Neuroanatomy Flashcards
1
Q
- CNS - Blood supply
A
- Internal carotid system (from internal carotid a.)
- Opthalmic a.
- ant. + middle cerebral a.
- inf. + sup. hypophyseal a.
- ant. choroid a.
- post. communicating a.
- Vertebrabasilar system (from vertebral + basilar a.)
- ant. + post. spinal a.
- post. inf. cerebellar a.
- basilar a.
2
Q
1.1 CNS - Blood supply - Circle of Willis
A
→ anastomosis of int. cartotid a. and vertebral a.
→ located in subarachnoid space
- ant. + post. cerebral arteries
- ant. + post. communicating arteries
- internal carotid artery
- Basilar artery
3
Q
1.2 CNS - Blood supply - Veins
A
- cerebral vein
- inferior
- middle
- superior
- great
- internal
- basal vein
4
Q
1.3 CNS - Dural venous sinuses
A
- between the 2 layers of cranial dura mater
- Unpaired
- sup. + inf. sagittal
- straight
- occipital
- Paired
- sphenoparietal
- cavernous
- sup. + inf. petrosal
- transverse
- sigmoid
5
Q
1.4 Blood brain barrier
A
- separates blood and CSF in the CNS
- because of tight junctions between endothelial cells
- layers:
- Choroidal endothelial cells: tight junctions
- Basement membrane
- Ependymal cells: tight junctions
- substances may cross via
- active transport
- diffusion
- facilitated diffusion
6
Q
- Meninges - Anatomy
A
- surrounds brain with 3 layers
- dura mater
- strong, thick, fibrous
- periosteal layer
- meningeal layer
- strong, thick, fibrous
- arachnoid membrane
- delicate nonvascular CT membrane
- allows one way flow of CSF to venous circulation
- pia mater
- delicate vascular CT membrane
- covers surface of brain
- dura mater
7
Q
2.1 Meninges - Blood supply
A
- meningeal art.
- anterior
- middle
- posterior
8
Q
2.2 Meninges - Innervation
A
→ rich nerve supply, because of vasoconstriction
- Trigeminal nerve (CN 5)
- Vagus nerve (CN 10)
- Hypoglossal nerve (CN 12)
9
Q
2.3 Meninges - Subarachnoid space
A
- space between:
- arachnoid membrane + dura mater
- contains CSF and arteries
- surrounds CNS → enlarges at times
- → subarachnoid cisternae
10
Q
- Brain ventricles
lateral + 3rd ventricle
A
-
Lateral ventricles
- located within cerebral hemispheres
- connected to 3rd ventricle via the interventricular foramina
- consists of:
- body
- frontal horn
- temporal horn
- occipital horn
- atrium
-
3rd ventricle
- between the two thalami
- filled with CSF
- connected to 4th ventricle via cerebral aqueduct
- has recesses:
- optic recess
- infundibular recess
- pineal recess
- suprapineal recess
11
Q
3.1 Brain ventricles
4th ventricle
A
- posterior to brainstem
- anterior to cerebellum
- communicates with
- 3rd ventricle via cerebral aqueduct
- spinal cord via central canal
- contains a pair of choroid plexi
- site of CSF production
- Borders:
- superior: sup. + inf. medullary veli
- inferior: rhomboid fossa
- lateral: cerebellar peduncles
12
Q
3.2 Choroid plexus
A
- 4 cisterns, one in each ventricle
- produce CSF
- modified ependymal cells
- 500ml/day
- total volume: 140 ml
- supports + cushions CNS
- transports hormones
- removes waste products
-
Circulation
- lateral ventricles
- 3rd ventricle
- 4th ventricle
- cerebellomedullary cistern
- subarachnoid space
- reabsorbtion into dural sinuses
- cerebellomedullary cistern
- 4th ventricle
- 3rd ventricle
- lateral ventricles
13
Q
3.3 Subarachnoid cisterns
A
→ expanded areas of subarachnoid space, also filled w/ CSF
- between arachnoid and pia mater
- Cerebello•medullary cistern
- Basal cistern
- Ponto•cerebellar cistern
- Interpeduncular cistern
- carotic cistern
- lumbar cistern
14
Q
- Cervival plexus
Muscular branches
A
- formed by rami of C1-C4
-
Muscular branches
- Ansa cervicalis (C1-C3, CN12)
- Genio•hyoid
- Thyro•hyoid
- Sterno•hyoid
- Omo•hyoid
- Phrenic nerve (C4)
- Diaphragm
- Pericardium
- Segmental branches (C1-C4)
- ant. + mid. scalenus m.
- suboccipital m.
- Ansa cervicalis (C1-C3, CN12)
15
Q
4.1 Cervical plexus
Cutaneous branches
A
- lesser occipital n.
- greater auricular n.
- transverse cervival n.
- supraclavicular n.
16
Q
- Brachial plexus
A
- from rami C5-C8 + T1
- “M A R M U”

17
Q
- Lumbar plexus
A
- formed by rami of L1-L4 + T12 (subcostal n.)
- Branches
- iliohypogastric
- ilioinguinal
- genitofemoral
- lat. femoral cutaneous
- obturator
- femoral
- muscular branches
18
Q
- Sacral plexus
A
- formed by rami of L4-L5 + S1-S4
-
Sciatic plexus
- sup. + inf. gluteal n.
- post. femoral cutaneous n.
- sciatic n.
- tibial n.
- common peroneal n.
-
Pudendal (hemorrhoidal) plexus
- Pudendal nerve
- Pelvic splanchnic nerve
19
Q
- sympathetic PNS - Anatomy and peripheral ganglia
A
- larger part of autonomic NS
- neurotransmitter: mainly ACh + NE
- induces fight-or-flight response
- 2 different kinds:
-
Paravertebral ganglia
- Cervical g. (3)
- Thoracic g. (11)
- Lumbar g. (5)
-
Prevertebral ganglia
- Celiac g.
- sup. + inf. Mesenteric g.
20
Q
8.1 sympathetic PNS - Plexuses
A
- Cavernous p.
- Carotid p.
- Cardiac p.
- Pulmonary p. (ant. + post.)
- Celiac p.
- sup. + inf. Mesenteric p.
- inf. Hypogastric p.
21
Q
8.2 sympathetic PNS - Nerves
A
- Cardiopulmonary n.
- Thoracic splanchnic nerves
- greater -
- lesser -
- least -
- Lumbar splanchnic n.
22
Q
- parasympathetic PNS - peripheral ganglia
A
- part of autonomic NS
- neurotransmitter: only ACh
- induces rest-and-digest action
-
Head and neck ganglia
- Ciliary g.
- Pterygopalatine g.
- Submandibular g.
- Otic g.
-
Intramural ganglia
- from vagus nerve
23
Q
9.1 parasympathetic PNS - Plexuses
A
- very similar to sympathetic plexuses!
- Cardiac p.
- Pulmonary p.
- Celiac p.
- sup. + inf. Mesenteric p.
- inf. Hypogastric p.
24
Q
9.2 parasympathetic PNS - Nerves
A
- Occulomotor n. (CN 3)
- Facial n. (CN 7)
- Glossopharyngeal n. (CN 9)
- Vagus n. (CN 10)
- Pelvic splanchnic n. (S2-S4)
- from pudendohemorroidal plexus
25
10. Spinal cord - Gross anatomy
* cylindrical portion of the CNS
* found in vertebral canal
* borders
* cranially: foramen magnum
* caudally: L2 vertebra
* **Anterior**:
* anterior median fissure
* anterior spinal art.
* antero•lateral sulcus
* exit of anterior spinal nerve roots
* **Posterior**:
* postero•lateral sulcus
* entrance of posterior spinal nerve roots
* posterior median sulcus
* dividing spinal cord into two symmetrical halfs
* posterior intermediate sulcus

26
10.1 Spinal cord - External features
1. Enlargements
* cervical
* lumbar (L4-L5 = thickest)
2. conus medullaris
* level of L2
3. cauda equina
* spinal nerve roots L1 + L2
4. filum terminale
* attaches conus medullaris to coccyx
27
10.2 Spinal cord - Crosssection
* grey matter (inside part)
* anterior-, lateral-, posterior column
* white matter (outside part)
* anterior-, lateral-, posterior funiculus
* cervical + lumbar part is bigger in diameter
* due to lumbar + sacral plexus

28
10.3 Spinal cord - Meninges
* consists of 3 layers
1. **pia mater**
* Denticulate lig.
* attach arachnoid- + dura mater
* subarachnoid space w/ cerebrospinal fluid
2. **arachnoid mater**
* forms perineurum of spinal nerves
3. **dura mater**
* makes up:
* cauda equina
* filum terminale
* further enclosed by:
* meningeal layer of spinal dura
* epidural space w/ fat tissue + vertebral venous plexus
* periosteal layer of spinal dura
* continous with cranial meninges at foramen magnum!

29
10.4 Spinal cord - Blood supply
**Arteries**
1. **vertebral (longitudinal) art.**
* ant. + post. spinal art.
* arterial anastomoses: arterial vasocorona
2. **segmental (radicular) art.**
* pass through intervertebral foramen
* ant. + post. radicular art.
* have anastomoses
* dominant artery: Art. of Adamkiewicz
**Veins** (like arteries)
* ant. + post. spinal veins
* ant. + post. radicular veins
* internal vertebral plexus in the epidural space
* which drains into: external vertebral plexus
* finally: intervertebral veins

30
10.5 Spinal cord segment
* anatomical + functional unit of the spinal cord
* consists of:
* gray matter
* central canal
* contains cerebrospinal fluid
* white matter (columns)
* grey matter (horns)
* contents:
* **one pair of spinal nerves**
* dorsal + ventral roots
* dorsal root ganglion
* sensory + motor neurons

31
11. Spinal cord - White matter
* contains:
* nerves
* glial cells
* blood vessels
* Nerve fibres with similar destinations:
* Tracts/Pathways - in funiculi!
* ascending
* descending
* intersegmental
32
11.1 Spinal cord - White matter - Ascending tracts
* PERIPHERY → SPINAL CORD → BRAINSTEM → THALAMUS → CORTEX
* may be crossed or uncrossed
* in ant. white commissure (post. to ant. median fissure)
* axons of a lower segmental origin lie more superficial
* "Somatotopy", Kahler's law

33
11.2 Spinal cord - White matter - Ascending tracts
**Antero-lateral funiculus**
1. Ant. + lat. spinothalamic tract
2. Ant. + post. spinocerebellar tract
**Posterior funiculus**
1. fasciculus gracilis (medial)
2. fasciculus cuneatus (lateral)

34
11.3 Spinal cord - White matter - Descending tracts
* CORTEX → BRAINSTEM → SPINAL CORD → PERIPHERY
* found more in the "anterior part" of the spinal segment

35
11.4 Spinal cord - White matter - Descending tracts
**Anterior funiculus**
1. Ant. corticospinal tract
2. Olivospinal tract
3. Vestibulospinal tract
4. Reticulospinal tract
**Lateral funiculus**
1. Lat. corticospinal tract
2. Rubrospinal tract

36
12. Spinal cord - Grey matter - Structure
* forms H-shape within white matter
* **anterior column**
* ant. horn
* mainly **motor neurons**
* alpha- + gamma-motor neurons
* **lateral column**
* lat. horn
* mainly **autonomic neurons**
* sympathetic + parasympathetic ganglia
* **posterior column**
* post. horn
* mainly **sensory neurons**
* substantia gelatinosa
* nucleus dorsalis

37
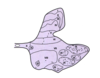
12.1 Spinal cord - Grey matter - Rexed laminae
* separates neurons from each other
* 10 layers to organize grey matter
* discovered by Bror Rexed in 1950s
* there are several motor neuron groups (lamina IX)
38
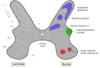
12.2 Spinal cord - Grey matter - Nuclei
1. Intermedio•lateral nucleus (lamina **VII**)
2. Intermedio•medial nucleus (lamina **VII**)
3. contains interneurons
4. Dorsal-/Clarke nucleus (lamina **VII**)
5. Nucleus proprius (laminae **III, IV**)
6. Substantia gelatinosa (lamina **II**)
7. Marginal nucleus (lamina **I**)
8. Motor neurons (laminae **IX**)
9. alpha neurons: extrafusal muscles (striated)
10. gamma neurons: intrafusal
39
12.2 Spinal cord - Grey matter - Transmitters
* Glutamate
* Glycine
* ACh
40
13. Brainstem - General information
* consists of:
* **medulla**
* **pons**
* **midbrain**
* can be seen only when brain is removed
* covered by cerebral hemispheres!
* extends from:
* inferior: pyramidal decussation to
* superior: posterior comissure
* two white nerve crossings

41
13.1 Medulla Oblongata/Myelencephalon - Structure
* most inferior part of brainstem
* pyramidal decussation to inf. pontine sulcus
* anterior parts are called "pyramids"
* contain motor fibers: "pyramidal tracts"
* contains autonomic centers regulating:
* respiration, circulation, GI motility
* gives rise to CN 9-12
* connected to the cerebellum by the inf. cerebellar peduncle
42
13.2 Medulla Oblongata/Myelencephalon - Proper Nuclei
* **Nucleus gracilis + -cuneatus**
* ****contain 2nd order neurons of the medial lemniscus tract (dorsal column)
* gives rise to internal arcuate fibres
* **Accessory cuneate nucleus**
* contains 2nd order neurons of the cuneocerebellar tract
* projects to cerebellum (via inf. cerebellar peduncle)
* **Inferior olivary nucleus**
* ****olivo•cerebellar fibres → cerebellum
* subdivided:
* medial- + lateral accessory olivary nucleus
* **Arcuate nucleus**
* ****on ventral surface of the pyramids
43
13.3 Medulla Oblongata/Myelencephalon - Cranial Nerve Nuclei
**Motor**
* Nucleus ambiguus (IX, X, XI)
* Accessory nucleus (XI)
* Hypoglossal nucleus (XII)
**Sensory**
* Spinal nucleus of trigeminal nerve (V)
* replaces substantia gelatinosa
* Nucleus of solitary tracts (VII, IX, X)
* Lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiter's nucleus)
* Ventral- + dorsal cochlear nucleus
**Autonomic**
* Dorsal motor nucleus of vagus nerve (X)
44
13.4 Medulla Oblongata/Myelencephalon - Tracts
**Ascending**
* Dorsal column tract
* gracile + cuneate tracts
* Spinothalamic tract
* Spinal trigeminal tract
* mediates pain, temp., touch from face
* Medial lemniscus
* Dorsal + Ventral spinocerebellar tract
* Medial longitudinal fascilus (MLF)
**Descending**
* Pyramidal tracts
45
14. Pons
Consists of:
* Base
* Corticobulbar tract
* Corticospinal tract
* Corticopontine tract
* Tegmentum (roof)
* cranial nerve nuclei
* reticular nuclei
* major ascending sensory pathways
* connected to cerebellum
* via middle cerebellar peduncle
* gives rise to CN 5-8
46
14.1 Pons - Nuclei - Cranial nuclei
**Motor nuclei**
* Trigeminal ncl.
* Abducent ncl.
* Facial ncl.
**Sensory nuclei**
* Pontine ncl.
* Solitary ncl.
* Vestibulo-cochlear ncl.
47
14.1.1 Pons - Nuclei II
* superior olivary complex
* nucleus of trapezoid body
* locus coeruleus
* nuclei pontis
48
14.2 Pons - Tracts
* Spinothalamic tract
* Med. + lat. lemniscus
* Central tegmental tract
* Med. + dorsal longitudinal tract
* Cortico•spinal tract
* Cortico•bulbar tract
* Cortico•pontine tract
* Ponto•cerebellar tract
* Spinal trigeminal tract
* Solitary tract
* Trigeminal lemniscus
49
15. Midbrain - Anatomy
* Most superior part of brainstem
* processes visual + auditory dara
* maintains consciousness
50
15.1 Midbrain - Cranial nuclei
**Motor nuclei**
* Occulomotor ncl.
* Trochlear ncl.
**Parasympathetic nuclei**
* Edinger-Westphal ncl.
**Other nuclei**
* red nucleus
51
15.2 Midbrain - Tracts
* Medial + trigeminal lemniscus
* spino•thalamic tract
* Medial + dorsal longitudinal fasciculus
* Central tegmental tract
* Rubro•spinal tract
* Tecto•spinal tract
* Cortico•bulbar tract
* Cortico•spinal tract
* Fronto•pontine tract
* Temporo•pontine tract
* Occipito•pontine tract
* Parieto•pontine tract
52
16. Cerebellum
* lies in posterior cranial fossa
* between
* occipital lobes
* temporal lobes
* brainstem
* 2 hemispheres divided by midline: *vermis*
* **3 lobes
* anterior, posterior
* flocculonodular lobe (small)
* consists of:
* gray matter: cerebellar cortex
* white matter: medullary body + arbor vitae
* connected to brain stem via peduncles
* superior-, middle-, inferior
53
16.1 Cerebellum - Histology
→ 3 main layers
1. **Stratum moleculare**
* outermost layer
* underlies pia mater
* climbing fibers from inferior olivary ncl.
2. **Stratum ganglionare******
* purkinje cells!
* connective layer between molecular- and granule cell layer
3. **Stratum granulosum**
* ****innermost layer
* overlies cerebellar white matter
54
16.2 Cerebellum - Connections
→ cerebellum is connected to other structures via **peduncles**
* 6 in total, 3 on either side
* collections of nerve fibers
1. superior cerebellar peduncle
* carries information **to** midbrain
2. middle cerebellar peduncle
* carries information **from** cortex
3. inferior cerebellar peduncle
* receives **proprioception**
55
16.3 Cerebellum - Movements
→ cerebellum receives proprioception via inf. peduncle
Functions in movement regulation:
1. maintenance of posture and balance
* in flucculonodular lobe + vermis
2. maintenance of muscle tone
* in anterior lobe
3. coordination of voluntary motor activity
* in posterior lobe
56
17. Hypothalamus
* part of diencephalon
* controlls
* emotion (part of limbic system)
* autonomic functions
* hormone production
* sits under thalamus (hence the name)
* above brainstem
57
17.1 Hypothalamus - Nuclei
1. **Lateral hypothalamic area**
* lateral preoptic
* lateral hypothalamic
2. **Medial hypothalamic area**
* medial preoptic
* paraventricular
* supraoptic
* ant. + post. hypothalamic
* suprachiasmatic
* dorso- + ventromedial
* arcuate
* mammillary body
58
17.2 Hypothalamus - Connections
* highly interconnected with other parts of the central nervous system:
* brainstem
* solitary tract
* ventrolateral medulla
* limbic system
* amygdala
* autonomous NS
* mostly nerve fibres run bidirectional
59
18. Thalamus
* large, oval mass
* relay and process sensory information
* contains closely-packed nuclei
* can be divided into:
1. relay nuclei
2. association nuclei
3. non-specific nuclei
60
18.1 Thalamus - Nuclei
1. **Anterior nucleus**
* connects to limbic system
2. **Medial nuclei**
* Mediodorsal nucleus
* Intralaminar nuclei
3. **Lateral nuclei**
* lateral dorsal- + posterior nucleus
* ventral nuclei
* lateral- + medial geniculate body
4. **Reticular nucleus**
* surrounds thalamus
61
18.2 Thalamus - Connections
* connected to the **hippocampus** via mammillo-thalamic tract
* passes mammilary body and fornix
* connected to **cerebral cortex** via the thalamo•cortical radiations
* receives sensory information via **spinothalamic tract**
* lateral spinothalamic tract
* transmits pain + temperature
* anterior spinothalamic tract
* transmits crude touch + pressure.
62
19. Basal ganglia - Anatomy
* group of nuclei in diencephalon working together:
1. **Caudate nucleus**
2. **Lentiform nucleus**
3. **Putamen**
* GLOBUS PALLIDUS
* internal part
* external part
4. **Amygdala**
63
19.1 Basal ganglia - Functions
* voluntary motor control
* learning behaviours/habits
* eye movements
* emotional functions
64
20. Gyri and sulci of neocortical lobes
* neocortex is divided into **lobes** and **gyri** by **sulci**!
* Lobes:
* frontal-
* parietal-
* occipital-
* temporal-
* insula
* Sulci:
* Central-
* Lateral-
* Parieto-occipital-

65
20.1 Gyri and sulci of neocortical lobes - Frontal lobe, Parietal lobe
**Frontal lobe - ASSOCIATION, BEHAVIOUR**
* precentral gyrus
* sup. + mid. + inf. frontal gyrus
* olfactory sulcus
* straight gyrus
* orbital gyri
**Parietal lobe - SENSORY INF. LOCOMOTOR SYSTEM**
* postcentral lobe
* sup. + inf. parietal lobe
66
20.2 Gyri and sulci of neocortical lobes - Occipital lobe + Temporal lobe + Insula
**Occipital lobe - VISION**
* Cuneus
* Lingual gyrus
**Temporal lobe - HEARING**
* sup. + mid. + inf. temporal gyrus
* Fusiform gyri
* Parahippocampal gyrus
**Insula**
* deals with taste + pain
67
20.3 Gyri and sulci of neocortical lobes - Blood supply
* arises on inside of brain
* branches further as it proceeds in the gyri
* Derives from cerebral artery
* Ant. cerebral artery *(from internal carotid art.)*
* Mid. cerebral artery *(from internal carotid art.)*
* Post. cerebral artery *(from basilar art.)*
68
20.4 Brodmann areas
→ neocortex is divided into 47 Brodmann areas
→ by Brodmann (german anatomist) in 1909
Most important:
* 1 - 3: Somatosensory cortex
* 4: Primary motor cortex
* 6: Premotor cortex
* 17: Visual cortex
* 21,22,42: Wernicke's area *(speech)*
* 41: Auditory cortex
* 43: Taste cortex
* 44/45: Broca's area *(speech)*
69
21. White matter of the hemispheres - Commissural connections
→ connect identical cortical areas **between the 2 hemispheres!**
* Corpus callosum
* ant. + post. commissure
* intherthalamic adhesion
* hippocampal commissure
70
21.1 White matter of the hemispheres - Association fiber system
→ connect cortical areas in the **same hemispheres**
* Sup. + inf. longitudinal fascicle
* Frontal-/Temporal lobe ⇔ Occipital lobe
* Uncinate fascicle
* Frontal lobe ⇔ Temporal lobe
* Cerebral arcuate fascicle
* Temporal lobe ⇔ Parietal lobe
* Cingulum
71
21. 2 White matter of the hemispheres - Centrum semiovale
* on surface of cerebrum, has slightly oval shape
* found underneath grey matter
* contains:
* projection fibers
* association fibers
* cortical fibers
72
21.3 White matter of the hemispheres - Internal capsule
* area in the white matter seperating
* Caudate nucleus
* Thalamus
* Lentiform nucleus
* results in 3 divisions:
* ant. + post. limb
* genu
73
22. Limbic system - Anatomy
→ plays a role in feeling, feeding, fighting, fleeing and mating
→ expressed through hypothalamus via ANS
9 Parts:
1. Orbitofrontal cortex (smell)
2. Mediodorsal nucleus of thalamus (memory)
3. Anterior nucleus of thalamus
4. Septal area w/ septal nuclei
5. Limbic lobe
6. Hippocampal formation
7. Amygdala
8. Hypothalamus
9. Limbic midbrain nuclei
74
22.1 Circuit of Papez
→ circular pathway connecting major limbic structures
1. Hippocampus
2. Fornix
3. Mamillary body
4. Mamillo•thalamic tract
5. Ant. nucleus of thalamus
6. Cingulare gyrus
7. Parahippocampal gyrus
8. Entorhinal cortex
75
23. Motor Pathways - Corticospinal tract + Corticobulbar tracts - Anatomy
→ concerned with motor activities
* origin of cells: **vertebral cortex** or **brainstem**
**Corticospinal tract**
* connects cerebral cortex ⇒ spinal motor neurons
* controls movements of thorax, UL + LL
* come from BA 6 + 4
* fibers collect in *post. limb of internal capsule* (white matter of brain)
* divides into ant. + lat. corticospinal tract
**Corticobulbar tract**
* connects cerebral cortex ⇒ brainstem
* fibers collect in *geno of internal capsule*
76
24. Spinothalamic tract - Anterior
* → sensory system for **protopathic** sensation
* heat, cold, pain
* 2 Parts:
1. **Anterior spinothalamic tract**
* mediates pressure + crude touch
* receives info from Merkel discs
1. order neuron: dorsal root ganglion
2. order neuron: nucleus proprius
* decussation in ventral white commissure
3. order neuron: VPL nucleus of thalamus
* → postcentral gyrus (BA 3, 1, 2)
77
24.1 Spinothalamic tract - Lateral
**Lateral spino•thalamic tract**
* itch, pain, temperature + proprioception
* receives info from nerve endings + thermal receptors
1. order neuron: dorsal root ganglion
2. order neuron: dorsal horn nucleus (substantia gelatinosa)
* decussation in ventral white commissure
3. order neuron: ventral posterolateral nucleus in thalamus
* → postcentral gyrus (BA 3, 1, 2)
78
24.2 Neuroanatomy of pain
* Classification:
1. somatic pain
* superficial: skin
* deep: muscle, bone, joint
2. visceral pain
* from viscera
* **nociceptors** conduct the pain from periphery to brain via
* lateral spino•thalamic tract
* ventral trigemino•thalamic tract
79
25. Ascending tracts of the spinal cord's dorsal column
→ responsible for **epicritic** sensation
* touch, vibration, pressure
* joint position, movment
Classification:
* **Cuneate tract**
* ****epiritic sensation from trunk + UL
1. order neuron: _Dorsal root ganglion_
2. order neuron: _cuneate nucleus_ in medulla
* decussates at medial lemniscus
3. order neuron: _VPL_ (ventral posterolateral nucleus of thalamus)
* → postcentral gyrus (BA 3,1,2)
* **Gracile tract**
* ****epicritic sensation from LL
1. order neuron: _Dorsal root ganglion_
2. order neuron: _gracile nucleus_ in medulla
* decussates at medial lemniscus
3. order neuron: _VPL_ (ventral posterolateral nucleus of thalamus)
* → postcentral gyrus (BA 3,1,2)
80
25.1 Medial lemniscus
* large ascending bundle of heavily myelinated axons which decussate in the medulla of brain stem
* formed by: the crossings of internal arcuate fibers from axons of:
* nucleus gracilis
* nucleus cuneatus.
81
26. Brain stem nuclei - Oculomotor nerve (CN III)
**Nuclei**
1. **Somatomotor neuron**
* in _motor ncl. of Oculomotor nerve_
* to superior orbital fissure
2. **Parasympathetic neuron**
* ****in _Edinger-Westphal ncl._ in midbrain
* innervated papillary sphincter and ciliary m.
**Peripheral branches:**
* sup. + inf. branches of oculomotor nerve
82
26.1 Brain stem nuclei - Trochlear nerve (CN IV), Abducent nerve (CN VI)
Trochlear nerve, CN IV
* **somatomotor neuron**
* in _motor ncl. of trochlear nerve_
* to sup. orbital fissure
* innervation: sup. oblique m.
Abducent nerve, CN VI
* **somatomotor neuron**
* in _motor ncl. of abducent nerve_
* to sup. orbital fissure
* innervation: lat. rectus m.
83
27. Brain stem nuclei - Trigeminal nerve (CN V)
**Motor nucleus of CN V**
* through trigeminal ganglion (Gasser's) → branches
* innervates:
* masticatory m.
* tensor tympani m.
* tensor veli palatini m.
* mylohyoid m.
**Sensory nucleus of CN V**
1. ****Mesencephalic nucleus (proprioception)
2. Principle nucleus (epicritic)
3. Spinal nucleus (protopathic)
84
27.1 Brain stem nuclei - Trigeminal nerve - peripheral branches
**Ophtalmic nerve (V1)**
* lacrimal n.
* frontal n.
* nasociliary n.
**Maxillary nerve (V2)**
* infraorbital n.
* zygomatic n.
* sphenopalatine n.
* greater palatine n.
**Mandibular nerve (V3)**
* masticatory n.
* inf. alveolar n.
* lingual n. (→ submandibular ggl.)
85
28. Brain stem nuclei - Facial nerve
**Motor neuron:**
* in _motor nucleus of facial n._
* runs through facial canal!
**Sensory neuron:**
* in _solitary nucleus_
* spinal nucleus of CN V
* innervates ant. 2/3 of tongue
**Parasympathetic neuron:**
* in _sup. salivatory nucleus in pons_
86
28.1 Brain stem nuclei - Facial nerve - Peripheral branches
* greater petrosal n. (!) *foramen lacerum*
* pterygopalatine ggl. → lacrimal gland
* chorda tympani (!)
* submandibular ggl. → submandibular- + sublingual gland
* post. auricular n.
Motor innervation of facial expression muscles:
* temporal br.
* zygomatic br.
* buccal br.
* mandibular br.
* cervical br.
87
29. Brain stem nuclei - Glossopharyngeal nerve
Nuclei:
**Motor neuron:**
* in _nucleus ambiguus_
* innervates: stylopharyngeus m.
**Sensory neuron:**
* in _solitary nucleus_ + _spinal nucleus of CN V_
* innervates: tonsil, pharynx, middle ear, tongue
**Parasympathetic neuron:**
* in _inf. salivatory ncl._ in medulla
* innervates parotid gland
88
29.1 Brain stem nuclei - Glossopharyngeal nerve - Peripheral branches
* Tympanic n.
* lesser petrosal n.
* parotid gland
89
29.2 Brain stem nuclei - Vagus nerve (CN X)
**Motor neuron:**
* in _ncl. ambiguus_
* nodose ganglion → pharyngeal plexus
* innervates muscles of the neck region
**Sensory neuron:**
* in _solitary nucleus_ + _spinal nucleus of CN V_
* innervates: epiglottis
**Parasympathetic neuron:**
* in _dorsal vagal nucleus_
* innervates: respiratory organs, heart, GI tract (until left colic flexure)
90
29.3 Brain stem nuclei - Vagus nerve (CN X) - Peripheral branches
1. Meningeal br.
2. Auricular n.
* comes out at tympanomastoid fissure
3. Pharyngeal n.
* → Pharyngeal plexus → Salpingopharyngeus m + palatine muscles
4. Sup. laryngeal n.
5. Recurrent laryngeal n.
6. Cardiac br.
7. Pulmonary + Esophageal plexus
91
29.3 Brain stem nuclei - Accessory nerve (CN XI) + Hypoglossal nerve
**Accessory nerve - motor neuron**
* in _nucleus ambiguus + spinal accessory ncl._
* comes through jugular foramen
* innervates: trapezius m.
**Hypoglossal nerve - motor neuron**
* in _motor nucleus of hypoglossal n._
* → hypoglossal canal
* innervates. tongue- + hyoid muscles
Peripheral branch:
* **Ansa cervicalis**
* part of cervical plexus
* from C1-C3 + hypoglossal nerve
92
30. Anatomy of the eye, external fibrous coat
External fibrous coat
1. **Cornea**
* transparent
* avascular
* bulged like watch glass
2. **Sclera**
* "white part of the eye"
* vascular
93
30.1 Histology of the eye, external fibrous coat
Layers:
1. **Cornea**
1. Corneal epithelium
2. Bowman's epithelium
3. Descemet's membrane
4. Corneal endothelium
2. **Sclera**
1. ****Lamina fusca sclerae
2. Scleral stroma
3. Episcleral layer
94
30.2 Anatomy of the eye, vascular coat
* highly vascular coat
* Parts:
1. **Choroid**
2. **Ciliary body** - *for* *accomodation*
1. Orbiculus ciliaris
2. Corona ciliaris
3. **Iris**
1. Pupil
2. Pupillary margin
3. Cilliary margin
95
30.3 Anatomy of the eye, refractive media
1. Cornea
2. Lens of the exe
* biconvex shape
* Capsule
* ant. + post. surface
3. Aqueous humour
4. Vitreous body
* 98% water
96
30.4 Cornea reflex
*
97
X. Muscles of facial expression
→ innervation: facial nerve
* Corrugator supercilii
* Orbicularis oculi (orbital part, palpebral part)
* Procerus
* Nasalis
* Depressor septi
* Orbicularis oris
* Levator anguli oris
* Levator labii superioris
* Levator labii superioris alequae nasi
* Zygomaticus major
* Zygomaticus minor
* Depressor labii inferioris
* Depressor anguli oris
* Risorius
* Buccinator
* Mentalis
* Auricularis ant., sup., post.

98
X. Superficial muscles of the neck
1. **Sternocleidomastoid m.**
* manubrium + clavicle ⇔ mastoid process
* innervation: accessory nerve
2. **Trapezius m.**
* occipital bone + spinous processes ⇔ clavicle, acromion, scapular spine
* innervation: accessory nerve
* make up posterior muscular triangle
* + Supra- and infrahyoid!

99
X. Muscle triangles
* Submandibular (digastric) triangle
* Submental triangle
* Carotid triangle
* Omotrapezoid triangle
* Omoclavicular triangle

100
X. Deep muscles of the neck
→ innervation: cervical + brachial plexus
* Rectus capitis ant.
* longus capitis
* Scalenus
* ant. + med. + post.
101
X. Suboccipital muscles
* Rectus capitis posterior major + minor
* Obliquus capitis superior + inferior
→ border suboccipital triangle
* vertebral art.
* cervical plexus
102
X. Deep axial muscles
→ innervation: cervical plexus
* Splenius capitis + cervicis
* Longissumus capitis + cervicis
* Semispinalis capitis
103
X. Muscles of mastication
→ innervation: mandibular branch of trigeminal n.
* Masseter: elevates mandible
* Temporalis: elevate and retract mandible
* Lateral pterygoid: pulls neck of mandible forward
* Medial pterygoid: elevates mandible


