Operative delivery and C-sections Flashcards
What is the advantage of instrumental vaginal delivery over caesarean second in the second stage of labour?
helps avoid maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality
What is the operative vaginal delivery rate in the UK?
10-15%
What factors determine whether to use forceps or ventouse?
they are comlementary to each other
operator’s skill and experience, as well as clinical findings
What 2 groups can indications for instrumental delivery be divded into?
- Maternal
- Fetal
What are 4 maternal indications for instrumental delivery?
- Exhaustion
- Prolonged 2nd stage:
- >1h of passive phase and 1h of active pushing in nulliparous women
- >2h of passive phase and 1h of active pushing in primiparous women
- Medical indications for avoiding Valsalva manoevre
- Pushing is not possiblle (paraplegia or tetraplegia)
What is the definition of a prolonged 2nd stage of labor for 1. multiparous women and 2. primiparous women?
- Multi: >1h passive phase and 1h active pushing
- Nulliparous: >2h passive phase and 1h active pushing
What are 3 examples of medical indications for avoiding Valsalva manoevre, indicating instrumental delivery?
- Severe cardiac disease
- Hypertensive crisis
- Uncorrected cerebral vascular malformations
Whata are 2 fetal indications for an instrumental delivery?
- Fetal compromise
- To control after-coming head of breech (forceps)
What are 4 things to discuss with a mother when an instrumental delivery is indicated?
- Why operative delivery indicated
- Instrument chosen
- Likelihood of success
- Alternatives available (emergency CS)
What is needed before carrying out an operative delivery?
consent - verbal or written, by explaining indication
record consent
What are 3 types of complications of forceps delivery?
- Increased maternal trauma (including anal sphincter trauma)
- Rotational forceps may cause spiral tears of vagina
- Fetal injuries rare but may occur
What usually causes fetal injuries to occur with a forceps delivery?
mostly due to incorrect application of the blades
What are 4 examples of types of fetal injuries with forceps?
- Facial nerve palsy
- Skull fractures
- Orbital injury
- Intracranial haemorrhage
What type of complications is delivery with Ventouse associated with?
fetal injuries
What are 4 fetal injuries that can be caused by the use of Ventouse at delivery?
- Scalp lacerations and avulsions (rarely, alopecia in long term)
- Cephalohaematoma
- Retinal haemorrhage
- Rarely - subgaleal haemorrhage and/or intacranial haemorrhage (subgaleal = bleeding in space between skull periosteum and scalp galea aponeurosis)
What is usually meant by the use of sequential instruments for delivery?
usually forceps after a failed ventouse
What is the risk of sequential instrument use at delivery?
increased risk of fetal trauma when attempted with no signficant descent
Why is there an apparently lower CS rate with ventouse deliveries compared with forceps deliveries, but more failed ventouse deliveries?
not uncommon for ventouse to slip when head is at introitus, then delivery is completed by a lift-out forceps
What are 3 examples of types of forceps?
- Low cavity forceps (Wrigley’s)
- Mid-cavity non-rotational forceps (Neville-Barnes’, Haig Ferguson, Simpson’s)
- Mid-cavity rotational forceps (Keilland’s)
What are forceps?
blades that sit around the fetal head and allow traction to be applied along the ‘flexion point’ of the head (3cm in front of the occiput)
What are 2 broad reasons why forceps are used?
- Speed up delivery
- Slow rate of head in breech delivery
What type of forceps are shown in the image?

Low cavity forceps - Wrigley’s

How can low cavity forceps (e.g. Wrigley’s) be described?
short and light
In additional to operative vaginal deliveries, when else are low cavity forceps used?
Caesarean section
Wha type of forceps are shown in the image?

Mid-cavity non-rotational : Simpson’s

What type of forceps are shown in the image?

Mid-cavity rotational: Keillands

When are mid-cavity non-rotational forceps (e.g. Simpson’s, Neville-Barnes, Haig Ferguson) used?
- when sagittal suture is in the direct anteroposterior position (usually direct occipito-anterior DOA)
What can be done so that mid-cavity non-rotational forceps can be used when the sagittal suture is not in direct occipito-anterior position?
malposition (direct occipito-posterior DOP or direct occipito-lateral DOL) can be corrected manually between contractions and blades applies once head in DOA position
What makes mid-cavity rotational forceps (Keilland’s) able to carry out their function?
reduced pelvic curve on the blades allows rotation about the axis of the handle
What is the function of mid-cavity rotational forceps (Keilland’s)?
helps correct asynclitism (oblique malpresentation of fetal head) and malposition
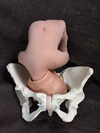
Who can use Keilland’s forceps?
experienced operator only
What is meant by vacuum extraction i.e. ventouse?
works on principle of creating negative pressure to allow scalp tissues to be sucked into the cup. This creates artificial caput called a “chignon”
cup held in place by atmospheric pressure on the cup against the negative pressure created
What is a chignon?
temporary swelling left on infant’s head after ventouse suction cap used to deliver him or her
When should vacuum extraction not be used at delivery?
should not be used to <34 weeks gestation
What are 3 types of ventouse devices?
- Metal cup
- Soft cup
- Kiwi Omni cup
What type of metal cups are available for ventouse?
60, 50 or 40mm stanadard anterior or posterior (for occipito-lateral) or occipito-posterior (OP) positions
How do metal cups work to perform vacuum extraction?
pressure created by a suction pump
What is a risk of using metal cups for ventouse?
excessive traction likely to cause fetal trauma
When is it easiest to apply a soft ventouse cup?
OA positions
How do soft ventouse cups work?
mould around fetal head covering a greater surface area
What is an advantage of soft cups for vacuum extraction?
causes fewer scalp abrasions
How do Kiwi Omni cups work for vacuum extraction?
single use cups, pressure created with hand pump (quick in an emergency)
What is an advantage of Kiwi Omni Cups for extraction delivery?
allows application to flexion point in OL and OP position
What are 5 differences in outcomes between ventouse and forceps?
- Ventouse more likely to fail
- Ventouse more likely to cause fetal trauma
- cephalohaemtoma, retinal haemorrhage
- Ventouse more likely to be associated with
- Forceps are mor elikely to cause significant maternal genital tract trauma
- Slightly less CS delivery with ventouse delivery
What are 2 types of fetal trauma more likely to be caused by ventouse than forceps?
- Cephalohaematoma
- Retinal haemorrhage
What are 2 types of outcome that have no difference with forceps vs ventouse delivery?
- No difference in 5 min apgar scores
- No difference in need for neonatal phototherapy
What is the bottom line statement about ventouse vs forceps in terms of safety?
ventouse appears safer for mother but forceps may be safer for baby
What is the way of remembering the criteria to satisfy before attempting an operative vaginal delivery?
FORCEPS
What do the letters of FORCEPS stand for when remembering the criteria to satisfy for operative vaginal delivery?
- F: fully dilated cervix
- O: obstruction should be excluded (head 1/5 palpable abdominally)
- R: ruptured membranes
- Consent, catheterise bladder (in and out technique, indwelling catheters must be removed), check instrument prior to application
- E: explain procedure to patient, epidural (or pudendal) analgesia, examine genital tract to exclude genital tract trauma
- P: presentation, position of head. power - are contractions effective? Placement of forceps bladers/ventouse cap - correct? no maternal tissues should be caght
- S: station of presenting part (not above ischial spines), senior help called if needed
What is a trial of operative vaginal delivery?
when it’s not possible to determine with sufficient confidence that an instrumental delivery will be successful, so should take place in theatre where it is possible to move to an immediate C-section, as delay in CS may compromise fetal wellbeing
What form should be used before performing a trial of instrumental vaginal delivery?
‘trial of instrumental vaginal delivery ± emergency CS’ - woman should be fully informed of likely success and sign form
If trial of instrumental vaginal delivery is abandoned and CS needed, what may need to be done during the CS to assist?
assistance may be required to push the head up from the vagina during CS as it may be impacted in the pelvis
What are 2 situations when you should abandon instrumental vaginal delivery and deliver by emergency Caesarean?
- If no evidence of progressive descent with each pull (care must be taken with the ventouse to not interpret increasing caput as descent of the head)
- Where delivery not imminent following 3 pulls of a correctly applied instrument by an experienced operator
What are 4 risk factors for failed operative vaginal delivery?
- BMI >30
- Estimated fetal weight (EFW) >4000g or clinically big baby
- OP position
- Mid-cavity delivery or if head is >1/5 palpable abdominally
What proportion of women delivering vaginally int he UK will sustain a degree of perineal trauma?
more than 85%
What is episiotomy?
surgical incision to enlarge the vaginal introitus
Who makes the decision to perform an episiotomy at birth?
birth attendant
What does the evidence suggest is the best approach to use of episiotomies with deliveries generally?
restricted use is best approach
What are 8 situations when episiotomy should be considered?
- Breech
- Shoulder dystocia
- Forceps
- Ventouse
- Female genital mutilation
- Poorly healed 3rd or 4th degree tears
- When there is fetal distress
- If there is an indication that there may be extensive perineal trauma e.g. multiple vaginal/perineal tears or perineal button-holing
What are 2 types of episiotomy?
- Mediolateral episiotomy
- Midline episiotomy

What is a mediolateral episiotomy?
extends from the fourchette laterally (thus reducing the risk of anal sphincter injury)
What is a midline episiotomy?
extends from the fourchette towards the anus (common in USA but not recommended in UK)
How is an episiotomy performed?
- if woman does not have working regional block (epidural) then perineum should be infiltrated with lidocaine (lignocaine)
- two fingers placed between baby’s head and perineum (to protect baby)
- sharp scissors make single cut in perineum 3-4cm long - ideally at height of contraction when perineum at thinnest
What timings must be considered when performing episiotomy?
- anaesthetise perineum early to provide sufficient time for effect
- episiotomy will cause bleeding so must not be done too early and should be repaired as soon as possible
What should you always check for after performing an episiotomy?
any extension or other tears, including PR examination to ensure no trauma to anal sphincter
What are 7 complications of perineal trauma (including episiotomy)?
- Bleeding
- Haematoma
- Pain
- Infection
- Scarring, with potential disruption to the anatomy
- Dyspareunia
- Very rarely, fistula formation
How should you approach episiotomy if a woman has undergone female genital mutilation?
should be seen antenatally and de-infibulation discussed
however if they present in labour, episiotomy should be anterior and upwards
What is the classification of perineal tears?
- First degree: injury to skin only
- 2nd degree: injury to perineum involving perineal muscles (including episiotomy)
- 3rd degree: injury to perineum involving anal sphincter complex
- 3a: <50% external anal sphincter (EAS) thickness torn
- 3b: >50% of EAS thickness torn
- 3c: internal anal sphincter (IAS) torn
- 4th degree: injury to perineum involving anal sphincter complex (EAS and IAS) and anal/rectal epithelium
When repairing perineal tears, what assessment must be performed before starting?
PR - to ensure no trauma to anal sphincter complex
When should you aim to perform a perineal repair?
suture as soon as possile to reduce bleeding and infection risk
Who should perform basic perineal tear repair?
should be someone with adequate training for type of tear; difficult trauma should be repaired in theatre under regional or genearl anaesthesia by an experienced operator
What position should the woman be in when a perineal tear repair is performed?
lithotomy position; should be good light source and adequate analgesia
What type of suture material should be used for perineal tears and why?
rapid-absorption polyglactin suture material
is associated with significant reduction in pain
What determines where to begin perineal tear repair with sutures?
apex of cut should be identified and suturing started frmo just above this point
What type of suturing technique is used to repair a perineal tear and why?
- loose, continuous non-locking suturing technique to appose each layer; associated with less short-term pain than traditional interupted method
- subcuticular suture for perineal skin - associated with less pain
What examination should be performed after repairing a perineal tear and why?
rectal examination - ensures no suture has accidentially passed into rectum or anal canal
What should be done after perineal tear repair and rectal examination have been performed?
needle and swabs must be counted - lost swabs are recurring cause of litigation in obstetrics
What are 10 factors associated with increased risk of anal sphincter trauma?
- Forceps delivery
- Nulliparity
- Shoulder dystocia
- 2nd stage >1h
- Persistent OP position
- Midline episiotomy
- Birth weight >4kg
- Epidural anaesthesia
- Induction of labour
What type of suturing and what material is used for 3rd and 4th degree perineal tears?
- end to end or overlapping for the EAS
- using either polydioxanone suture (PDS) or vicryl suture material
- IAS should be repaired with vicryl using interrupted sutures
What 3 types of treatment must women receiving following management of 3rd and 4th degree perineal tears receive?
- broad-spectrum antibiotics
- stool softeners
- physiotherapy
When must women who have had a repair of 3rd or 4th degree perineal tears be reviewed?
6 weeks later by obstetrician or gynaecologist
What lasting issues may women who have had a repair of a third or fourth degree perineal tear experience and when should intervention be considered?
- incontinence of flatus, faeces and fluid
- if experiencing symptoms at 6 weeks should be referred to specialist gynaecologist or colorectal surgeon for investigation with endoanal ultrasonography
What is the overall prognosis for women following a 3rd or 4th degree perineal tear repair?
60-80% will have a good result and be asymptomatic at 12 months (despite risks of incontinence)
What should women be advised about following a repair of a 3rd or 4th degree tear for subsequent deliveries?
the result may not be so good from a 2nd repair; if symptomatic they should be given the option of delivery by CS
What is a Caesarean section?
delivery of the fetus through a direct incision in the abdominal wall and the uterus
What is the rate of Caesarean sections for nulliparous women in the UK vs multiparous women who have not previous had a CS, vs women who have had at least 1 previous CS?
24% vs <5% vs 67%
What are 5 risks of Caesarean section that are increased compared with a vaginal delivery?
- Abdominal pain
- Venous thromboembolism
- Bladder or ureteric injury
- Hysterectomy
- Very rarely maternal death
What are 3 risks that are lowered with Caesarean section vs vaginal delivery?
- Perineal pain
- Urinary incontinence
- Uterovaginal prolapse
What are 8 interventions to decrease the morbidity from CS?
- Preoperative haemoglobin check and correction of anaemia
- Intraoperative prophylactic antibiotics given just before skin incision
- Risk assessment and appropriate thrombo-prophylaxis (graduated stockings, hydration, early mobiilisation, low molecular weight heparin)
- In-dwelling bladder catheterisation during the procedure
- Antacid and H2 receptor analogues before surgery
- Antiemetics as appropriate
- Regional rather than general anaesthesia
- Risk of hypotension reduced with IV ephedrine or phenylephrine infsuion, volume preloading with crystalloid or colloid, lateral tilt of 15o
What are 3 ways to reduce the risk of hypotension from Caesarean section?
- Intravenous ephedrine or phenylephrine infusion
- Volume preloading with crystalloid or colloid
- Lateral tilt of 15o
What should be done if general anaesthesia is performed for emergency CS?
Should include preoxygenation and rapid sequence induction to reduce the risk of aspiration
What is VBAC?
Vaginal birth after Caesarean section
What is the risk of vaginal birth after CS?
Uterine rupture - rare but increased risk
50/ 10 000 with VBAC and spontaneous onset of labour, 1/ 10 000 with repeat CS
What is recommended during labour for vaginal delivery after previous C-section and why?
- EFM (electronic fetal monitoring) during labour as fetal heart rate changes may be the earliest signs of scar rupture
- Women should deliver in unit where there’s immediate access to CS and on-site blood transfusion
What are 2 things that increase the risk of uterine rupture with vaginal delivery after C-section?
- Oxytocin infusion
- Prostaglandins
What increases the likelihood of a woman giving birth vaginally after previous C-section?
if she has also had a previous vaginal birth
What are the 4 main indications for Caesarean section?
- Repeat CS
- Fetal compromise
- Failure to progress in labour
- Breech presentation
What proportion of C-section is accounted for by maternal request and is this an indication for CS?
7%; on its own, not indication for CS
What are the 4 different types of Caesarean section?
- Category 1: Immediate, ‘crash CS’
- Category 2: Urgent
- Category 3: Scheduled
- Category 4: Elective
When is a category 1 C-section indicated and what are 5 exampes of this?
- Immediate threat to life of woman or fetus
- Placental abruption with abnormal FHR or uterine irritability
- Cord prolapse
- Scar rupture
- Prolonged bradycardia
- Scalp pH <7.20
What is the accepted standard for timing of category 1 C-section?
should be within 30 minutes
What is the indication for category 2 C-section?
maternal or fetal compromise which is not immediately life-threatening; failure to progress with pathological CTG
When is a category 3 C-section indicated and what are 3 examples of this?
- No maternal or fetal compromise but needs early delivery
- Severe pre-eclampsia
- IUGR with poor fetal function tests
- Failed induction of labour
When is a category 4 C-section indication and what are 6 examples of indications?
- Delivery timed to suit woman and staff
- Term singleton breech (if ECV is contraindicated or has failed)
- Twin pregnancy with non-cephalic first twin
- Maternal HIV
- Primary genital herpes in third trimester
- Placenta praevia
- Previous hysterotomy or classical CS
At what point is elective Caesarean section usually carried out and why?
After 39 weeks, as risk of respiratory morbidity (transient tachypnoea of newborn) is increased at lower gestational ages
What are the 2 key types of Caesarean section?
- Lower uterine segment incision
- Classical CS
What are the 2 main types of skin incision which can be used for lower uterine segment incision for Caesarean section?
- Pfannenstiel incision: straight horizontal incision 2cm above symphysis pubis
- Joel-Cohen incision: straight horizontal incision but 3cm below level of anterior superior iliac spines (ASIS) - higher
What is a benefit of the Pfannenstiel incision for a lower uterine segment incision?
superior cosmetic result
What is a benefit of the Joel-Cohen incision for a lower uterine segment incision?
Allows quicker entry to the abdomen
In what proportion of C-sections is the lower segment incision used?
>90%
What are 3 reasons why a lower uterine segment incision is used for C-setions in the vast majority of cases?
- Reduced adhesion formation
- Decreased blood loss
- Lower incidence of scar dehiscence in subsequent pregnancies
What is a risk of lower uterine segment incisions for C-sections and when does this occur?
- low transverse incision carries risk of lateral extension into uterine vessels and haemorrhage
- if lower segment is poorly developed
What is done following delivery of the baby with a lower segment incision C-section?
lower uterine segment is closed in one or two layers; double layer closure usually practised by research comparing single with double has no long term results to compare scar integrity, but short-term morbidity showed no difference
What is a classical Caesarean section?
vertical incision into upper uterine segment
Despite being rarely performed, what are 8 indications for classical Caesarean section?
- Structural abnormality of the uterus
- Difficult access to the loewr uterine segment due to fibroids or severe adhesions over the lower segment
- Postmortem CS delivery (if fetus is viable)
- Anterior placenta praevia with abnormally vascular lower uterine segment
- Contraction ring
- Very preterm fetus (especially breech presentation) where lower segment is poorly formed
- Elective Caesarean hysterectomy
- Transverse lie of fetus with ruptured membranes
What are 2 advantages of a classical Caesarean section?
- Allos rapid delivery
- Lower risk of bladder injury
What are 4 disadvantages of classical C-section?
- Closure more complicated and time-consuming than lower uterine segment incision
- Higher incidence of infection
- Higher incidence of adhesion formation
- Greater risk of uterine rupture in subsequent pregnancies, greater risk of fetus being expelled into peritoneal cavity - therefore absolute contraindication to trial of vaginal delivery (VBAC)
What is an absolute contraindication to vaginal birth after C-section (VBAC)?
previous classical incision for C-section
What type of C-section is most associated with major complications?
emergency C-sections (cat 1), and most frequently with analgesia
What are 7 intra-operative complciations of C-sections?
- Uterine or uterocervical lacterations
- Blood loss
- Bladder laceration
- Blood transfusion
- Hysterectomy
- Bowel lacterations
- Ureteral injury
What are 4 risk factors predisposing to uterocervical lacterations in C-sections?
- Low station of the presenting part and full dilatation
- Birth weight >4000g
- Increased maternal age
- Category 1 CS
What are 3 risk factors predisposing to intraoperative haemorrhage during C-section?
- Placenta praevia or abruption
- Extremes of fetal birth weight
- BMI >25
What are 5 postoperative complications of C-sections?
- Endometritis
- Wound infections
- Pulmonary atelectasis
- Venous thromboembolism
- Urinary tract infections
What are 7 risk factors associated with infection from a C-section?
- Preoperative remote infection
- Chorioamnionitis
- Matrnal severe systemic disease
- Pre-eclampsia
- High BMI
- Nulliparity
- Greater surgical blood loss
What are 4 risks in subsequent pregnancies following C-section?
- Uterine rupture
- Placenta praevia
- Placenta accreta
- Antepartum stillbirth: risk doubles with a previous CS
What are 5 things that women undergoing multiple C-sections (3 or more) are at increased risk of?
- Excessive blood loss
- Difficult delivery of the neonate
- Dense adhesions
- Risk of any major complication higher
- Complications are increased with increased number of CS


