Optical networks Flashcards
WDM
Wavelength division multiplexing
Transmission of multiple lights signals on the same strand of fiber.
DWDM: Dense WDM
- Sophisticated and expensive
CWDM: Coarse WDM
- lower number of wavelenghts → cheaper
Initial application
- Increase transmission capacity o fiber
- Increase utilization
- Point to point configs.
- Trunk bandwidth
Step further
- Wavelength switching
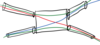
Interim WDM Application
Ring topologies with WDM add/drop multiplexers
Mostly static or semipermanent interconnection configurations.

Ultimate WDM application
Wavelength switched networks
Arbitrary mesh topologies of wdm links and wavelength switches.
Potential to be simple, hence delivering at low cost per switched bit.

Optical core
Deploy physical properties of materials to deflect light from incoming fiber to outgoing fiber
- Tilting mirrors
- micro-electro-mechanical systems
- voltage operated
- Holographic reflecting surfaces
- voltage operated
- Materials change properties with heat, pressure, voltace/current
- Properties:
- potentially inexpensive: material and process
- bit rate and signal independent
- low power consumption
- High production cost
- High attentuation, regeneration is not provided
*
Electrical core
Convert optical signal into an electric one and use circuit interconnection network
- optical-electrical conversion
- receive the bits and switch them
- It loses all the nice properties of an optical core
- bit-rate independnce
- low-power consumption
- low-cost
- Cheper than optical core currently
- Less complex/costly than packet switching
Optical network deployment
Provisioning
- Router (ip/mpls) can request channel to the switch with RSVP
protection
- pre-determined action: non-optimal resource utilization
restoration: dynamically determined action



