Module 2 - Cloud Infra Flashcards
(102 cards)
What are the 4 areas of Cloud Infrastructure?
- Foundation
- Core Services
- Scaling and Automation
- Container and Services
What is under Cloud Infrastructure - Foundation?
- Intro to GCP
- VPC Networking
- VMs
What falls under Infrastructure - Core Services?
- Cloud IAM
- Data Storage Services
- Resource Management
- Resource Monitoring
What falls under Cloud Infra - Scaling and Automation?
- Interconnected Networks
- Load Balancing
- Autoscaling
- Infra automation with Cloud API
- Infra Automation with Deployment Manager
- Managed Services
What comes under Cloud Infrastructure - Container and Srvices?
- Application Infrastructure Services
- Application Development Services
- Containers
Is there usually more than one solution fo a task or application in GCP?
YES
What are 2 common tools allow you to interact with GCP?
- Cloud Console which is a web based, GUI that you access through console.cloud.google.com
- Google Cloud SDK which is a command-line interface that can be installed locally or accessed through Cloud Shell.
What is the difference between Cloud Console and Cloud Shell?
Cloud shell is a command line tool, Cloud Console is a GUI
How would you define GCP’s networking?
GCP uses software defined network that is built on a global fiber infrastructure that makes GCP one of the largest and fastest.
How should one think about resources in GCP?
Thinking resources as services as opposed to hardware - will help with options available and their behavior
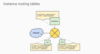
What are VPCs objects?
- Projects
- Networks
- Default, auto mode, custom
- Subnetworks
- Regions
- Zones
- IP Addresses
- Internal, external, range
- VMs
- Routes
- Firewall rules
What can you do with a VPC?
With Google Cloud Platform VPC, you can provision your GCP resources, connect them to each other and isolate them from one another in a virtual private cloud
How would you describe a VPC?
Essentially, VPC is a comprehensive set of Google managed networking objects
What are different modes of networks in VPC?
Default
Auto
Custom
What do sub-networks help accomplish?
Sub-networks let you divide and segregate your resources.
What is the key organizer of the infrastructure resources?
Project
What is a key role played by the project?
A project associates objects and services with Billing
How many networks(VPCs) can a project have?
Five
How would you describe a VPC?
A VPC network is somply a construct of all of the individial IP addresses, or services that are within that network
What are some features of a network?
- No IP address range
- Is global and spans all available regions
- Contains sub-networks
- Can be of type default, auto or custom
What is one feature of auto network?
Auto networks can be promoted to custom, but once custom they stay custom.
How do things get isolated using networks(VPC)

How do sub-networks cross zones?
- Subnetworks can extend across zones in the same region
- One VM and an alternate VM can be on the same subnet but in different zones
- A single firewall rule can apply to both VMs even though they are in different zones

What are subnetworks mostly designed for?
Subnetworks are for managing resources.
- Networks have no IP range, so subnetworks don’t need to fit into an address hierarchy
- Instead, subnetworks can be used to groop and manage resources.
- They can represent departments, business dunctions or systems