Normal RAD EXAM 2 Flashcards
(209 cards)
Name the line of mensuration and give the maximum measurements for the child and the adult:

Atlantodental Interspace Child: 3mm Adult: 5mm
Name the line of mensuration and explain what a normal finding:

George’s Line Normal: Smooth vertical alignment of each posterior body corner
Name the line of mensuration and explain what a normal finding:

Posterior Cervical Line Normal: When each spinolaminar junction point is joined, a smooth arc-like curve results. At the C2 level, the spinolaminar junction line in children should not be > 2 mm anterior to this line
Name the line of mensuration: Canal stenosis may be present when the measurement is less than _______

Sagittal dimension of the cervical spinal canal Stenosis: <12mm
Name the line of mensuration and explain what a normal finding:
Atlantoaxial alignment Normal: The lateral margins of the atlas lateral masses are compared to the opposing lateral corner of the axis articular surface should be in vertical alignment.
Name the line of mensuration and explain what a normal finding:

Cervical gravity line Normal: A vertical line is drawn through the apex of the odontoid process should pass through the C7 body
Name the line of mensuration and list the minimum and maximum degrees for the angle:
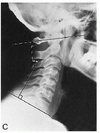
Cervical lordosis i.e. Angle of the cervical curve Minimum: 35deg Maximum: 45deg
Name the line of mensuration and explain what a normal finding:

Stress lines of the cervical spine Normal Flexion: These lines normally should intersect at the level of the C5-C6 disc or facet joints Normal Extension: These lines normally should intersect at the level of the C4-C5 disc or facet joints
Name the line of mensuration and list the normal values for the neutral position:

Prevertebral soft tissues C-1: 10mm C-2: 5mm C-3: 7mm C-4: 7mm C-5: 20mm C-6: 20mm C-7: 20mm
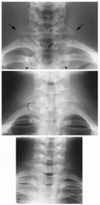
Name the view and identify the numbered structures 1-6:

A-P Lower Cervical 1. C7 spinous process 2. C7 lamina 3. C7 pedicle 4. C7 transverse process 5. C6 articular pillar 6. C5-C6 von Luschka joint
Name the view and identify the numbered structures 7-12:

A-P Lower Cervical 7. T1 spinous process 8. T1 lamina 9. T1 pedicle 10. T1 transverse process 11. 1st costotransverse joint 12. 1st rib
Name the view and identify the numbered structures 13-19:

A-P Lower Cervical 13. 2nd costotransverse joint 14. Medial clavicle 15. Trachea 16. Mastoid process 17. Angle of mandible 18. C5 intervertebral foramen 19. Lung apex
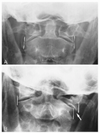
Name the view and identify the numbered structures 1-5:

A-P Open Mouth 1. Atlas lateral mass 2. Atlas anterior arch 3. Atlas posterior arch 4. Atlas transverse foramen 5. Atlas transverse process
Name the view and identify the numbered structures 1-7:

Cervical Oblique 1. C6 vertebral body 2. C5 transverse process 3. C6 pedicle 4. C5 lamina 5. C6 articular pillar 6. C6 spinous process 7. C6-C7 intervertebral foramen
Name the view and identify the numbered structures 11-16:

(C) A-P Open Mouth 11. Axis spinous process 12. Axis transverse foramen 13. Axis transverse process 14. Mandible 15. Tongue 16. Styloid process
Name the view and identify the numbered structures 6-10:

A-P Open Mouth 6. Atlanto-occipital joint 7. Mastoid process 8. Odontoid process 9. Axis pedicle 10. Axis lamina
Name the view and identify the numbered structures 8-14:

Cervical Oblique 8. C5-C6 von Luschka joint 9. C4 pedicle 10. C3 pedicle 11. C6 transverse process 12. First rib 13. Trachea 14. Mandible
Name this cervical view?

Right Anterior Cervical Oblique (RACO)
Name this cervical view?

Left Anterior Cervical Oblique (LAO)
Name this cervical view?

Right Posterior Cervical Oblique (RPO)
Name this cervical view?

Left Posterior Cervical Oblique (LPO)
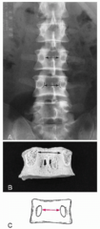
Name the view of image C on the left and identify the numbered structures 1-6:

A-P Thoracic 1. Rib 2. Transverse process 3. Costotransverse joint 4. Costovertebral joint 5. Pedicle 6. Spinous process
Name the view of image C on the left and identify the numbered structures 7-13:

A-P Thoracic 7. Inferior endplate 8. Intervertebral disc space 9. Clavicle 10. Diaphragm 11. Trachea 12. Paraspinal line (arrowheads) 13. Aorta (arrows)
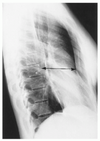
Name the view of image C on the left and identify the numbered structures 8-16:

(C) Lateral Thoracic 9. Rib head 10. Posterior rib 11. Lateral rib 12. Diaphragm 13. Posterior costophrenic sulcus 14. Heart 15. Lung hilus 16. Trachea