Oesophagus Flashcards
What are the normal oesophageal contour deformities?
- Cricopharyngeus
- postcricoid impressions- mucosal fold over vein
- Aortic impression
- Left mainstem bronchus-LMB
- Left atrium-LA
- Diaphragm
- Peristaltic waves
- Mucosa
- Thin transient transverse fold- feline oesophagus
- Thick fold in chronic reflux disease
- Tiny nodules in elderly: glycogenic acanthosis.
What is a feline oesophagus?
AKA oesophageal shiver- ie the transient transverse bands seen in the lower (distal 2/3) oesophagus on a double contrast barium swallow after swallowing, its asso w active gastro-oesophageal reflux. It results in shortening of the oesophagus and ‘bunching up’ of the overlying mucosa.

List the different types of ring in the GOJ:
- A ring-(Above; wolf ring) indentation at the upper boundary of the phrenic ampulla.
- B ring-(Below) indentation at the lower boundary of the phrenic ampulla- not seen unless there is hiatus hernia.
- Z line- (Zigzag line) squamocolumnar mucosal jnctn bwn oesophagus and stomach- not visible Rx.
- C ring - Diaphragmatic impression
What types of rings are present?

A and B ring
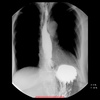
Schatzki rings-symptomatically narrow oesophageal B-ring.
10% population with 30% being symptomatic
What is Schatzki ring associate with?
More than half of patients will have an associated oesophageal condition such as:
- hiatus hernia
- reflux oesophagitis
- oesophageal web
- oesophageal diverticulum
The oesophagus lacks a serosa. Upper 1/3 has…………muscle and lower 2/3 have ……..
The oesophagus lacks a serosa. Upper 1/3 has..striated …muscle and lower 2/3 have …smooth muscle…..
What is the difference bwn web and a ring?
A ring is symmetrical whereas a web is asymmetrical.
What are the asso of web/rings?
- Fe def anaemia- cervical web: Plummer vinson syndrome
- hypopharyngeal ca
What are the two types of hiatus hernia?
- sliding hernia- most common 95%-
- reflux
- mixed when hernia and oesophagus are not in straight axis
- paraoesophageal hernia- 5%
- GOJ is at normal position
- Reflux not necessarily associated
- non reducible
- prone to mechanical complications-surgery
What are the imaging features of sliding hiatus hernia?
- gastric folds above diaphragms
- concentricindentation-B line above diaph
- Schatzki’s ring above diaph
What is a lateral pharyngeal pouch?
lateral outpouchings through weakness in thyrohyoid membrane
Large in glass blower and wind instrument player.

What are the complications of the zenker’s diverticulum?
- Aspiration.
- ulceration
- Carcinoma
Where would you see a Zenker’s diverticulum?
in the midline of the posterior wall of the hypopharynx** at anatomic weakpoint known as **Killian’s dehiscence

What is a Killian-Jamieson diverticulum ?
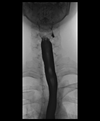
located just below the cricopharyngeal muscle, anteriorly and laterally, as a left sided or less commonly bilateral out pouchings from the cervical oesophagus.
-Off midline in Cervical oesophaus
- smaller than Zenker’s diverticulum (usually < 1.5 cm),
- rarely symptomatic.
What does this picture show?

Epiphrenic diverticula:
These are pulsion diverticula of the distal oesophagus arising just above the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), more frequently on the right posterolateral wall.
What does this picture show?

outpouching of mid oesophagus due to adjacent inflammatory process-eg TB
Calcified mediastinal lymphnode.
What does this picture show?

Pseudodiverticulosis:
- numerous, tiny (1-4 mm), flask-shaped outpouchings
- may be diffusely distributed or clustered.
- clustering may occur next to peptic strictures
- viewed in profile, often appear “floating” next to the oesophageal wall, as the channel to the lumen is imperceptible
- viewed en face, may look like ulcers
What are the 3 underlying diseases for pseudodiv?
- candidiasis
- Diabetes
- Alcoholism
What are the asso findings with pseudodiv?
- oesophageal stricture
- oesophagitis
Flask shaped
What are the different types of oesophagitis?
- Infectious:
- Herpes/Candidiasis/CMV
- Chemical
- Reflux oesophagitis
- Corrosive
- Iatrogenic
- Radiotherapy/ NGT/ Drugs:
- Tetracycline/ NSAID/ K/Fe
- Radiotherapy/ NGT/ Drugs:
- Other
- HIV/Scleroderma/Crohn’s disease
- Dermatological manifestation:
- Pemphigoid/ dermatomyositisbullosa
What are the imaging features of infectious oesophagitis- Herpes simplex?
- Small ulcers, <5 mm
- Normal mucosa between ulcers
- More diffuse than reflux ulcers

What are the imaging features of infectious oesophagitis- Candidiasis?
- Plaquelike, reticular
- Shaggy margins
- Often involve entire esophagus
What are the imaging features of infectious oesophagitis- CMV and HIV?
- Typically elliptical large ulcers but may be tiny ulcers such as herpes
- Aetiologic distinction between CMV and HIV ulcers is important because therapies are different.
- Behçet disease may have a similar appearance.







