Neurology Flashcards
(53 cards)
Define Multiple Sclerosis
MS is an autoimmune disorder which results in the loss of myelin from neurons of the central nervous system
List the 6 main symptoms of multiple sclerosis.
How do these symptoms tend to present themselves?
Blurred vision (Usually in one eye, described as looking through petroleum jelly, may have pain moving eye and color discrimination)
Fatigue
Difficulty walking
Parathesia in different parts of the body (tingling or numbness)
Muscle stiffness and spasms
Symptoms usually last for over 48 hours, and are often asymetric, involving one side of the body or one limb (bilateral can occur however)
Parathesia can be band-like or hemi-band like which is indicative of a spinal cord lesion
What are the 4 main risk factors for multiple sclerosis?
Female
Age (20-40)
Family history of MS
Northern latitude (North hemisphere regions)
Detection of fibrilations can be detected using which medical investigation?
Electromyography (EMG)
What findings can be found in patients with multiple sclerosis on an EMG?
EMG shows no abnormalities as it is a condition affecting the CNS
What imaging test should be performed in patients suspected of multiple sclerosis?
MRI

List 6 investigations that should be performed in patiens suspected of multiple sclerosis.
MRI- Brain
MRI - Spinal cord
FBC (to rule out differentials and concurrent illness)
Comprehensive metabolic panel (Calcium, billirubin, glucose, pottasium ect)
TSH blood test
Vitamin B12 blood test
What are 2 other investigations to consider in patients suspected of MS and when would you justify using them?
Evoked potentials (When MRI is contraindicted)
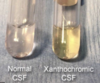
CSF evaluation (When all non-invasive investigations have been pursued due to its invasiveness)
What CSF evaluation finding supports the diagnosis of MS?
Elevation in IgG and IgG synthesis rates
Oligoclonal bands

What MRI findings are indicative of MS?
MRI Brain: Lesions involving the corpus callosum (e.g. finger-like projections perpendicular to corpus callosum)
MRI spinal cord: Lesions (appearing white) usually affecting the cervical spinal cord

What treatment should be given to a patient with MS suffering from an acute relapse episode?
Glucocorticoid (Methylprednisolone) IV administered
For patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis, what is the first line ongoing treatment option?
Immunomodulators (e.g. Interferon beta 1a or 1b)
Define Aparaxia
Disorder of skilled movement. Patients are not paretic but have lost information about how to perform skilled movements (e.g. tie up shoelace or button up shirt)
What brain lesion areas tend to result in the presentation of aparaxia?
Inferior parietal lobe
Frontal lobe (Supplementary and premotor areas)

What are the two most common causes of aparaxia?
Stroke
Dementia
Define Motor Neurone Disease (MND).
What is an alternative name for MND?
Spectrum of proggresive neurodegenrative disorders affecting the motor system.
AKA Ayomyotrphic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)

List 6 upper motor neurone signs and 5 lower motor neurone signs of multiple sclerosis
Upper:
Spasticity (increased tone) of limbs and tongue
Brisk limbs and jaw reflexes
Babinski’s sign
Loss of dexterity
Dysarthria (difficulty speaking)
Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
Lower:
Weakness
Nasal speech
Toungue fasciculations and wasting
Muscle wasting
Define Parkinson’s Disease.
A neurological disease characterised by uncontrollabale movement caused by degenrative changes in dopaminergic neurones of the substania nigra.

List 5 main symptoms and signs of Parkinson’s Disease.
Bradykinesia (Slowed movement)
Akinesia (Difficulty initiation movement)
Hypomimic face
Rigidity
Tremor at rest (Pin rolling tremor) [Usually starting in one hand and then spreads to other parts of the body overtime]

How is Parkinson’s Disease diagnosed?
Condition is diagnosed clinically and investigations are usually not required
What are the 5 first line treatment options for patients with Parkinson’s Disease?
Carvidopa/Levodopa
Dopamine agonists
MAO-B Inhbitors
Amantidine (increases dopamine release and reduced re-uptake)
Trihexyphenidyl (antispasmodic drug)
What 2 non-pharmacological treatment options are also offered to patients with Parkinson’s Disease?
Exercise
Physiotherapy
Define Huntington’s Disease.
Genetic neurodegenerative disorder characterised by degeneration of GABAergic neurones in the striatum, cuadate and putamen

What are the main signs and symptoms of Huntington’s Disease?
Cognitive, Mood and Physical manifestations
Motor: Choreic movements, Dysphagia, Unsteady gait, Saccadic eye movements, Motor impersistence (e.g. cant stick toungue out and hold it for more than 10 seconds).
Mood: Deppresion, Anxiety
Cognitive: Loss of coordination (e.g. dropping things, car accidents), Impaired concentration, changes in personal habits and hygeine