Module 1 Flashcards
(20 cards)
Pricing the derivative by forming a replicating portfolio
To form a replicating we use the underlying stock and a risk free bond.
Strategy:
- invest Δ no. of shares in stock and B dollars in a risk-free bond at time 0
- reinvest all dividends of the stock by buying additional shares. Gives Δe𝛿h shares at t=h
- the replicating portfolio at t=h is worth Δe𝛿hSh + Berh
Calculating Cu and Cd
Cu = Δe𝛿hS0u + Berh
Cd = Δe𝛿hS0d + Berh
Calculating Δ for the replicating portfolio
Note: Δ can be thought of as the sensitivity of the option to a change in the stock price. It will be positive for a call and negative for a put.
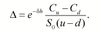
Calculating B for the replicating portfolio

Calculating the price of the replicating portfolio at time 0,
C<span>0</span>
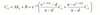
Arbitrage a mispriced option
- Option overpriced: The price of the option is greater than that of the replicating portfolio, ΔS0 + B. To arbitrage, we sell the option and buy the replicating portfolio.
- For a call option: We sell the call, buy Δ shares and borrow $B
- For a put option: We sell the put, sell Δ shares and invest $B
- Option is underpriced: The price of the option is less than that of the replicating portfolio, ΔS0 + B. To arbitrage, we buy the option and sell the replicating portfolio.
- For a call option: We buy the call, sell Δ shares and invest $B
- For a put option: We buy the put, buy Δ shares and borrow $B
REMEMBER: Buy low, sell high
Calculating the risk-neutral probability,
p*
p*: the risk-neutral probability of an increase in the stock price. Used in the risk neutral world. Is not the true probability that the stock price will go up.
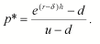
Risk-neutral pricing formula based on a one-period binomial tree
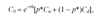
The expectation in the risk-neutral world,
E*
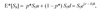
Volatility, σ
The volatility of a stock, σ, is the standard deviation of the stock return
Estimating u and d using a forward tree
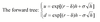
Estimating u and d using a Cox-Ross-Rubenstein Binomial Tree
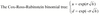
Estimating u and d using a Lognormal/Jarrow-Rudd Binomial Tree

Calculating Δ and B for an option on a currency
Where rf is the foreign risk-free rate and xo is the exchange rate at t = 0

Calculating u and d if the annualized volatility of the exchange rate is given (for a option on a currency)
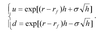
The put-call parity for options on currencies
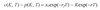
Calculating Δ and B for the replicating portfolio for futures contracts
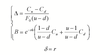
The put-call parity for futures options
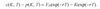
Calculating p* if the annualized volatility of the exchange rate if given (for options on currencies)
p*
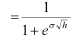
Calculating u and d if a volatility is given (for futures contracts)



