Neoplasia 3 Flashcards
How much do environmental factors contribute to cancer risk?
85 %
What are the 5 leading behavioural factors that increase risk of cancer?
- high BMI
- low fruit and veg intake
- lack of physical activity
- alcohol use
- tobacco use
What are the 3 main categories of extrinsic carcinogens
- chemicals
- radiation
- infection
What 3 lessons do malignant neoplasms caused by 2-napthylamine teach use
1) there is a long delay between carcinogen exposure and neoplasm onset
2) risk of cancer depends on total carcinogen dosage
3) there is sometimes organ specificity for particular carcinogens
Explain how to Ames test works
- A strain of salmonella that requires histadine to grow is mixed with rat liver extract
- possible mutagen added to sample and spread on media with minimal histadine
- strain with no possible mutagen added as a control plate
- if the substance is mutagenic, will see a high number of revertants that grow. Shows it has caused a mutation

What are pro-carcinogens?
Chemicals that only become carcinogens by CYP450 enzyme conversion in the liver
What are complete carcinogens?
Carcinogens that acts as both initiators AND promotors
Why is rat liver extract required in the Ames test?
To convert any possible pro-carcinogens to carcinogens
How can radiation directly damage DNA?
- alter bases
- induce single/ double stranded breaks
How can radiation cause indirect DNA damage?
By crashing into H20 to produce FREE RADICALS
What is the most important type of radiation and why?
UV exposure as we’re exposed to it daily
What are the 2 main types of ionising radiation we are exposed to?
- radon gas
- medical tests (X-Ray/CT)
How does HPV cause cervical cancer?
It expresses proteins E6 and E7
- E6 inhibits p53
- E7 inhibits Rb protein
How do Hep B and C cause cancer?
Indirect carcinogens that cause chronic liver injury and regeneration
How is HIV involved in cancer?
Lowers host immunity allowing other potentially carcinogenic infections to occur
How does Heliobacter pylori increase risk for gastric cancer?
Causes chronic gastric inflammation, increasing risk of carcinoma
How do parasitic flukes lead to bladder carcinoma?
Cause inflammation of bile ducts and bladder mucosa
Explain Knudson’s two hit hypothesis
2 mutations are required in the same cell for cancer to occur
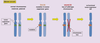
Explain the difference between the number of mutations required for tumour suppressor genes and proto oncogene to cause cancer
Tumour suppressor gene - both alleles need a mutation
Proto oncogene- only 1 allele needs to be mutated
Explain how mutations in RAS can cause neoplasia?
Normal RAS encodes a G protein that causes the cell to move past the restriction point when activated
In mutation - RAS the protein will always be active so is constantly driving cell proliferation past the restriction point
In what proportion of malignant neoplasms is the RAS gene mutated?
1/3
How does RB gene mutation cause neoplasia?
Normal Rb gene acts as a inhibitor of the cell cycle by acting on the restriction point
Both Rb alleles need mutations to allow cells to pass through the restriction point.
What are caretaker genes?
Genes that prevent the accumulation of DNA damage by repairing defects
Explain how BRCA1 and BRCA2 is associated with familial breast cancer
Normal BRCA1 and BRCA2 repair DNA double strand breaks
Mutations mean repair isn’t fixed which drives proliferation



