MSK Flashcards
The human body consists of 4 main tissue types:
◦Epithelial Tissue
◦Connective Tissue
◦Muscle Tissue
◦Nerve Tissue
General Functions of the epithelium:
◦Protection
◦Absorption
◦Secretion
◦Excretion
Where can you find epithelium?
- Covers us (skin)
- Lines body cavities (e.g. abdominal cavity)
- Lines hollow organs (e.g. small intestine)
Always has a free surface & is attached to connective tissue layer by basement membrane
What is the Integumentary System?
skin + associated organs (nails, hair, glands, etc.)
What are the functions of the skin?
◦Protective covering
◦Maintaining body temp
◦Prevents water loss
◦Houses sensory receptors
◦Synthesis of various chemicals (Vit. D)
◦Waste excretion
What are the componenets of the lymphatic system?
- lymph nodes
- lymph vessels
- right lymphatic duct
- thoracic duct
- lymphoid organs
(knowledge of lymph drainage important in cancer management)
What are the components of the CNS?
- Brain
- Spinal cord
What are the components of the PNS?
•Cranial nerves
•12 pairs [CN I - XII]
•Spinal nerves
- 31 pairs represent segments
- 8C, 12T, 5L, 5S, 1Co
•Ganglia
- dorsal root ganglia
- sympathetic ganglia
- cranial nerve ganglia
function of the skeletal system?
- Framework for body
- Protection
- Mineral Storage (Ca, Phosphorous)
- forms blood cells in bone marrow
List the different bone shapes.
Long bones (typically cylindrical, e.g. humerus, femur)
Short bones: cuboidal, w/ length & width almost equal ex:carpals, tarsals
Flat bones: plate-like, broad surface, e.g. scapula, some skull bones
Irregular bones: variety of strange shapes, vertebrae, many facial bones (sphenoid, ethmoid, etc.)
Sesamoid bones: small, round bones usually imbedded w/in a tendon (patella). Only bone that is defined by its location
Name the two types of bony tissue that make up bone
- compact (aka cortical bone or cortex)
- cancellous bone (aka spongy or trabecular bone)
You can use either term, but know ALL of them.
Where are the two types of bone found?
Compact (cortical or cortex): outside of bone
Cancellous (spongy or trabecular): inner portion, concentrated at the ends

Define the diaphysis. What is contained within it?
- main shaft of cortical bone; a hollow cylinder
- the space inside is the medullary cavity or marrow cavity, and is filled w/ yellow marrow

Define the epiphysis and what it contains.
- The enlarged ends of the bone; mostly spongy bone.
- Spaces between the trabeculae are filled w/ red marrow.
(Attachment site of ligaments and tendons)

Define Articular Cartilage
The parts of the epiphysis that form the joint surfaces are covered with hyaline cartilage.


Define Periosteum & Function:
- A tough membrane of dense, irregular, fibrous CT that covers the entire bone except at joint surfaces.
- Anchors ligaments and tendons to the bone. Involved in bone formation & repair

Define Endosteum and function.
- A thin CT membrane that lines the medullary cavity
- Functions in bone growth & remodeling

What are the 2 classifications of joints?
- Structural = Joints are often classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together at the articulation.
- Functional = Joints can also be classified according to their movement potential.
These often overlap.
Define Fibrous Joints
◦Bones are held together very tightly by dense, fibrous CT

Define Cartilaginous Joints
◦Bones held together by hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage

Define Synovial Joints
◦Complex, fluid-filled joint structure
Most mobile

Which joints are classified based on structure?
Fibrous
Cartilaginous
Synovial
(there is some overlap between structual and functional)

Which joints are classified by function?
- synarthrosis: immoveable
- amphiarthrosis: slight movement (no articular cavity)
- diarthrosis (freely moveable)
Define Syndesmosis. Functional classification?
- Bones bound together by fibrous CT that forms an interosseous ligament
- Amphiarthrotic
e.g. distal tibia-fibula, sacroiliac joint
(NOT to be confused w/synovial which is a structural classification or synarthrosis, which is a functional classification)

Name three fibrous joints.
suture
syndesmosis
gomphosis (only teeth)
What is the name of this joint and what are the structural and functional classifications?

- Gomphosis
- fibrous
- synarthrotic
Name two cartilaginous joints (structural classification) and their functional classification.
symphysis: amphiarthrotic (connected to pad of fibrocartilage)
synchondrosis: synarthrotic (typically temporary)

Define Synovial joints.
Articular cartilage component, with joint capsule (multiple layers of CT), synovial fluid.
(do not confuse with syndesmosis which is a type of fibrous joint or synarthrosis which is a functional classification)

Which joints are classified by their shape?
Ball and Socket: Condylar, ellipsoid, and spheriod types
Condyloid: (Gliding or Plane)
Hinge (Ginglymus)
Pivot
Saddle (Sellar)
Explain the anatomical organization of skeletal muscle.
Muscles are made up of fasciculi which are made up of fibers. Each is bundled up and covered in its respective CT (endomysium, perimysium, epimysium).

List the muscle shapes
Parallel: good ROM, weak contraction
pennate: less ROM, strong contraction

Define origin and insertion.
- Origin is the anchor
- Insertion moves the structure closer to the body.
These change depending on the movement. Ex: push-up vs. bicep curl. The Origin and Insertion of the bicep muscle change for each exercise.

Define the different types of muscle contraction.
Isotonic: no change in foce, change in length
Isometric: change in force, not length
Concentric: muscle shortens
Eccentric: muscle lengthens
(eccentric is important and missed during strength training –>injury)

Explain the different muscle roles.
Limit movement (active & passive insufficiency)
stabilize (dynamic stabilization as opposed to static which is ligaments)
synergists: help when injured or need extra force production
What is the function of fascia in muscle?
- It extends beyond the muscle fibers, forming tendon for the muscle.
- provides route for nerves and blood vessels to access the muscle.
Define active insufficiency in regard to limited muscle movement.
A muscle is not capable of actively contracting to its full ROM at the joint that it crosses
(This is mainly in muscles that cross two joints. ex: hamstring contraction with flexed kee)
Define passive insufficiency in regard to limited muscle movement.
When a non-contracting muscle is stretched so far that it has trouble activating and something is preventing it from stretching any further.
Of the acting muscle cannot contract any further due to the limitation of the stretched antagonist.
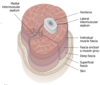
What are the key characteristics of superficial fascia?
- Loose CT & adipose tissue
- Varying thickness
- Contains superficial nerves and vessel

What are the key characteristics of deep fascia?
◦Dense CT
◦Contains no adipose tissue
◦“investing layer”, intermuscular septa
◦Fascial planes