Oesophageal varices Flashcards
Describe gastro-oesophageal varices?
- Submucosal venous dilatation
- Secondary to elevated portal pressures
- Suspect if alcohol history
What are the different categories of portal hypertension?
- Pre-hepatic
- Intra-hepatic
- Post-hepatic
Pre-hepatic causes of portal hypertension?
Thrombosis (portal or splenic vein)
Intra-hepatic causes of portal hypertension?
- Cirrhosis
- Schistosomiasis
- Myeloproliferative diseases
Post-hepatic causes of portal hypertension?
- Budd-chiari syndrome
- Right heart failure
- Constrictive pericarditis
Risk factors for variceal bleeds?
- Raised portal pressure
- Variceal size
- Advanced liver disease
Describe the immediate management of GO varices?
- Endoscopic banding (oesophageal)
- Scleropathy (gastric)
Prophylaxis of GO varices?
- Beta-blocker (propanolol)
- Repeat endoscopic banding
- Resistant varices: TIPS
- Transjugular intrahepatic porto-systemic shunt
Draw the full treatment pathway for variceal bleeding
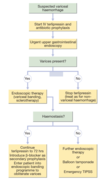
Describe the special management of patients with cirrhosis and upper GI bleeding?
- Should be given prophylactic broad spectrum antibiotics
- eg IV Cephalosporin
Describe the use of Terlipressin in variceal bleeding?
- Synethtic vasopressin analogue
- Aims to reduce portal venous pressure
- Reduces portal blood flow and hepatic resistance
- (Octreotide can be used as an alternative if Terlipressin unavailable)
Describe variceal ligation (banding)?
- Ligation involes varices being suck into cap on endoscope, allowing them to be occluded with a tight rubber band
- Repeated every 2 weeks until all varices are obliterated
- Prophylactic PPIs to reduce risk of bleeding banding-induced ulceration
Describe the use of variceal scleropathy?
- Gastric fundal varices
- Thrombin/cryoacrylate injected directly into varix to induce thrombus
- Cryoacrylate can cause glue embolism to the lungs
Describe the use of balloon tamponade?
- Employs a Sengstaken-blakemore tube
- Two balloons attached which compress lower oesophagus and the fundus .
- Endotracheal intubation prior to tube insertion reduces risk of pulmonary aspiration

Describe TIPSS?
- Stent placed between the portal vein and heptatic vein in the liver to provide a portosystemic shunt
- Reduces portal pressure
- Radiological pressure, entry through the internal jugular vein
- Hepatic encephalopthy may occur following TIPSS
- Treatment by reduced shunt diameter



