
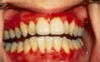
Mucous membrane pemphigoid
This is a chronic, autoimmune blistering mucocutaneous ds
Autoantibodies to basement membrane antigens: Laminin 5 (epiligrin) & BP180
Subepithelial split involved.
Oral lesions of mucous membrane pemphigoid: has Vesicles, bullae, and ulcerations, desquamative gingivitis and nikolsky sign
They do not respond to steroids but do respond to Cellcept
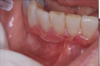
Mucous membrane pemphigoid
This is a chronic, autoimmune blistering mucocutaneous ds
Autoantibodies to basement membrane antigens: Laminin 5 (epiligrin) & BP180
Subepithelial split involved.
Oral lesions of mucous membrane pemphigoid: has Vesicles, bullae, and ulcerations, desquamative gingivitis and nikolsky sign
They do not respond to steroids but do respond to Cellcept
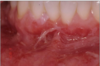
this shows
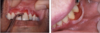
positive nikolsky sign in mucous membrane pemphigoid

Mucous membrane pemphigoid
This is a chronic, autoimmune blistering mucocutaneous ds
Autoantibodies to basement membrane antigens: Laminin 5 (epiligrin) & BP180
Subepithelial split involved.
Oral lesions of mucous membrane pemphigoid: has Vesicles, bullae, and ulcerations, desquamative gingivitis and nikolsky sign
They do not respond to steroids but do respond to Cellcept

Mucous membrane pemphigoid
This is a chronic, autoimmune blistering mucocutaneous ds
Autoantibodies to basement membrane antigens: Laminin 5 (epiligrin) & BP180
Subepithelial split involved.
Oral lesions of mucous membrane pemphigoid: has Vesicles, bullae, and ulcerations, desquamative gingivitis and nikolsky sign
They do not respond to steroids but do respond to Cellcept

Mucous membrane pemphigoid
This is a chronic, autoimmune blistering mucocutaneous ds
Autoantibodies to basement membrane antigens: Laminin 5 (epiligrin) & BP180
Subepithelial split involved.
Oral lesions of mucous membrane pemphigoid: has Vesicles, bullae, and ulcerations, desquamative gingivitis and nikolsky sign
They do not respond to steroids but do respond to Cellcept

Mucous membrane pemphigoid
This is a chronic, autoimmune blistering mucocutaneous ds
Autoantibodies to basement membrane antigens: Laminin 5 (epiligrin) & BP180
Subepithelial split involved.
Oral lesions of mucous membrane pemphigoid: has Vesicles, bullae, and ulcerations, desquamative gingivitis and nikolsky sign
They do not respond to steroids but do respond to Cellcept

Mucous membrane pemphigoid
This is a chronic, autoimmune blistering mucocutaneous ds
Autoantibodies to basement membrane antigens: Laminin 5 (epiligrin) & BP180
Subepithelial split involved.
Oral lesions of mucous membrane pemphigoid: has Vesicles, bullae, and ulcerations, desquamative gingivitis and nikolsky sign
They do not respond to steroids but do respond to Cellcept

Mucous membrane pemphigoid
nasal involvement
This is a chronic, autoimmune blistering mucocutaneous ds
Autoantibodies to basement membrane antigens: Laminin 5 (epiligrin) & BP180
Subepithelial split involved.
Oral lesions of mucous membrane pemphigoid: has Vesicles, bullae, and ulcerations, desquamative gingivitis and nikolsky sign
They do not respond to steroids but do respond to Cellcept

Mucous membrane pemphigoid
ocular involvement
This is a chronic, autoimmune blistering mucocutaneous ds
Autoantibodies to basement membrane antigens: Laminin 5 (epiligrin) & BP180
Subepithelial split involved.
Oral lesions of mucous membrane pemphigoid: has Vesicles, bullae, and ulcerations, desquamative gingivitis and nikolsky sign
They do not respond to steroids but do respond to Cellcept
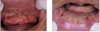
Mucous membrane pemphigoid
This is a chronic, autoimmune blistering mucocutaneous ds
Autoantibodies to basement membrane antigens: Laminin 5 (epiligrin) & BP180
Subepithelial split involved.
Oral lesions of mucous membrane pemphigoid: has Vesicles, bullae, and ulcerations, desquamative gingivitis and nikolsky sign
They do not respond to steroids but do respond to Cellcept

Erythema multiforme is an immunologically mediated self limited mucocutaneous ds
Seen in young adults
Sudden onset of widespread painful superficial mucosal ulcers and target lesion soft skin. Will see “target” “bullseye” lesion
Crusted ulcers on lips. Lesions might be limited to the oral mucosa.
May be recurrent.
Prodromal symptoms (fever, mailase)
This ds is self-limiting can last up to 2-6 weeks
Want to avoid dehydration

Erythema multiforme is an immunologically mediated self limited mucocutaneous ds
Seen in young adults
Sudden onset of widespread painful superficial mucosal ulcers and target lesion soft skin. Will see “target” “bullseye” lesion
Crusted ulcers on lips. Lesions might be limited to the oral mucosa.
May be recurrent.
Prodromal symptoms (fever, mailase)
This ds is self-limiting can last up to 2-6 weeks
Want to avoid dehydration

Erythema multiforme is an immunologically mediated self limited mucocutaneous ds
Seen in young adults
Sudden onset of widespread painful superficial mucosal ulcers and target lesion soft skin. Will see “target” “bullseye” lesion
Crusted ulcers on lips. Lesions might be limited to the oral mucosa.
May be recurrent.
Prodromal symptoms (fever, mailase)
This ds is self-limiting can last up to 2-6 weeks
Want to avoid dehydration

Erythema multiforme is an immunologically mediated self limited mucocutaneous ds
Seen in young adults
Sudden onset of widespread painful superficial mucosal ulcers and target lesion soft skin. Will see “target” “bullseye” lesion
Crusted ulcers on lips. Lesions might be limited to the oral mucosa.
May be recurrent.
Prodromal symptoms (fever, mailase)
This ds is self-limiting can last up to 2-6 weeks
Want to avoid dehydration

Erythema multiforme is an immunologically mediated self limited mucocutaneous ds
Seen in young adults
Sudden onset of widespread painful superficial mucosal ulcers and target lesion soft skin. Will see “target” “bullseye” lesion
Crusted ulcers on lips. Lesions might be limited to the oral mucosa.
May be recurrent.
Prodromal symptoms (fever, mailase)
This ds is self-limiting can last up to 2-6 weeks
Want to avoid dehydration
seen on a young adult with some prodromal symptoms
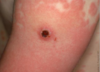
Erythema multiforme is an immunologically mediated self limited mucocutaneous ds
Seen in young adults
Sudden onset of widespread painful superficial mucosal ulcers and target lesion soft skin. Will see “target” “bullseye” lesion
Crusted ulcers on lips. Lesions might be limited to the oral mucosa.
May be recurrent.
Prodromal symptoms (fever, mailase)
This ds is self-limiting can last up to 2-6 weeks
Want to avoid dehydration

Erythema multiforme is an immunologically mediated self limited mucocutaneous ds
Seen in young adults
Sudden onset of widespread painful superficial mucosal ulcers and target lesion soft skin. Will see “target” “bullseye” lesion
Crusted ulcers on lips. Lesions might be limited to the oral mucosa.
May be recurrent.
Prodromal symptoms (fever, mailase)
This ds is self-limiting can last up to 2-6 weeks
Want to avoid dehydration

Erythema multiforme is an immunologically mediated self limited mucocutaneous ds
Seen in young adults
Sudden onset of widespread painful superficial mucosal ulcers and target lesion soft skin. Will see “target” “bullseye” lesion
Crusted ulcers on lips. Lesions might be limited to the oral mucosa.
May be recurrent.
Prodromal symptoms (fever, mailase)
This ds is self-limiting can last up to 2-6 weeks
Want to avoid dehydration

Erythema multiforme is an immunologically mediated self limited mucocutaneous ds
Seen in young adults
Sudden onset of widespread painful superficial mucosal ulcers and target lesion soft skin. Will see “target” “bullseye” lesion
Crusted ulcers on lips. Lesions might be limited to the oral mucosa.
May be recurrent.
Prodromal symptoms (fever, mailase)
This ds is self-limiting can last up to 2-6 weeks
Want to avoid dehydration

Erythema multiforme is an immunologically mediated self limited mucocutaneous ds
Seen in young adults
Sudden onset of widespread painful superficial mucosal ulcers and target lesion soft skin. Will see “target” “bullseye” lesion
Crusted ulcers on lips. Lesions might be limited to the oral mucosa.
May be recurrent.
Prodromal symptoms (fever, mailase)
This ds is self-limiting can last up to 2-6 weeks
Want to avoid dehydration
24 yo pt. Has noticed difference on the palate for about 3 weeks. Had some fever.

Erythema multiforme is an immunologically mediated self limited mucocutaneous ds
Seen in young adults
Sudden onset of widespread painful superficial mucosal ulcers and target lesion soft skin. Will see “target” “bullseye” lesion
Crusted ulcers on lips. Lesions might be limited to the oral mucosa.
May be recurrent.
Prodromal symptoms (fever, mailase)
This ds is self-limiting can last up to 2-6 weeks
Want to avoid dehydration

Erythema multiforme is an immunologically mediated self limited mucocutaneous ds
Seen in young adults
Sudden onset of widespread painful superficial mucosal ulcers and target lesion soft skin. Will see “target” “bullseye” lesion
Crusted ulcers on lips. Lesions might be limited to the oral mucosa.
May be recurrent.
Prodromal symptoms (fever, mailase)
This ds is self-limiting can last up to 2-6 weeks
Want to avoid dehydration
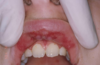
Erythema multiforme is an immunologically mediated self limited mucocutaneous ds
Seen in young adults
Sudden onset of widespread painful superficial mucosal ulcers and target lesion soft skin. Will see “target” “bullseye” lesion
Crusted ulcers on lips. Lesions might be limited to the oral mucosa.
May be recurrent.
Prodromal symptoms (fever, mailase)
This ds is self-limiting can last up to 2-6 weeks
Want to avoid dehydration
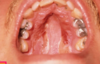
Erythema multiforme is an immunologically mediated self limited mucocutaneous ds
Seen in young adults
Sudden onset of widespread painful superficial mucosal ulcers and target lesion soft skin. Will see “target” “bullseye” lesion
Crusted ulcers on lips. Lesions might be limited to the oral mucosa.
May be recurrent.
Prodromal symptoms (fever, mailase)
This ds is self-limiting can last up to 2-6 weeks
Want to avoid dehydration

Erythema multiforme Major
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome is the severe form of EM
Triggered by a drug not an infection.

Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (Lyell ds)
The most severe form of EM
Seen in older individuals
Triggered by a drug exposure
There is diffuse sloughing of epidermis leading to a scalded appearance, fluid loss and infection
Treated as a sever burn pt in the hospital.

Lupus is a multisystem autoimmune ds
Most common in adult woman in child-bearing years
Autoantibodies - antinuclear antibodies (ANA)
Immune complexes are deposited throughout the body, especially kidney and blood vessels
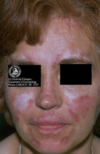
Discoid LE
Chronic, limited to skin and mucosa
Sun-exposed skin
Scaly, erythematous patches
Cosmetic problems: cutaneous atrophy, scarring and pigmentation (hypopigmentation)
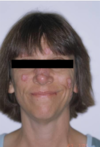
Discoid LE
Chronic, limited to skin and mucosa
Sun-exposed skin
Scaly, erythematous patches
Cosmetic problems: cutaneous atrophy, scarring and pigmentation (hypopigmentation)

Discoid LE
Chronic, limited to skin and mucosa
Sun-exposed skin
Scaly, erythematous patches
Cosmetic problems: cutaneous atrophy, scarring and pigmentation (hypopigmentation)
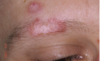
Discoid LE
Chronic, limited to skin and mucosa
Sun-exposed skin
Scaly, erythematous patches
Cosmetic problems: cutaneous atrophy, scarring and pigmentation (hypopigmentation)

Oral mucosal lesions in LE
Seen in ANY form of LE
Red and white lesions that may be clinically identical to erosive lichen planus
Dependent on blood work to tell the difference

Oral mucosal lesions in LE
Seen in ANY form of LE
Red and white lesions that may be clinically identical to erosive lichen planus
Dependent on blood work to tell the difference

Systemic LE
The most common form of lupus
Has the highest morbidity
Kidney involvement - glomerulonephritis- renal failure
50% have a butterfly rash
Malar area and nose, aggravated by sunlight.
Libman-sacks endocarditis
Other clinical involvement: arthritis, arthralgia, heart and lung involvement, anemia, bone marrow depression, vasculitis, skin rashes
Tx and prognosis:
- Systemic corticosteroids
- Antimalarial drugs – plaquenil. Causes hyperpigmentation of mucsa.
- Avoid excessive exposure to sunlight
- Prognosis depends on organs affected and ds activity
- Renal failure is most frequent cause of death
Systemic LE
The most common form of lupus
Has the highest morbidity
Kidney involvement - glomerulonephritis- renal failure
50% have a butterfly rash
Malar area and nose, aggravated by sunlight.
Libman-sacks endocarditis
Other clinical involvement: arthritis, arthralgia, heart and lung involvement, anemia, bone marrow depression, vasculitis, skin rashes
Tx and prognosis:
Systemic corticosteroids
Antimalarial drugs – plaquenil. Causes hyperpigmentation of mucosa.
Avoid excessive exposure to sunlight
Prognosis depends on organs affected and ds activity
Renal failure is most frequent cause of death

SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS = an autoimmune ds of adults, predom females
Characterized with excessive fibrosis
May be limited to the skin or be widespread affecting various organ systems
Clinically see: Microstomia, xerostomia, generalized widening of PDL space, and mandibular resorption. Mask-like face. Telangiectasia - dilated small vessels on the skin, face, mucosa. Raynaud phenomenon (=Arterial spasm in response to cold or emotional stress) Hands and fingers can show fibrosis, stiffness, deformity
Limited hand dexterity can be reason for poor oral hygiene.

SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS = an autoimmune ds of adults, predom females
Characterized with excessive fibrosis
May be limited to the skin or be widespread affecting various organ systems
Clinically see: Microstomia, xerostomia, generalized widening of PDL space, and mandibular resorption. Mask-like face. Telangiectasia - dilated small vessels on the skin, face, mucosa. Raynaud phenomenon (=Arterial spasm in response to cold or emotional stress) Hands and fingers can show fibrosis, stiffness, deformity
Limited hand dexterity can be reason for poor oral hygiene.
this is a sign for

SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS = an autoimmune ds of adults, predom females
Characterized with excessive fibrosis
May be limited to the skin or be widespread affecting various organ systems
Clinically see: Microstomia, xerostomia, generalized widening of PDL space, and mandibular resorption. Mask-like face. Telangiectasia - dilated small vessels on the skin, face, mucosa. Raynaud phenomenon (=Arterial spasm in response to cold or emotional stress) Hands and fingers can show fibrosis, stiffness, deformity
Limited hand dexterity can be reason for poor oral hygiene.
a sign for

SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS = an autoimmune ds of adults, predom females
Characterized with excessive fibrosis
May be limited to the skin or be widespread affecting various organ systems
Clinically see: Microstomia, xerostomia, generalized widening of PDL space, and mandibular resorption. Mask-like face. Telangiectasia - dilated small vessels on the skin, face, mucosa. Raynaud phenomenon (=Arterial spasm in response to cold or emotional stress) Hands and fingers can show fibrosis, stiffness, deformity
Limited hand dexterity can be reason for poor oral hygiene.
this is associated with:

Morphea - a localized form of scleroderma “coup de sabre”
Limited skin involvement, no systemic involvement
Progressive hemifacial atrophy (Pierre Romberg syndrome may be a form of scleroderma)
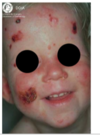
Hereditary epidermolysis bullosa
Primarily a severe and debilitating skin ds in which blisters form at sites of minor trauma and may heal with scarring → nikolsky positive.
NOT an autoimmune ds. Has defective structural proteins.
Orally: Normal diet produces bullae that heals with scarring leading to obliteration of vestibule. Can cause: ankyloglossia, microstomia, and esophageal stricture
Skin: “mitten”, ulceration on hands and fingers, dystrophic
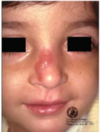
Hereditary epidermolysis bullosa
Primarily a severe and debilitating skin ds in which blisters form at sites of minor trauma and may heal with scarring → nikolsky positive.
NOT an autoimmune ds. Has defective structural proteins.
Orally: Normal diet produces bullae that heals with scarring leading to obliteration of vestibule. Can cause: ankyloglossia, microstomia, and esophageal stricture
Skin: “mitten”, ulceration on hands and fingers, dystrophic
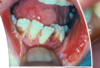
Hereditary epidermolysis bullosa
Primarily a severe and debilitating skin ds in which blisters form at sites of minor trauma and may heal with scarring → nikolsky positive.
NOT an autoimmune ds. Has defective structural proteins.
Orally: Normal diet produces bullae that heals with scarring leading to obliteration of vestibule. Can cause: ankyloglossia, microstomia, and esophageal stricture
Skin: “mitten”, ulceration on hands and fingers, dystrophic

Hereditary epidermolysis bullosa
Primarily a severe and debilitating skin ds in which blisters form at sites of minor trauma and may heal with scarring → nikolsky positive.
NOT an autoimmune ds. Has defective structural proteins.
Orally: Normal diet produces bullae that heals with scarring leading to obliteration of vestibule. Can cause: ankyloglossia, microstomia, and esophageal stricture
Skin: “mitten”, ulceration on hands and fingers, dystrophic
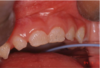
Hereditary epidermolysis bullosa
Primarily a severe and debilitating skin ds in which blisters form at sites of minor trauma and may heal with scarring → nikolsky positive.
NOT an autoimmune ds. Has defective structural proteins.
Orally: Normal diet produces bullae that heals with scarring leading to obliteration of vestibule. Can cause: ankyloglossia, microstomia, and esophageal stricture
Skin: “mitten”, ulceration on hands and fingers, dystrophic
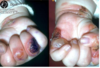
Hereditary epidermolysis bullosa
Primarily a severe and debilitating skin ds in which blisters form at sites of minor trauma and may heal with scarring → nikolsky positive.
NOT an autoimmune ds. Has defective structural proteins.
Orally: Normal diet produces bullae that heals with scarring leading to obliteration of vestibule. Can cause: ankyloglossia, microstomia, and esophageal stricture
Skin: “mitten”, ulceration on hands and fingers, dystrophic

Hereditary epidermolysis bullosa
Primarily a severe and debilitating skin ds in which blisters form at sites of minor trauma and may heal with scarring → nikolsky positive.
NOT an autoimmune ds. Has defective structural proteins.
Orally: Normal diet produces bullae that heals with scarring leading to obliteration of vestibule. Can cause: ankyloglossia, microstomia, and esophageal stricture
Skin: “mitten”, ulceration on hands and fingers, dystrophic

Hereditary epidermolysis bullosa
Primarily a severe and debilitating skin ds in which blisters form at sites of minor trauma and may heal with scarring → nikolsky positive.
NOT an autoimmune ds. Has defective structural proteins.
Orally: Normal diet produces bullae that heals with scarring leading to obliteration of vestibule. Can cause: ankyloglossia, microstomia, and esophageal stricture
Skin: “mitten”, ulceration on hands and fingers, dystrophic

PSORIASIS = A common, chronic, genetically-determined inflammatory and hyperproliferative skin ds
Associated with certain HLA types. Immunoregulatory disorder - T cells trigger inflammation
Defect in control of keratinocyte proliferation- turnover rate 8x normal.
Clinically: well-demarcated, red plaques covered by silvery scales. Auspitz Sign - removal of scale leaves pinpoint bleeding area. Koebner phenomenon - lesions develop following trauma to normal-appearing skin. Nail involvement. Psoriatic arthritis- 15% polyarthritis, TMJ involvement rare

PSORIASIS = A common, chronic, genetically-determined inflammatory and hyperproliferative skin ds
Associated with certain HLA types. Immunoregulatory disorder - T cells trigger inflammation
Defect in control of keratinocyte proliferation- turnover rate 8x normal.
Clinically: well-demarcated, red plaques covered by silvery scales. Auspitz Sign - removal of scale leaves pinpoint bleeding area. Koebner phenomenon - lesions develop following trauma to normal-appearing skin. Nail involvement. Psoriatic arthritis- 15% polyarthritis, TMJ involvement rare
This is a sign of what

PSORIASIS = A common, chronic, genetically-determined inflammatory and hyperproliferative skin ds
Associated with certain HLA types. Immunoregulatory disorder - T cells trigger inflammation
Defect in control of keratinocyte proliferation- turnover rate 8x normal.
Clinically: well-demarcated, red plaques covered by silvery scales. Auspitz Sign - removal of scale leaves pinpoint bleeding area. Koebner phenomenon - lesions develop following trauma to normal-appearing skin. Nail involvement. Psoriatic arthritis- 15% polyarthritis, TMJ involvement rare

PSORIASIS = A common, chronic, genetically-determined inflammatory and hyperproliferative skin ds
Associated with certain HLA types. Immunoregulatory disorder - T cells trigger inflammation
Defect in control of keratinocyte proliferation- turnover rate 8x normal.
Clinically: well-demarcated, red plaques covered by silvery scales. Auspitz Sign - removal of scale leaves pinpoint bleeding area. Koebner phenomenon - lesions develop following trauma to normal-appearing skin. Nail involvement. Psoriatic arthritis- 15% polyarthritis, TMJ involvement rare
sign of what

PSORIASIS = A common, chronic, genetically-determined inflammatory and hyperproliferative skin ds
Associated with certain HLA types. Immunoregulatory disorder - T cells trigger inflammation
Defect in control of keratinocyte proliferation- turnover rate 8x normal.
Clinically: well-demarcated, red plaques covered by silvery scales. Auspitz Sign - removal of scale leaves pinpoint bleeding area. Koebner phenomenon - lesions develop following trauma to normal-appearing skin. Nail involvement. Psoriatic arthritis- 15% polyarthritis, TMJ involvement rare

WHITE SPONGE NEVUS
= hereditary, autosomal dominant mutation of keratin genes that requires NO tx.
Clinically: asymptomatic, bilateral white lesions with a thick, folded, consistency “spongy” appear before puberty
Primarily involves buccal mucosa, but may affect other mucosal surfaces- anogenital, esophageal.
Histopath: perinuclear keratin condensation

WHITE SPONGE NEVUS
= hereditary, autosomal dominant mutation of keratin genes that requires NO tx.
Clinically: asymptomatic, bilateral white lesions with a thick, folded, consistency “spongy” appear before puberty
Primarily involves buccal mucosa, but may affect other mucosal surfaces- anogenital, esophageal.
Histopath: perinuclear keratin condensation

WHITE SPONGE NEVUS
= hereditary, autosomal dominant mutation of keratin genes that requires NO tx.
Clinically: asymptomatic, bilateral white lesions with a thick, folded, consistency “spongy” appear before puberty
Primarily involves buccal mucosa, but may affect other mucosal surfaces- anogenital, esophageal.
Histopath: perinuclear keratin condensation

WHITE SPONGE NEVUS
= hereditary, autosomal dominant mutation of keratin genes that requires NO tx.
Clinically: asymptomatic, bilateral white lesions with a thick, folded, consistency “spongy” appear before puberty
Primarily involves buccal mucosa, but may affect other mucosal surfaces- anogenital, esophageal.
Histopath: perinuclear keratin condensation

WHITE SPONGE NEVUS
= hereditary, autosomal dominant mutation of keratin genes that requires NO tx.
Clinically: asymptomatic, bilateral white lesions with a thick, folded, consistency “spongy” appear before puberty
Primarily involves buccal mucosa, but may affect other mucosal surfaces- anogenital, esophageal.
Histopath: perinuclear keratin condensation

NASOPALATINE DUCT CYSTAka incisive cyst canal
The most common odontogenic cyst of oral cavity
A developmental cyst that arises from epithelial remnants of nasopalatine duct
ONLY place you will EVER see is at the midline of the maxilla between 8 and 9. Can cause roots to resorb. Teeth are vital!!!!!!
Seen in adults 4th to 6th decade.
Symptoms: RL ~0.6cm in the upper limit of normal for the incisive foramen. Swelling of the anterior palate. Drainage and pain, if it is inflamed.

NASOPALATINE DUCT CYSTAka incisive cyst canal
The most common odontogenic cyst of oral cavity
A developmental cyst that arises from epithelial remnants of nasopalatine duct
ONLY place you will EVER see is at the midline of the maxilla between 8 and 9. Can cause roots to resorb. Teeth are vital!!!!!!
Seen in adults 4th to 6th decade.
Symptoms: RL ~0.6cm in the upper limit of normal for the incisive foramen. Swelling of the anterior palate. Drainage and pain, if it is inflamed.

NASOPALATINE DUCT CYSTAka incisive cyst canal
The most common odontogenic cyst of oral cavity
A developmental cyst that arises from epithelial remnants of nasopalatine duct
ONLY place you will EVER see is at the midline of the maxilla between 8 and 9. Can cause roots to resorb. Teeth are vital!!!!!!
Seen in adults 4th to 6th decade.
Symptoms: RL ~0.6cm in the upper limit of normal for the incisive foramen. Swelling of the anterior palate. Drainage and pain, if it is inflamed.
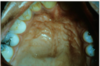
Median palatine cyst
Well-circumscribed palatal lucency
Epithelium entrapped during fusion of palatal shelves
Stratified squamous or pseudostratified columnar
May be difficult to distinguish from nasopalatine duct cyst
On XR nasopalatine is more anterior and median palatine is more post. The location is how you can tell them apart.

Periapical cyst
A inflammatory odontogenic cysts: RL at the apex of a non-vital tooth
Arises from the rests of malassez
If you have multiple periapical cysts, then you would also need multiple non vital teeth
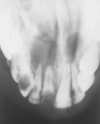
Periapical cyst
A inflammatory odontogenic cysts: RL at the apex of a non-vital tooth
Arises from the rests of malassez
If you have multiple periapical cysts, then you would also need multiple non vital teeth

Buccal bifurcation cyst
An inflammatory odontogenic cyst. Paradental cyst
Buccal bifurcation of vital md molar teeth with cervical enamel projection
Most commonly seen on the md M.
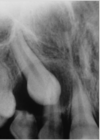
Dentigerous cyst
Most common type of developmental odontogenic cyst but you must have an impacted tooth
Arises from dental follicle - attached to the cervix, enclosing the crown of an unerupted tooth
Enlarged follicular space >4mm
A possibility that a dentigerous cyst can transform into a unicystic ameloblastoma (an odontogenic tumor, XR large pericoronal radiolucencies looks just like a dentigerous cyst)

Dentigerous cyst
Most common type of developmental odontogenic cyst but you must have an impacted tooth
Arises from dental follicle - attached to the cervix, enclosing the crown of an unerupted tooth
Enlarged follicular space >4mm
A possibility that a dentigerous cyst can transform into a unicystic ameloblastoma (an odontogenic tumor, XR large pericoronal radiolucencies looks just like a dentigerous cyst)

Dentigerous cyst
Most common type of developmental odontogenic cyst but you must have an impacted tooth
Arises from dental follicle - attached to the cervix, enclosing the crown of an unerupted tooth
Enlarged follicular space >4mm
A possibility that a dentigerous cyst can transform into a unicystic ameloblastoma (an odontogenic tumor, XR large pericoronal radiolucencies looks just like a dentigerous cyst)

Dentigerous cyst
Most common type of developmental odontogenic cyst but you must have an impacted tooth
Arises from dental follicle - attached to the cervix, enclosing the crown of an unerupted tooth
Enlarged follicular space >4mm
A possibility that a dentigerous cyst can transform into a unicystic ameloblastoma (an odontogenic tumor, XR large pericoronal radiolucencies looks just like a dentigerous cyst)
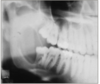
unicystic ameloblastoma
A possibility that a dentigerous cyst can transform into a unicystic ameloblastoma (an odontogenic tumor, XR large pericoronal radiolucencies looks just like a dentigerous cyst)

Eruption cyst
The soft tissue variant of dentigerous cyst. It is associated with the crown of an erupting tooth
Clinically: will have a blue-ish color. Tooth will erupt through it.
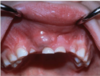
Eruption cyst
The soft tissue variant of dentigerous cyst. It is associated with the crown of an erupting tooth
Clinically: will have a blue-ish color. Tooth will erupt through it.
where is this

Globulomaxillary cyst - A developmental “globulomaxillary cyst” dn exist
Located at the junction of maxilla with premaxilla and between MX LI and C
No developmental fissural cyst in this position. More of a position than a ds.

Globulomaxillary cyst - A developmental “globulomaxillary cyst” dn exist
Located at the junction of maxilla with premaxilla and between MX LI and C
No developmental fissural cyst in this position. More of a position than a ds.

Lateral periodontal cyst
Arises from dental lamina rests (rests of Serres)
VITAL teeth of adult males (3:1)
Md pm area
Mx I-C area

Lateral periodontal cyst
Arises from dental lamina rests (rests of Serres)
VITAL teeth of adult males (3:1)
Md pm area
Mx I-C area
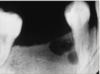
Botryoid odontogenic cyst
Polycystic variant of the lateral periodontal cyst
A developmental odontogenic cyst that presents as a multilocular lucency associated with the vital md PM of adults
Difference between botryoid vs lateral is that botryoid is multicystic and lateral is unicystic.

Gingiva cyst of adult
Soft tissue variant of lateral periodontal cyst
NO XR PRESENTATION
Arises from dental lamina
Vital teeth M 3:1 F
Seen @ md PM and mx I-C area
Clinically sometimes has a blue-ish swelling. Can never be mucocele or a mucoepidermoid carcinoma bc not in salivary gland area, it is in the mucosa

Gingiva cyst of adult
Soft tissue variant of lateral periodontal cyst
NO XR PRESENTATION
Arises from dental lamina
Vital teeth M 3:1 F
Seen @ md PM and mx I-C area
Clinically sometimes has a blue-ish swelling. Can never be mucocele or a mucoepidermoid carcinoma bc not in salivary gland area, it is in the gingival mucosa

Gingiva cyst of adult
Soft tissue variant of lateral periodontal cyst
NO XR PRESENTATION
Arises from dental lamina
Vital teeth M 3:1 F
Seen @ md PM and mx I-C area
Clinically sometimes has a blue-ish swelling. Can never be mucocele or a mucoepidermoid carcinoma bc not in salivary gland area, it is in the mucosa


