Nerves 1-3 Flashcards
What are the dendrites on a nerve cell?
Where the nerve cell receives information
What is the name given to the body of a nerve cell?
Soma
What are the 4 different types of glial cell?
Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia and appendimal cells
What is the function of astrocytes?
Maintains chemical concentrations and gradients Removes waste Repair Important contribution in the BLOOD BRAIN BARRIER
What are the glial cells in the PNS?
Satellite cells and schwann cells
What do satellite cells surround?
They surround the sensory and autonomic ganglia
What is the function of satellite cells?
They regulate the microenvironment of the ganglia in the peripheral nervous system
Which glial cells are responsible for providing the myelin sheath around the axons?
Oligodendrocytes and schwann cells
What is the function of microglial cells?
Immune role, Ingest cells and pathogens
What is the function of appendimal glial cells?
Filters blood to make CSF
What portion of the nervous system is responsible for gut activity?
The enteric system
The cortex contains grooves, what is the name given to a groove that surrounds a gyrus?
A sulcus
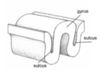
What is the cortex?
The outer layer of the cerebrum consisting of folded grey matter
What is the cerebellum responsible for?
Coordinates and regulates muscular activity
What is the function of the cerebrum?
It is associated with higher brain power such as thought and action
What is the name given to the 4 lobes of the cerebrum?
Occipital, frontal, temporal and parietal

What does the brain stem contain?
Midbrain, pons and the medulla oblongata
What does the diencephalon contain?
It is the posterior part of the brain and it contains the epithalamus, thalamus and the hypothalamus
Which part of a nerve cell triggers the action potential?
Axon hillock
Where can you find interneurones?
In the CNS
What is deplarization?
When the cell membrane potential becomes more positively charged
Why is a cell normally electronegative?
Because of a higher portion of positive ions outside the cell
What causes the cell to hyperpolarise?
The movement of potassium ions out of the cell via potassium channels
Give examples of graded potentials
Generator potentials, post synaptic potentials, end plate potentials end plate potentials


