Neuroscience & Behaviour Flashcards
What are the different contributors to our behaviour? (31 cards)
What question did Rene Descartes bring forth?
Presented Monism vs Dualism
What is Monism, how does it differ from Dualism?
Monism: mind and body are one
Dualism: body and mind are separate
What theory did Descartes’ bring forth? What theory did it precede?
Descartes brought forth: the Reflex Action theory - hypothesized: “animal spirit” that traveled via the gland to the “mind”, and agitates muscles on the way (involuntary) - precursor to S-R behaviourism
What does the mind-body interaction theory assume?
- Mind provides body with information about the external world (in brain) - Physical motion (animal spirit) -> mental quality (sensation)
What did Luigi Galvani study?
The first to study “Animal Electricity” - nerve impulses = electrical - Galvanic Skin Conductance- muscles can be stimulated without fluid from brain - used frogs in thunderstorm
Giovanni Aldini was Galvani’s nephew
Used galvanism for medical applications
What are the two components of nerve fibers?
- Neurons 2. Synapses
What are neurons?
Cells of the nervous system that synapse to perform information-processing tasks.
Threads of each neuron are physically attached to other neurons T or F
False, they do not touch
What are the 3 parts of a neuron

Cell body: information processing tasks
Dendrite: receives information from other neurons and relays to cell body
Axon: transmission to other neurons, muscles and glands
What is the name of the junction between dendrite and axon
Synaptic cleft, where synapses are completed
What are the 3 major types of neurons?
- Sensory neurons: stimulus conveyed to brain via spinal cord
- Motor neurons: communicates stimulus to spinal cord, then to muscles to produce movement
- Interneurons: connect sensory and motor neurons, or other interneurons
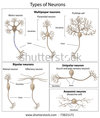
What are the different specialized neurons?
Purkinje cells (treelike assemblage of dendrites)
Pyramidal cells: triangular body, single long dendrites with many small dendrites
Bipolar cells: one dendrite with a single axon
What are the two stages of electrochemical action?
- Conduction
- Transmission
How is electrical signalling conducted within a neuron?
As information is passed, charge is altered from resting potential, through movement of ions between cell membrane
What is the resting potential?
difference in electric charge between inside and outside neuron’s cell membrane (-70mV)
What is the action potential?
electrical signal, conducted along axon to synapse
- must reach threshold to be conducted
- time required before next action potential can be conducted: refractory period
What are the steps leading to an action potential?
Resting -> threshold -> action potential (depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization)
What are the 2 types of messages?
- Excitatory messages: initiated by chemicals, usually neurotransmitters
* stimulate change in electrical potential of neuron
- Inhibitory messages: reduce/block effect of excitatory messages from another neuron
*lack of excitatory messages-> nothing happens
What are myelin?
Insulating layer of fatty material composed of glial cells
* helps efficient transmission of signals to other cells
What is the name of the gaps in Myelin Sheaths?
Nodes of Ranvier
How does trasmission occur between neurons
Chemical signals through neurotransmitters release from terminal buttons, to bind to receptors
What are the 3 steps of synaptic transmission?
1) action potential travels down axon
2) stimuates neurotransmitter release
3) neurotransmitter binds to receptor on dendrite of postsynaptic neuron
What are the 3 possibilities of termination for synaptic transmission?
1) reuptake of neurotransmitter
2) enzymatic breakdown in synapse
3) binding to autoreceptors on sending neuron



