Nonlinear equations Flashcards
What is the big question about non-linear equations?
How do we find the roots of the equations
When there is no explicit formula to find the root(s) what types of methods do we have to use?
Iterative method
What is the first step when trying to find any root?
Plot the graph so you can check your answer
What is the notation for any root?
x*
What is the Intermediate Value Theorem?

What is the Interval bisection algorithm?

If f(a)f(b) < 0 what does this tell you about f?
It changes sign at leats once in [a,b] , so by the IVT theorem there must be a point x* ∈ [a,b] where f(x*) = 0.
What length does the interval have after k iterations of interval bisection?
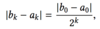
What is the error of the midpoint of an interval after k interations of interval bisection?
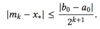
How many iterations do we need to make the error of the midpoint |mk - x*| ≤ δ?
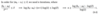
What is the general method for fixed point iteration?
Transform f(x) = 0 into the form g(x) = x, so that a root x* of f is a fixed point of g, meaning g(x*) = x*. To find x*, we start from some initial guess x0 and iterate xk+1 = g(xk) until |xk+1 - xk| is sufficiently small.
What is a problem with fixed point iteration?
Not all rearrangements g(x) = x will converge
A contractiln map f, is a map L ➝ L (for some closed interval) satisfying?
For some λ< 1 and for all x, y ∈ L.

What is the Contraction Mapping Theorem?

Prove the following theorem.


How do you show g is a contraction map?

What is the Local Convergence theorem?

Prove the following theorem.


What do we compare to measure the speed of convergence?
The error |x* - xk+1| to the error at the previous step |x* - xk|
Define linear convergence.
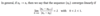
What is λ called?
The rate or ratio
What λ shows superlinear convergence?
0
What is meant by superlinear convergence?
The error decreases ar a faster and faster rate
What is the theorem about liner and superlinear convergence?

Prove the following theorem.


How can we further classify superlinear convergence?
By the order of convergence, defined as

What is a famous iterative method that usually converges superlinearly?
Newton’s Method
What is the iterative function for Newton’s method?

How can derive the iteration function for Newton’s method algebraically?

Prove that Newton’s method gives superlinear convergence.

What does the forth column in the following show?

The convergence is quadratic
Why don’t you want to start iterative near f’(x) = 0 in Newton’s method?
You will get stuck in a infinite loop and not find the root.
Write the following in matrix form.


What is the Jacobian matrix J(xk) equal to?

Write the following in a more simplified version.


How do you derive Newton’s method for systems from the following?

Rearrange for xk+1

If m=1, in Newton’s method for systems what does the Jacobian reduce too?
1\f’(x), which is the usual scalar formula
What is the convergence for Newton’s method for systems?
Quadratic provided that J(x*) is non singular
What is the Aitken a trick for?
Accelerating the convergence of a linearly convergent sequence
If we have the following and take two successibe iterations show how we can eliminate λ.

In Aitken acceleration what do we replace every third iterate by?

What is the aim of Aitken acceleration?
The extrapolation will get closer to x٭ than before
What is one problem with Aitken acceleration?
Rounding erros can affect ∆2xk
What does ∆xk equal?
xk-1 - xk
What does ∆2xk equal?
∆(∆xk)
What is the formula for solving f(x) = 0 with the iteration function g(x) = x + f(x)?

What are three drawbacks of Newton’s method?
- The derivative must be computed at each iteration
- Expensive to compute
- Formula to do so might not be available
What method can we use instead of a Newton method when we don’t want to find a derivative?
Quasi-Newton method
What is the formula for a quasi-Newton method?

What does gk stand for in the following?
Some easily-computed approximation to f’(xk)
What is the formula for Steffensen’s method and what gk do we use?

How many function evaluations does the following require per iteration?

Two
Once the iteration has started for the following quasi-Newton method we can appoximate f’(xk) by what backward difference?


What is the following method called?

The secant method
Why is the secant method a two-point method?

What is the theorem about the order of convergence of the secant method?

What is the formula for the secant method?

Prove the following theorem.




