Oral Biology Flashcards

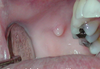
Incisive (nasopalatine) papilla
(Part of Hard Palate)
Incisive (nasopalatine) papilla Bulbous nodule located behind maxillary central incisors formed by dense fibrous tissue, which extends deep from the lamina propria.
Within the fibrous tissue are:
large blood vessel and nerves
ducts formed by columnar or pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium which represent remnants of nasopalatine ducts
small remnants of minor salivary gland tissue
occasionally, there are small rests of cartilage: vestigial extensions of paraseptal cartilage
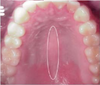
Midline palatal raphe:
Lamina propria extends directly into periosteum: this arrangement is called a mucoperiosteum.
(Part of the hard Palate)

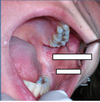
Rugae
Dense fibrous ridges extending laterally from the incisive papilla and the anterior part of the palatal raphe.
(Part of Hard Palate)

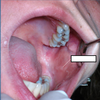
Fovea palatinae
- bilateral pits found on either side of the mid palatal raphe in the posterior hard palatal mucosa
- poorly described in most anatomy texts but they are present in an unknown but significant fraction of the population
- represent blind ended tunnels; minor salivary glands can secrete into this space
(Part of hard palate)

Soft palate
- non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium (superficial layer: called stratum superficiale); occasional taste buds are interposed into epithelium
- lamina propria: fibrous tissue, dermal papilla are not as pronounced
- submucosa: contains minor salivary gland lobules

A: Attached gingiva.
B: Free gingiva or marginal gingiva.
C: Interdental papilla.
D and E: Alveolar mucosa, frenum and muccobuccal fold (Vestibular fornix).
F: Muccogingival junction.
G: Gingival crevice (or sulcus)
H: Free gingival groove.

Hamulus

A: Soft palate
B: Uvula
C: Palatalglossal arch (anterior tonsillar pillar)
D: Palatopharyngeal arch (posterior tonsillar pillar)
E: Palatine tonsil
F: Pharyngeal wall
G: Gingival zone of hard palate
H: Tongue dorsum.

Foliate Papilla

Foliate Papilla
Filiform Papilla

Fungiform Papilla

Circumvallate Papillae
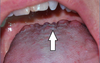
Circumvallate Papillae

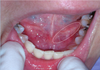
A: Lingual frenum
B: Location of sublingual caruncula
C: Attachment to lingual mandibular mucosa
D: Non-keratinized floor of mouth mucosa