Notes Flashcards
(22 cards)
Program to an interface, not an implementation
Example: imagine an absract class Animal, with two concrete implementations, Dog and Cat. Programming to an implementation would be: Dog d = new Dog(); d.bark(); But programming to an interface/supertype would be Animal animal = new Dog(); animal.makeSound();
Favor composition over inheritance
Is the principle that classes should achieve polymorphic behavior and code reuse by composition (containing other classes that implement the desired functionality), instead of through inheritance (being a subclass). An implementation of composition over inheritance typically begins with the creation of various interfaces representing the behaviors that the system must exhibit. Classes implementing the identified interfaces are built and added to business-domain classes as needed. Thus, system behaviors are realized without inheritance.
Polymorphism
polymorphism refers to a programming language’s ability to process objects differently depending on their data type or class. More specifically, it is the ability to redefine methods for derived classes. For example, given a base class shape, polymorphism enables the programmer to define different area methods for any number of derived classes, such as circles, rectangles and triangles. No matter what shape an object is, applying the area method to it will return the correct results. Polymorphism is considered to be a requirement of any true object-oriented programming language (OOPL).
is-a vs has-a
There are two ways we can do code reuse either by implementation of inheritance (IS-A relationship), or object composition (HAS-A relationship).
What is Composition?
Composition(HAS-A) simply mean use of instance variables that are references to other objects.
What is the strategy pattern?
It enables an algorithm’s behavior to be selected at runtime. The strategy pattern - defines a family of algorithms, - encapsulates each algorithm, and - makes the algorithms interchangeable within that family using composition.
What is the observer pattern?
Defines a one-to-many dependency between objects so that when one object changes state, all of its dependents are notified and updated automatically.
What is the power of loose coupling?
When two objects are loosely coupled, they can interact, but have very little knowledge of each other.
Describe the design principle: Classes should be open for extension, but closed for modification
Our goal is to allow classes to be easily extended to incorporate new behavior without modifying existing code. Example: Area calculator. Could create rectangle class with area method and in the parent area calculator make all the types rectangle.area. OR make shape interface that has area method and make rectangle derive from shape. That way area calculator will iterate over list of shapes and call area. No need to change area calculator and if needed to add shape, just derive from that interface.
Describe the Decorator Pattern
Attaches additional responsibilities to an object dynamically. Decorators provide a flexible alternative to subclassing for extending functionality. Decorators have the same supertypes as the objects they decorate. Each decorator HAS-A component, which means the decorator has an instance variable that holds a reference to a component.

Why use the factory pattern?
When you have code that makes use of lots of concrete classes, you’re looking for trouble. That code may have to be changed as new concrete classes are added. So, in other words, your code will not be “closed for modification”. To extend it with new concrete types, you’ll have to reopen it.
What is the diagram of a factory pattern?
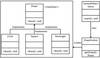
Describe the Dependency Inversion Principle.
Depend upon abstractions. Do not depend upon concrete classes. Reduces depdnecies to concrete classes in our code.
What are a few guidlines to follow the DPI
- No variable should hold a reference to a concrete class. Use a factory to get around that.
- No class should derive from a concrete class. Derive from an abstraction, like an interface or an abstract class.
- No method should override an implemented method of any of its base classes. Methods implemented in a base class are meant to be shared by all your subclasses.
- These are impossible to all follow but good to keep in mind.
Describe the Singleton Pattern
It ensures a class has only one instance, and provides a global point of access to it.
- The getInstance() method is static
- The uniqueInstance class variable would hold our one and only instance of Singleton.
Describe the Command Pattern
is a behavioral design pattern in which an object is used to encapsulate all information needed to perform an action or trigger an event at a later time. This information includes the method name, the object that owns the method and values for the method parameters.
Four terms always associated with the command pattern are command, receiver, invoker and client. A command object knows about receiver and invokes a method of the receiver. Values for parameters of the receiver method are stored in the command. The receiver then does the work. An invoker object knows how to execute a command, and optionally does bookkeeping about the command execution. The invoker does not know anything about a concrete command, it knows only about command interface. Both an invoker object and several command objects are held by a client object. The client decides which commands to execute at which points. To execute a command, it passes the command object to the invoker object.
What is the Adapter pattern?
A pattern that allows the interface of an existing class to be used from another interface. It is often used to make existing classes work with others without modifying their source code.

What’s the process of how the client uses the Adapter?
- The client makes a request to the adapter fby calling a method onit using the target interface.
- The dapter translates the request into one or more class on teh adaptee using the adaptee interface.
- The client receives the results of the call and never knows there is an adapter doing the translation.
Describe the Facade Pattern.
It provides a unified interface to a set of interfaces in a subsystem. Hides all the complexity of one or more classes behind a clean, well-lit facade. They don’t encapsulate the subsystem classes; they merely provide a simplified interface to their functionality. It decouples a client from a subsystem of components.
Describe the MVC Compound Pattern with design patterns.
The model uses Observer to keep the views and controllers updated on the latest state changes. The view and the controller, on the other hand, implement the Strategy Pattern. The controller is the behavior of the view, and it can be easily exchanged with another controller if you want different behavior.
What is the Template Method Pattern?
Defines the skeleton of an algorithm in a method, deferring some steps to subclasses. It lets subclasses redefine certain steps of an algorithm without changin the algorithm’s structure.

What is the State Pattern?
Allows an object to alter its behavior when its internal state changes. The object will appear to change its class. Because the pattern encapsulates state into separate classes and delgates to the object represengint the current sttae, we know that behavior changes along with the internal state.



