Neurosurgery Board Review Flashcards
To rock the neurosurgery board examination.
Alexander disease
- AD leukodystrophy on chrom 17
- GFAP protein problem
- Rosenthal fibers
- widespread demyelination in brain (frontal lobes involved first)
Metachromatic leukodystrophy
- AR leukodystrophy
- sulfatase A
- increased cerebroside sulfate
- pathology -> PAS with macrophages
- Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome (MPS) has deficient sulfatase B
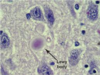
Krabbe disease (globoid leukodystrophy)
- AR leukodystrophy on chrom 14
- galactocerebrosidase deficiency
- pathology shows globoid macrophages
- psychosine accumulates
- moderate/severe brain atrophy with firm white matter

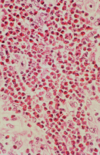
Tay-Sachs disease (GM2 gangliosidoses)
- AR on chrom 15 (lysosome)
- mutated hexosaminidase A (B is increased)
- cherry red macula
- also see Sandhoff’s disease (deficient B enzyme)
- gangliosides stain strongly for Luxol fast and Sudan black
- Balloon neurons on pathology
Wolman Disease
- AR (lysosomes)
- deficient acid lipase -> accumulated lipids
- calcification of the adrenal gland may be seen
Turner syndrome
- 45X
- short stature, no major CNS issues, aortic coarctation
Miller-Deiker syndrome
- chromosome 17p (most cases are sporadic and not inherited)
- lissencephaly
Batton Disease
- AR multiple genes
- most are due to thioesterase deficiency
- most common neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis
Prader-Willi Syndrome
- chromosome 15p
- MR, hypogonad, obese
Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Syndrome
- X-LINKED leukodystrophy
- myelin proteolipid abnormality
- pathology -> segmental demyelination
Adrenoleukodystrophy
- X-LINKED leukodystrophy
- ATP binding protein (ABCD1) peroxisome membrane transport protein
- pathology -> perivascular inflammation
- parieto-ccipital and deep white matter most affected
- spares subcortical U fibers -
- treatment is with Lorenzo’s oil
Gaucher disease
- AR leukodystrophy
- deficient beta-glucocerebrosidase (increased glucosylceramide levels)
- pathology -> crumbled paper tissue cells
Nieman-Pick disease
- AR leukodystrophy on chromosome 11
- type A/B 2/2 sphingomyelinase
- type C 2/2 cholesterol esterification
- cherry red macula
- Gaucher cells can be seen anywhere in the body, positive for PAS
Farber Disease
- AR
- acid ceramidase deficiency
Fabry disease
- X-LINKED
- deficient alpha-galactosidase (beta galactosidase in GM1 gangliosidoses)
- purple skin lesions and pain in hands/feet
GM1 gangliosidosis
- AR
- deficient beta-galactosidase (increased levels of gangliosides, oligo and polysaccharides)
- increased keratin sulfate -> Morquio syndrome
- cherry red macula
Kearns-Sayre Disease
- mitochondrial disease, +RRF, negative LA
- progressive external ophthalmoplegia
- heart block, retinitis pigmentosa
- DDX is myasthenia gravis which improves with cholinergics
- pathology -> spongiform cerebral and midbrain lesions
MERRF (myoclonic epilepsy with ragged red fibers)
- mitochondrial DNA (8344)
- epilepsy and delay
- +RRF, NO lactic acidosis
MELAS (myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke)
- mitochondrial DNA
- +LA and +RRF (only mt dz that has BOTH)
- strokes that straddle vascular distributions (immediate subcortical white matter with hyperintense gyri on FLAIR/T2)
- MRS shows lactate doublet
Cowden syndrome
- AD on chromosome 10
- PTEN loss of function (tumor suppressor)
- increased risk of many cancers
- CNS -> macrocephaly/hydrocephalus and dysplastic gangliocytoma of cerebellum (Lhermittos Duclos disease)
Refsum disease
- AR (peroxisomes)
- deficient phytanoyl hydroxylase (increased phytanic acid = long chain FA)
- night blindness
- demyelinating sensory neuropathy
- hearing loss
- cardiomyopathy
Gerstmann syndrome
- dominant parietal lobe (angular and supramarginal gyrus) insult
- symptoms: acalculia, agraphia, finger agnosia, left/right confusion
Raeder’s Syndrome (paratrigeminal syndrome)
- lesions in and around carotid siphon
- trigeminal neuralgia (involving V1 and V2, NOT V3)
- Partial Horners (sweating is intact)
Gradenigo’s Syndrome
- petrous apex lesions (otits, tumors, inflammation)
- retro-orbital pain
- 6th nerve palsy
- ear drainage if secondary to petrositis from ear infection
Vernet’s Syndrome
- jugular foramen lesions
- CNs IX, X, XI
Villaret Syndrome
- posterior retroparotid space
- CNs IX, X, XI, XII, sympathetic chain
Tapia Syndrome
- posterior retroparotid space
- CNs X, XII (sometimes IX, VII, and sympathetic chain)
Schmidt Syndrome
- CNs X, XI
Garcin Syndrome
- skull base lesions (nasopharyngeal tumors and carcinomatous meningitis secondary to leukemia)
- all 12 cranial nerves
Collet-Sicard Syndrome
- Villaret syndrome WITHOUT sympathetic chain
- anterior occipital condyle lesions (tumors, vertebral aneurysms)
- CNs IX, X, XI, XII
Leber’s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy
- mitochondrial DNA (3 known mutations)
- NEITHER lactic acidosis or RRF
- central visual loss bilaterally (not always complete) due to AV shunting in retina
Leigh Disease (Subacute Necrotizing Encephalomyelopathy)
- mitochondrial DNA and nuclear DNA (RANBP2 nuclear pore protein)
- lactic acidosis
- spongy necrosis 2/2 myelin degeneration in the thalami, putamen, brainstem, and cord (hemispheres are spared)
Wyburn-Mason Syndrome
- multiple intracranial AVMs (mostly mesencephalic / optic pathway including retina)
- cutaneous nevi
- similar to Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome
- not considered hereditary, congenital in origin
Osler-Weber-Rendu (hereditary hemorrhagic telangectasia)
- AD inheritance 2/2 numerous mutations (related to TGF and BMP signalling)
- multi-organ AVM formation
- cerebral abscesses / strokes 2/2 pulmonary AVMs
- many mucocutaneous telangiectasias
Tuberous sclerosis (Bourneville-Pringle disease)
- AD inheritance chrom 9 (hamartin) or 16 (tuberin)
- cortical tubers (ddx is Taylor focal cortical dysplasia, T1 dark, T2 bright gyrus)
- subependymal nodules -> SEGAs in 15%
- white matter lesions extending radially from ventricles to cortex
- seizures (infantile spasms)
- cardiac rhabdomyomas, kidney angiomyolipomas/ADPCKD/RCC
- skin shagreen patches (lethargy regions), adenoma sebaceum, ash leaf spots
- peringual fibromas
Cri du Chat
- chromosome 5p
- cat-like cry
Trisomy 9
- Dandy-Walker malformation
- Subependymal and choroid plexus cysts
Patau Syndrome
- trisomy 13
- holoprosencephaly (no hemispheric division)
- retinoblastoma
- rocker-bottom feet and polydactyl
Edward’s Syndrome
- trisomy 18
- gyrus dysplasia, cerebellar hypoplasia
- callosal agenesis
- Chiari II malformations
- scaphocephaly (dolichocephaly)
Dermatomyositis
- B-cell disease -> myositis and vasculitis
- heliotrope rash and Gottron’s papules (scaly macules on extensor surfaces of arms)
- 10% malignancy association
Canavan disease (aminoacidopathy)
- AR -> aspartoacylase (unable to break down acetyl-aspartate to aspartate and acetate)
- white matter vaculoziation with Alzheimer’s type II astrocytes (enlarged clear nuclei), does NOT spare subcortical U-fibers (in fact, preferentially demyleinates subcortical U-fibers)
- megaloencephaly
- abnormally long mitochondria

Wilson’s disease (hepatolenticular degeneration)
- AR chromosome 13
- ATPase-7B protein (7A for Menkes) = cation transporter on mitochondria
- increased copper levels and decreased ceruloplasmin levels (both are decreased in Menkes)
- Alzheimer’s type II astrocytes (large pale nuclei) -> also seen in hepatic encephalopathy
- Opalski cells -> microglia with eccentric prominent nuclei
- copper in putamen > caudate > BG/thalamus/cortex
- T1 and T2 show bright basal ganglia (hyperintense)
Von Gierkes (GSD type I)
- AR -> glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency
- hepatomegaly
- severe hypoglycemia
McArdle’s (GSD type V)
- AR -> myophosphorylase deficiency
- most benign GSD
- renal failure 2/2 myoglobinuria
- increased serum CK
- excersize induced cramping
Pompe’s (GSD type II)
- AR -> acid-maltase deficiency
- infantile and juvenile/adult onsets
- early death for all forms 2/2 myopathy, cardiomegaly, and respiratory failure
Cori’s (GSD type III)
- AR -> amylo-1/6-glucosidase deficiency (debranching enzyme)
- hepatomegaly, seizures, growth retardation
Tauri’s (GSD type VII)
- AR -> phosphofructokinase deficiency
- symptoms are similar to McCardles (type V)
GSD type IX
- X-LINKED (only GSD that is X-linked) -> phosphoglycerate kinase deficiency
- symptoms different than other GSDs: hemolytic anemia, MR, seizures/tremor
Sialidosis (mucolipidoses type I)
- alpha-neuramidase deficiency
- cherry red macula
- macroglossia
- coarse facial features
Sandhoff syndrome (GM2 gangliosidoses)
- AR chromosome 5
- hexosaminidase B gene deficiency (A accumulates)
- in Tay-Sachs (A mutation, and B accumulates)
Crouzon Syndrome (acrocephalosyndactyl type II)
- AD chromosome 10
- FGF-receptor 2 gene
- most common craniosynostosis syndrome
- NORMAL intelligence
Apert syndrome (acrocephalosyndactyl type I)
- AD chromosome 10 (FGF-receptor 2 gene)
- bicoronal craniosynostosis (most common) -> brachycephaly or turricephaly
- Harlequin orbit (elevation / elongation of superolateral orbit on craniosynostotic side)
- MENTAL RETARDATION (different than Crouzon)
- intracranial abnormalities in 50% (callosal dysgenesis, hydrocephalus, cavum veragae)
- cervical spine issues
Saethre-Chotzen Syndrome (acrocephalosyndactyl type III)
- AD chromosome 7 (TWIST gene)
- “cotton beaten” skull xrays
- coronal synostosis most common
- syndactyl between 2nd-3rd digits (Carpenter syndrome is 3rd-4th digits)
- normal intelligence
Waardenburg syndrome (acrocephalosyndactyl type IV)
- AD >> AR (multiple genes involved - SOX, PAX, etc)
- depigmentation syndrome (skin, eyes, hair)
- hearing loss common
- cerebellar/cortial hypoplasia
- peripheral nerve demyelination -> Hirschsprung’s disease
Pfeiffer syndrome (acrocephalosyndactyl type V)
- AD (FGF receptors 1 AND 2)
- several subtypes (normal intelligence in type I)
- multi-suture synostosis (kleeblattschadel)
- brachydactyl (also thumb/big toe point away from other digits)
Carpenter syndrome
- AR (RAB23 gene -> vesicle trafficing protein, ONLY AR synostosis syndrome)
- syndactyl (3rd/4th digits)
- crypthorchidism in all males
- heart abnormalities (dextrocardia)
MEN type I (Wermer syndrome)
- AD -> MEN1 gene
- pituitary adenomas (only MEN with pit adenomas)
- pancreatic tumors (gastrinoma most common)
- lipoma / angiolipoma
- parathyroid hyperplasia
Greig syndrome
- AD (GLI3 gene on chromosome 7)
- metopic and/or sagittal synostosis
- poly and syndactylyl
- callosal dysgenesis and ventriculomegaly
MEN type IIa (Sipple syndrome)
- AD chromosome 10 (RET gene)
- pheochromocytoma (33%)
- medullary thyroid cancer (100%)
- parathyroid hyperplasia
MEN type IIb
- RET gene
- pheochromocytoma (50%)
- medullary thyroid cancer (85%)
- marfanoid
- mucosal neuromas (100%)
Turcot syndrome
- AD
- type I = hereditary non-polyposis colorectal CA -> DNA mismatch mutations -> GI/GU tumors + astrocytomas
- type II = familial adenomatous polyposis -> APC gene -> GI tumors + medulloblastomas + craniofacial exostosis
von-Hippel-Lindau syndrome
- AD on chromsome 3 - increased erythropoeitin, PDGF, VEGF, TGF - hemangioblastomas of brain and retina - endolymphatic sac tumors of posterior petrous bone - clear cell RCC (type I and type IIb) - pheochromocytomas (type II VHL)
Basal cell nevus syndrome (Gorlitz syndrome)
- AD chromosome 9 - PTCH gene - Tumors: basal cell carcinomas, odontogenic tumors (80%), medulloblastoma (4 to 25%) - dural calcification along falx and tentorium - skeletal anomalis (ie: bifid ribs)
Schwannomatosis
- sporadic mutations in SMARCB1 (IN11/hSNF5) -> chormatic remodeling protein - multiple schwannomas of spine/equina/cutaneous/and nonvestibular CNs