Muscles of the eyelids and adjacent face Flashcards
(51 cards)
What are 4 key muscles of facial expression around the eye and eyelids?
- Orbicularis oculi
- Levator palpebrae superioris
- Corrugator supercilii
- Occipitofrontalis
What is the function of orbicularis oculi in relation to the eye?
lid closure
What is the function of levator palpebrae superioris in relation to the eye?
it raises the eyelid
What is the overall shape of the orbicularis oculi muscle?
broad, flat sheet of skeletal muscle with orbital, palpebral and lacrimal portions
What are the 3 portions of the orbicularis oculi split into?
- orbital
- palpebral
- lacrimal
What is the orientation of muscle fibres in orbicularis oculi and what does this reflect?
circular orientation - sphincter-like function of muscle
From where does the orbital portion of the orbicularis oculi arise?
from the medial palpebral ligament and adjacent orbital margin
What is the orientation of fibres in the orbital portion of orbicularis oculi?
the fibres run circumferentially in an elliptical fashion around and beyond the orbital margin
most pass arounf the lateral orbital margin without interruption, but some (depressor supercilii) are inserted into the skin and connective tissue of the eyebrow
What are the depressor supercilii?
some fibres of the orbital portion of the orbicularis muscle, which are inserted into the skin and connective tissue of the eyebrow
Where is the insertion of the depressor supercilli of the orbicularis oculi (orbital portion)?
skin and connective tissue of the eyebrow
What is the palpebral portion of the orbicularis oculi muscle?
extremely thin muscle that originates from the medial palpebral ligament
Where does the palpebral portion of the orbicularis oculi muscle arise from?
medial palpebral ligament
What is the arrangement of muscle fibres in the palpebral portion of the orbicularis oculi?
fibres pass laterally within the eyelid anterior to the orbital septum and tarsal plate, and interlace to form the lateral palpebral raphe
Where is the lacrimal portion of the orbicularis oculi located?
passes deep to the medial palpebral ligament, is attached to posterior lacrimal crest (behind lacrimal sac) as two muscle slips (upper and lower)
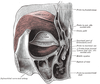
where are the muscle fibre from the lacrimal part of orbicularis oculi inserted?
laterally into the tarsi close to the lacrimal canaliculi
What is the function of the lacrimal portion of orbicularis oculi?
help draw the eyelids and lacrimal papillae medially and in addition dilate the lacrimal sac during blinking
helps suck tears into lacrimal punctum from lacus lacrimalis
Identify the orabital and palpebral portions of orbicularis oculi on the image.

What is the nerve supply of orbicularis oculi?
temporal and zygomatic branches of facial nerve, CNVII
What is the action of the orbital portion of orbicularis oculi?
acts like purse string due to elliptical form and medial attachments: draws skin of forehead, temple, check and orbital margin towards the medial angle of the orbit, firmly closing the lids (e.g. in very bright light)
What is the action of the palpebral portion of orbicularis oculi?
can act under both voulntary and involuntary control to close the eyelids during normal blinking (and sleeping)
Why is the blink reflex important?
essential to integrity of ocular tear film and function of the cornea
What is the corrugator supercilii and where is it located?

small pyramidal muscle at medial aspect of eyebrow, beneath occipitofrontalis and orbicularis oculi
What is the action of the corrugator supercilii?
draws the eyebrow downwards and medially (frowning), producing vertical skin furrows on the forehead
What does the corrugator supercilii protect the eyes from?
assists in protecting eyes in bright light





