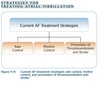
Module 5 - Atrial Fibrillation Treatment Landscape Flashcards
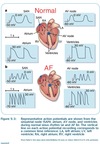
Normal VS AF Action Potentials
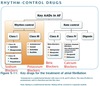
AADs designed to treat AF act by one of two primary mechanisms:
- Suppressing the initiating mechanism
- Altering a reentrant circuit
Some drugs may suppress the initiator but promote reentry.
What is APD?
Action Potential Duration
The extent of sodium channel block depends on:
- Heart rate and membrane potential
- Drug-specific physicochemical characteristics that determine the time required to recover from a previous depolarization
- pH
When sodium channels are blocked, greater membrane depolarization is needed to bring sodium channels from the rest state to the open state.
ACTION POTENTIAL PROLONGATION
Another mechanism by which AADs affect the heart is by changing the duration of the action potential. Action potential prolongation is often caused by block or inhibition of cardiac potas- sium channels, which also results in a reduction of normal automaticity.

Adverse Effects of Beta-blockade include:
- Fatigue
- Bronchospasm • Hypotension
- Impotence
- Depression
- Aggravation of heart failure
- Worsening of symptoms due to peripheral vascular disease
- Masking of the symptoms of hypoglycemia in diabetic patients
A decrease in current or other functional modifications occurs because _______________ drugs bind to specific sites on the ion channel proteins.
a. Ion channel–blocking*
_________________ are thought to be as effective as agents with predominant sodium channel–blocking properties in both atrial and ventricular arrhythmias.
c. Amiodarone and sotalol*
With most drugs, the action potential is prolonged by block- ing potassium currents. It can also be caused by enhanced ______________.
c. Inward sodium current*
Antiarrhythmic therapy is also approved by the FDA to _____________.
Reduce ventricular rate in atrial flutter or AF*
_________________ can increase the energy needed to fibrillate the heart, in acutely ischemic tissue.
Beta-blockers*
T/F: The class IA drug quinidine is rarely used today because of increased mortality rates observed in AF patients.
True
What were the main outcomes (1 or more) of the Flecainide Multicentre Atrial Fibrillation study?
- Both treatment groups experienced high discontinuation rates.*
- Both flecainide and quinidine were equally effective in preventing paroxysmal AF.*
Adverse effects related to propafenone usage include which one or more of the following?
- Proarrhythmia*
- Bradycardia*
The RAFT and ERAFT studies showed which (1 or more) of the following?
- Higher propafenone doses result in longer times to AF recurrence.*
- There was a dose-dependent increase in the occurrence of adverse events.*
What is the main indication for class IC drugs? (1 answer)
Paroxysmal AF and atrial flutter*
Match the antiarrhythmic drug with its drug class
Amiodarone
Propafenone
Quinidine
Dofetilide
Amiodarone – class III
Propafenone – class IC
Quinidine – class IA
Dofetilide – class III
The following agents are primarily used for rate control in AF. (Assign them to the correct class. )
Verapamil
Carvedilol
Bisoprolol
Diltiazem
Verapamil – calcium channel blocker Metoprolol – beta-blocker
Carvedilol – beta-blocker
Bisoprolol – beta-blocker
Diltiazem – calcium channel blocker
The indications for beta-blockers vary by country are generally approved by the FDA in which of the following (1 or more)?
a. Hypertension*
b. CHF*
c. LV dysfunction following MI*
d. MI*
e. Angina pectoris*
There have been 3 generations of beta-blockers. Assign the generation to the correct description.
First generation
Second generation
Third generation
First generation – Nonselective
Second generation – Beta1-selective (cardioselective)
Third generation – Nonselective and exhibit other properties
Which of the following best describes what the METAFER study showed?
Metoprolol reduced the risk of AF relapse after cardioversion in persistent AF patients.*
A retrospective analysis of the US Carvedilol Heart Failure Trials Program showed which of the following?
Carvedilol improved ejection fraction in CHF patients with AF.*
Which of the following is correct?
- Verapamil and diltiazem are approved by the FDA for rate control in AF patients.
- Only verapamil is approved by the FDA for rate control in AF patients and diltiazem is not used in this indication.
- Only verapamil is approved by the FDA for rate control in AF patients, but both are used in this indication.
- Only verapamil is approved by the FDA for rate control in AF patients, but both are used in this indication.
Digoxin falls into which one of the Vaughan Williams AAD classes?
Digoxin does not fit into one specific class.*