Notes Flashcards
(19 cards)
Difference between routing protocol and routed protocol
ROUTING protocols are used to find all networks in internetwork so that all routers have the same routing table. Also determines the best path a packet should take.
RIP, RIPv2, EIGRP, and OSPF are examples ROUTED protocols are used to send packets. They are assigned to and interface and determine method of packet delivery. Examples are IP and IPv6
What does the term routing mean?
It means sending a packet from one device and sending it through the network to a device on another network.
Minimum factors a router must know to be able to effectively route packages
-Destination address -Neighbor routers from which it can learn about emote networks -Possible routes to all networks -Best route to each network -How to maintain and verify routing info
What is static routing method?
Requires someone to hand-type all network locations into routing table.
What is dynamic routing method?
A protocol on one router communicates with the same protocol on another router. This way they can automatically update each other on any changes in the network and place into the routing table.
What command is used to show routing table of router?
show ip route
What are the three different packet-forwarding techniques? Explain difference.
-Process switching: Involves looking up every destination in the routing table and finding the exit interface for every packet. It is very complex for today’s world. It was used when routers began back in the day. -Fast switching: uses a cache to store the most recently used destinations so that lookups are not required for every packet -Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF): The default packet-forwarding method used on all the latest Cisco routers. It makes many different cache tables to help improve performance and is change triggered, not packet triggered. So when the network topology changes, the cache changes along with it.
What must happen in relation to source port numbers when multiple hosts are communicating to the server using HTTP?
They must all use different source port numbers.
Host 4 has received an ARP reply. Host 4 will now build a packet, then place this packet in the frame. What information will be placed in the header of the packet that leaves Host 4 if Host 4 is going to communicate to the Sales server?

Since it’s packets, not frams, the source address will be the IP address of Host 4 and the destination address will be the IP address of the Sales server.
The Lab_A router has received the packet and will send it out Fa0/0 onto the LAN toward the server. What will the frame have in the header as the source and destination addresses?

The source MAC address will be the Lab_A router’s Fa0/0 interdace, and the destination MAC address will be the Sales server’s MAC address because all MAC addresses must be local on the LAN
Host 4 is displaying two web documents from the Sales server in two browser windows at the same time. How did the data find its way to the correct browser windows?
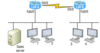
TCP port numbers are used to direct the data to the correct application window
What if Host 4 needs to communicate with Host 1—not the server, but with Host 1. Which OSI layer 3 source address will be found in the packet header when it reaches Host 1?

At layer 3, the source IP address will be Host 4 and the destination address in packet will be the IP address of Host 1.
What would be the layer 2 destination address leaving Host 4? What will be the source MAC address when the frame is received at the Sales server?
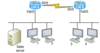
The layer 2 destination address leaving Host 4 is the MAC address of the Fa0/0 interface on the Lab_B router and that the source layer 2 address that the Sales server will receive is the Fa0/0 interface of the Lab_A router
What is a good idea to configure on every router?
Configure the hostnames on each router: hostname [name]
Set interface description, banner, and router passwords for your router:
description [description of interface]
[ip address and mask]
What is the ‘logging sync’ command?
Stops console messages from writing over what you are typing in
What are the PROS of static routing?
- No overhead on router CPU, so probably can use chaeper router
- No bandwidth usage between routers, save money on WAN links and minimize overhewad on router since no routing protocol is used
- Adds security since administators chooses routing acces to certain networks only
What are the CONS of static routing?
- Administrator must have vault-tight knowledge of internetwork and how each router is connected
- If you add a network to internetwork, you have to add a route to it on all routers by hand
- Not feasible to use in most large networks
What is RIP?
Routing Information Protocol
A routing protocol. RIP sends the complete routing table out of all active interfaces every 30 seconds. It relies on hop count to determine the best way to a remote network, but it has a maximum allowable hop count by 15 by default
Difference between RIP v1 and v2
Version 1 was broadcast. Version 2 is multicast. Goes from classful to classless.


