Neurology Flashcards
(175 cards)
Define the different layers of organisationa and classification of the nervous system

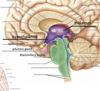
What are the gross regions of the brain and what are their functions?
Frontal lobe: personality
pariental = sensory
Occipital –> vision processing
Temporal: personality (fear and anxiety)
Cerebelllum: fine motor skills

What are Gyri and Sulci in the brain?
What is their function?
folds in brain –> larger suface area

List the Cranial nerves

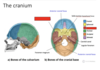
What is the function of the meningines?
Describe their organisation
The meningines protect the brain

What are other important structures in the brin, than just the major regions?

How is the spinal cord arranged? (inkl. grey matter, white matter, dorsal route, ventral route)

How can the PNS regenerate in comparison to the CNS?
PNS : regeneration possible (phagocytes remove inhibitory cells)
CNS: barely any regeneration –> glia cells inhibit and form scaring
Dorsal-comumn-medial lemniscus pathway
What is its function?
Which route does it take?
Sensory pathway
Crossing over in medulla oblangata

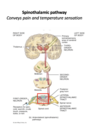
Spinothalamic pathway
What is its function?
Which route does it take?
Sensory pathway
Crosses over while entering the spinal cord
List two examples of motor pathways
What is their function and which route do they take?
Lateral corticospinal tract:
–> e.g. arm movine –> crosses sides in medulla oblangata
Vesibulospinal tract
–> ear and balance
–> ipsilateral side all the time
Ipsilateral
Same side
Contralateral
entgegengesetze Körperseite oder hälfte
Define a neuron
structional and functional unit of nervous system
conduction of electrical siganals and communication via chemical synapse
Describe the structure of a neuron

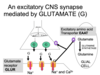
What is the function of an axo-dendritic synapse?
How abundant is it?
“normal” synapse, most abundant
usually exitation
Explain the organisation of the Cytoskeleton in Neurons
very abundant to ensure size and shape
intermediate fillaments: stability
Microtubule: transport of vesicles along axon
How abundant is a Axo-somatic synapse?
What is its usual function?
rarer, usually inhibitory
Describe the structure of a axo-axonic synapse
end at next cells axon
Explain the function of Astroglia (Astocytes)
most abundant, gap junctions suggest astroglia-astrogial signaling
–> Barrier function (form Brain-Blood Barrier, signaling between blood and neurons)
–> Remove Neurotransmitter
fibrous and protoplasmic

What is the function of Oligodendrocytes?
What are their characteristics?
Form Myelin and retian for lifetime (CNS)
highly metabolic active (ER, Golgi, Mitochondria)
What is the origin of Microglia cells?
What is their function?
- derive from bone marrow,
immune function –> Macrophage activation
What is the function Schwann cells?
Where are they found?
Astrocytes and Oligodendrocytes function in PNS
–> myelinate one axon (wrap around one axon as a cell)
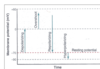
Define Electrochemical equilibrium
and Equilibrium potential
Electrical force balances diffustion force
Potential at which equilibrium is achieved