Mock Exam Flashcards
Which of these lab tests may indicate bleeding or blood loss? (choose all correct)
Platelet count
Hemoglobin
Hematocrit
WBC count
Hemoglobin
Hematocrit
Acquiring an infectious agent through the hospital ventilation system is what kind of transmission?
Direct Contact
In-direct Contact
Droplet
Airborne
Airborne
What is the minimum amount of iodinated contrast that may induce an allergic reaction?
>1 ml
50
10 ml
1% of the patient’s total blood volume
>1 ml
Which of the following are clinical signs of anaphylaxis? (Choose all correct)
Vasoconstriction
Hypertension
Airway edema
Mucus secretions
Airway edema
Mucus secretions
Which of these procedures is also called clean technique? Medical Asepsis
Sterile Technique
Medical Asepsis
What is the iodinated contrast agents with these chemical properties.
Ionic, 300 mgl/mL, Osmolality = 1550
Hypaque
What is the iodinated contrast agents with these chemical properties.
Non-ionic, 320 mgI/mL, Osmolality=290
Visipaque
What is the iodinated contrast agents with these chemical properties.
Non-ionic, 350 mgI/mL, Osmolality=884
Omnipaque
Pneumonia requires what kind of isolation precaution? Standard Precaution
Contact Isolation
Droplet Isolation
Airborne Isolation
Droplet Isolation
Disrupting the body’s electrolyte balance is one risk associated with using which of the following contrast types for IV infusion? Ionic
Hypertonic
Non-ionic
High osmolar
Ionic
What type of isolation precaution is most relevant when infectious agents can be suspended in air for long periods of time over long distances?
Standard Precaution
Droplet Isolation
Contact Isolation
Airborne Isolation
Airborne Isolation
Which of the following represents a normal pulse rate for a healthy adult? (choose all correct)
50
75
65
105
75
65
Which of these medication would be valuable to a patient experiencing hypotension or bradycardia during a medication reaction? (Choose all correct)
Benedryl
Atropine
Epinephrine
Versed
Atropine
Epinephrine
Which of these procedures include hand washing, routine equipment cleaning, and proper personal hygiene?
Medical Asepsis
Sterile Technique
Medical Asepsis
Which of the following represents the amount red blood cells in whole blood? (choose all correct)
WBC count
Hemoglobin
Hematocrit
Platelet count
Hematocrit
Which of these lab tests may help to indicate if a patient has anemia? (choose all correct)
Hemoglobin
Hematocrit
PTT
Platelet count
Hemoglobin
Hematocrit
Which of these compensatory mechanisms are associated with CHF? (Choose all correct)
Decreased heart rate
Increased blood volume
Increased cardiac filling pressure
Decrease myocardial mass
Increased blood volume
Increased cardiac filling pressure
Definition of Duration of Action
The time during which the drug is in the body and elicits a therapeutic response
Definition of First Pass Effect
The metabolization of drugs by the liver prior to systemic circulation.
Definition of Onset of Action
The point at which a drug reaches its intended effect
Definition of Maximum Peak
This is when a drug reaches its highest potential and begins to subside
Which of the following indicate a mild contrast reaction? (Choose all correct)
Hives
Itching
Tachycardia
Hypotension
Feeling of warmth
Hives
Itching
What drug classification is Valium
Sedative
What drug classification is Tetracycline
Antibiotic
What drug classification is Coumadin
Anticoagulant
What drug classification is Aspirin
Analgesic
What drug classification is Morphine
Narcotic
What drug classification is Atenolol
beta blocker
Which of the following signs/symptoms are often associated with CVA? (Choose all correct)
Acute Dysphasia
Permanent brain infarction
Acute confusion
Unilateral weakness
All of the above
Defibrillation is used for which of the following conditions? Ventricular Tachycardia
TIA/CVA
Respiratory Arrest
Asystole
Ventricular Tachycardia
Asystole
Deoxygenated blood is emptied into which chamber of the heart?
Right Ventricle
Left Atrium
Left Ventricle
Right Atrium
Right Atrium
The thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage, and the epiglottis are all structures of the:
Trachea
Larynx
Oropharynx
Esophagus
Larynx
Which of the following marks the beginning of the distal stomach?
Fundus
Cardia
Pylorus
Antrum
Antrum
The appendix extends from what portion of the colon? Transverse colon
Descending colon
Ascending colon
Cecum
Cecum
Which of the following is the most superior aspect of the stomach?
Pylorus
Cardia
Antrum
Fundus
Fundus
The parotid glands are oriented posterior to what aspect of the mandible?
Body
Ramus
Mentum
None of the above
Ramus
Which of the following vessels circulate blood from the Circle of Willis into the brain?
Cerebral arteries
Communicating arteries
Internal carotids
Basilar artery
Cerebral arteries
The crus, covering the aorta, are an extension of what structure?
Diaphragm
Lungs
IVC
Peritoneum
Diaphragm
Most of the Stomach is located within which quadrant of the abdomen?
RLQ
LUQ
RUQ
LLQ
LUQ
Which aspect of the sternum is visualized on an axial image displaying the articulation of the clavicles with the sternum? Manubrium
Any of the above
Body
Xiphoid process
Manubrium
Which of the following describes the most anterior structure of the female pelvis?
Uterus
Bladder
Rectum
Prostate
Bladder
What term describes the last segment of the GI tract? Descending colon
Sigmoid colon
Anus
Rectum
Rectum
Which of the following structures marks the transition of the larynx into the trachea?
Epiglottis
Cricoid cartilage
Thyroid cartilage
Soft palate
Cricoid cartilage
The optic nerve and the ophthalmic artery pass through the optic canals in which cranial bone?
Ethmoid
Sphenoid
Occipital
Parietal
Sphenoid
Which of the following is used a as landmark dividing the abdominal and pelvic cavities?
Lateral masses
Sacral Foramina
Sacral promontory
Sacral hiatus
Sacral promontory
The SB receives arterial blood from what branch of the aorta? IMA
All of the above
Celiac Trunk
SMA
SMA
Which of the following organs helps to produce antibodies? Spleen
Kidneys
Pancreas
Liver
Spleen
T/F: The fluid-filled outer ring of the intervertebral discs is termed the nucleus pulpous.
False
Which of the following defines the anterior border of the pelvis? Iliac bones
Abdominal muscles
Sacral Prominens
Quadratus lumborum
Abdominal muscles
The foramen ovale provides passage for which of the following? Maxillary Nerve
Optic Nerve
Middle meningeal artery
Mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve
Mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve
Which of the following is least likely to be identified in the pelvis?
Duodenum
Jejunum
Cecum
Ileum
Duodenum
Which of the following is also known as the ala?
Sacral promontory
Sacral hiatus
Lateral masses
Sacral Foramina
Lateral masses
The middle and inner ear are formed by which portion of the temporal bones?
Tympanic
Mastoid
Squamous
Petrous
Petrous
The most anterior bone of the pelvic bone is the:
Ischium
Pubis
Ilium
Pubis
The confluence of the common iliac veins forms which of the following?
Internal iliac arteries
Common femoral arteries
Common iliac arteries
IVC
IVC
The perpendicular plate articulates with which bone to form the boney nasal septum?
Sphenoid
Vomer
Occipital
Ethmoid
Vomer
Which of the following is the chief venous pathway of the trunk and lower body?
IVC Azygos vein
Left brachiocephalic vein
Right brachiocephalic vein
IVC
T/F: All vertebrae of the cervical spine share the same characteristic features.
False
Which vertebral ligament covers the dorsal surface of the vertebral bodies of the spine?
Anterior longitudinal ligament
Posterior longitudinal ligament
Ligamentum flavum
Interspinous ligament
Posterior longitudinal ligament
The spine is nearest what surface of the body?
Anterior
Dorsal
Ventral
Rostral
Dorsal
Which of the following is the most posterior structure in the male pelvis?
Uterus
Rectum
Prostate
Iliac
muscles
Rectum
The lobes of the cerebellum are connected medially by which of the following structures?
Insula
Midbrain
Corpus Callosum
Vermis
Vermis
Which of the following is accessed and injected with contrast for a myelogram?
None of the above
Central canal
Subarachnoid
space Subdural space
Subarachnoid space
Which of the following may be found below and behind the urinary bladder?
Rectum
Prostate
Iliac muscles
Uterus
Prostate
Which of the following correctly describes the appearance of gastric cancer in sectional imaging? (Choose all correct)
focal wall thickening with mucosal irregularity
wall thickening with loss of normal rugal folding pattern
focal mass/polyp with or without ulceration
gas-filled ulceration
All of the above
Which of the following describes the appearance of uterine fibroids in sectional imaging? (Choose all correct)
Solid
Calcified
Cystic
Variable size
Solid
Calcified
Variable size
Which of the following are common causes of renal stones? (Choose all correct)
recurrent yeast infections
low fluid intake
metabolic abnormalities
dehydration
low fluid intake metabolic abnormalities dehydration
Pulmonary Fibrosis is a severe form of which of these conditions?
Tuberculosis
COPD
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
Interstitial Lung Disease
Interstitial Lung Disease
Pancreatic cancers primarily affect what aspect of the pancreas?
Uncinate process
Body
Tail
Head
Head
Which of these conditions is imaged as progressive scarring of the lung tissue?
Pneumothorax
Interstitial Lung Disease
Hemothorax
COPD
Interstitial Lung Disease
T/F: Imaging studies alone always allow for differentiation between benign and malignant neoplasms.
False
Which of these injuries can sometime be associated with more serious injuries to the ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses?
Blow-out fractures
Zygomaticomaxillary complex fractures
Nasal fractures
LeFort fractures
Nasal fractures
Which of these lesions grows from the Schwann cell’s of the 8th cranial nerve?
Pituitary adenoma
Medulloblastoma
Astrocytoma
Meningiomas
Acoustic Neuromas
Acoustic Neuromas
What is the most common primary brain tumor?
Astrocytoma
Medulloblastoma
Meningiomas
Acoustic Neuroma
Pituitary adenoma
Astrocytoma
Which of these fractures may result in injury to the maxillary sinus? (choose all correct)
Blow-out fractures
Mandibular fracture
Nasal fractures
Zygomaticomaxillary complex fractures
Blow-out fractures
Zygomaticomaxillary complex fractures
Which of the following statements are true concerning imaging of the spleen? (Choose all correct)
Malignant splenic lesions may appear as single or multi-focal
Patchy contrast enhancement during arterial imaging indicates splenic infarct or laceration
During the venous phase of contrast enhancement the spleen should appear homogenous
Malignant splenic lesions may appear as single or multi-focal
During the venous phase of contrast enhancement the spleen should appear homogenous
Which of the following is a kind of organ infarct? (Choose all correct)
MI
TIA/CVA
Malignancy
Ascites
MI
TIA/CVA
Which of the following statements are true concerning imaging of Crohn’s disease? (Choose all correct)
May affect the mesentery
Imaged primarily as large bowel thickening
Shows chronic inflammation without remission
May be associate with abscess
May affect the mesentery
May be associate with abscess
Which of these conditions is a result of infection in the brain? (Choose all correct)
Meningitis
Encephalitis
Brain abscess
ICB
Meningitis
Encephalitis
Brain abscess
Which of these fractures is comparable to a green stick fracture in long bones?
Ping-pong fracture
Diastatic fracture
Basilar skull fracture
Depressed skull fracture
Ping-pong fracture
Which of these conditions are most likely to be associated with changes in cardiac function? (choose all correct)
MI
Pericardial effusion
Myxoma
CHF
MI
Pericardial effusion
CHF
T/F: Hemangiomas appear only in the liver.
False
Which of these are common causes of liver cirrhosis? (Choose all correct)
Alcoholism
Pancreatitis
Hepatitis
Renal failure
Alcoholism
Hepatitis
Which of these conditions is most likely to metastasize?
Uterine leiomyoma
Wilm’s tumor
BPH
Urolithiasis
Wilm’s tumor
Which of the following are imaging indications of organ laceration? (Choose all correct)
Contrast extravasation in or around the organ
Hematoma in the area of the organ
Limited or absence of contrast perfusion through the organ
Atypical contrast perfusion through the organ
All of the above
Which of the following describes the early-stage appearance of endometrial cancer?
necrosis
loculations
hemorrhage
wall thickening
wall thickening
Which of these terms specifically describes a cancerous tumor? Neoplasm
Benign
Abscess
Malignant
Malignant
T/F: Careful timing of post contrast pituitary scans is important because eventually the pituitary gland enhances itself, as well as a microadenoma, if present.
True
T/F: Contrast is routinely used in the cervical spine for patients with a diagnosis of MS.
True
T/F: Toe movement will not affect MR foot image quality.
False
T/F: Spinal schwannomas arise from nerves within the spinal canal.
True
T/F: MR knee arthrography can be useful to identify recurrent tears in the knee following meniscectomy.
True
Which of the following describes a typical injury pattern observed after a posterior glenohumeral dislocation?
Hill-Sachs lesion
Adhesive capulitis
Paralabral joint cyst
Trough lesion
Trough lesion
T/F: There are five ventricles in the brain.
False
CNR between pathology and other structures can best be demonstrated by which of the following?
Suppression of normal tissues via sequences that null signal from certain tissues (i.e. FLAIR, STIR)
Non-contrast studies
Lower field strength magnets
Utilizing T1 sequences
Suppression of normal tissues via sequences that null signal from certain tissues (i.e. FLAIR, STIR)
Which of the following is considered the most common cause of PAD?
Shiny skin on legs
No pulse or weak pulse in the legs or feet
Leg numbness or weakness
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis
T/F: Chemical shift artifact occurs when anatomy that lies within the boundaries of the receiver coil exists outside the FOV.
False
Spatial resolution may be increased by selecting which of the following?
Thin Slices
Coarse matrices
Thick slices
A large FOV
Thin Slices
T/F: False aneurysms are usually the result of knee trauma, surgery/intervention or infection.
True
T/F: Closed and open mouth views are performed for TMJs.
True
T/F: The choice of coil for any examination is one of the most important factors that determines the resultant SNR of the image.
True
T/F: Scar tissue enhances immediately after the injection, but disc material does not.
True
To minimize aliasing in axial slices of the thoracic spine, one would use:
Breath holds
Saturation pulses
Chemical presaturation
Oversampling
Oversampling
T/F: If a patient has had a hysterectomy, axials and coronals would be straight and not angled with any anatomy.
True
T/F: Inversion recovery sequences begin with a 180 degree pulse.
True
Which of the following is thought to be due to chronic entrapment of the nerve by the intermetatarsal ligament?
PVNS
Morton’s Neuroma
Synovial sarcoma
Calcaneal fatigue fracture
Morton’s Neuroma
Axial slices through the head/brain are prescribed from:
Right to Left
Superior to Inferior
Left to Right
Inferior to Superior
Inferior to Superior
Which of the following sequences is known for its sensitivity to magnetic susceptibility?
Perfusion
FLAIR
GRE
SE
GRE
Axial slices through the thoracic spine are angled parallel to: spinous processes
spinal cord
disc spaces
Z joints
disc spaces
To minimize magnetic susceptibility artifact from a hip prosthesis, a technologist should:
Use GRE sequences
Increase the SNR
Use as small a FOV as possible
Use SE or FSE sequences with a broad receive bandwidth
Use SE or FSE sequences with a broad receive bandwidth
A hamartoma is best described as:
a ganglion that often appears as a bump on the hand or wrist.
a benign tumor composed of mature hyaline cartilage.
a bone cyst.
a benign tumor-like malformation made up of an abnormal mixture of cells and tissues found in the body.
a benign tumor-like malformation made up of an abnormal mixture of cells and tissues found in the body.
Which of the following is the most common mass in the popliteal fossa?
Popliteal aneurysm
Ganglion cyst
Synovial sarcoma
Baker cyst
Baker cyst
Which of the following best describes the appearance of acute stroke on an axial DWI?
Bright
Dark
Bright
Scan time can be decreased by using which of the following?
A long TR
The most NEX allowable
A short TR
A fine matrix
A short TR
T/F: All halos are MRI safe.
False
Positioning for a female pelvis MR exam would include centering the horizontal alignment light to pass:
through a point midway between the symphysis pubis and the iliac crest
through the level of the umbilicus
through the symphysis pubis
through the iliac crest
through a point midway between the symphysis pubis and the iliac crest
T/F: Intra-voxel dephasing occurs as a result of the phase difference between stationary and flowing nuclei in the same voxel causing dephasing and signal loss.
True
On T1 weighted images of the spine, the CSF appears:
Isointense to the spinal cord
Hypointense to the spinal cord
Hyperintense to the spinal cord
None of the above
Hypointense to the spinal cord
T/F: Positioning the feet close together and at the same level is the best method to reduce wrap for ankle imaging.
False
T/F: Patients are positioned supine head first for run-off exams.
False
T/F: If a technologist increases the matrix on a sequence (assuming the FOV remains the same), the spatial resolution will increase, but the SNR will decrease.
True
The optimal plane to use when evaluating patients for cruciate ligament tears of the knee is the:
Sagital
Axial and coronal
Coronal
Axial
Sagital
The imaging sequences best used to visualize bruises or contusions within the bone are:
Spin echo
Gradient echo
Fast spin echo
Short Tau Inversion Recovery (STIR)
Short Tau Inversion Recovery (STIR)
T/F: A bursa is a fat filled sac that allows smooth motion between two uneven surfaces.
False
T/F: The emotional well being of a patient is just as important as their physical condition.
True
T/F: Increasing the TR results in increased SNR and increased scan time.
True
Which of the following sequences fills all of K space in one repetition by using very long echo trains?
EPI
STIR
SE
GRE
EPI
T/F: The most common site of aneurysms in the thoracic aorta is the ascending aorta.
True
T/F: FOV boundaries for sagital thoracic spine images include from T2 to L1.
False
A patient presents with pain in the neck and shoulder, numbness and tingling in the fingers, and a weak grip. Which of the following is most likely the cause?
Thoracic outlet syndrome
Schwannoma
Herniated thoracic disc
Whiplash
Thoracic outlet syndrome
Which of the following separates the right atrium and right ventricle?
Semilunar valve
Septum
Mitral valve
Tricuspid valve
Tricuspid valve
T/F: The optimal imaging window for evaluation of breast cancer is immediately following the start of the menstrual cycle.
False
T/F: A Chiari Malformation can be see on a cervical spine image.
True
T/F: Ideal ankle positioning includes dorisflexion of the foot.
True
T/F: The main source of artifact in the brain is from flow motion of the popliteal artery.
False
T/F: There are four ventricles in the brain.
True
Generally, 3D TOF-MRA acquisitions are optimal for high resolution, for the evaluation of:
Velocity-induced phase shifts
Slower flowing arterial vasculature and vessels with a large area of coverage (carotids and/or femoral arteries)
Phase and magnitude images
Smaller vessels with high velocity blood flow (intracranial vessels associated with the Circle of Willis, COW)
Smaller vessels with high velocity blood flow (intracranial vessels associated with the Circle of Willis, COW)
After gadolinium administration, it is recommended that which images are acquired?
Multiple T2 weighted images
Multiple T1 weighted images
One T1 weighted image
One T2 weighted image
Multiple T1 weighted images
T/F: Intrinsic parameters are those that cannot be changed because they are inherent to the body’s tissues.
True
In which of the following sequences is all the transverse magnetization rewound at the end of each TR period?
Coherent gradient echo
Incoherent gradient echo
EPI
Coherent gradient echo
T/F: The purpose of magnetic field shimming is to reduce the size of the fringe field.
False
What signal intensity is an area of abnormality likely to have on an ADC map?
Hypointense
Hyperintense
Isointense
Hypointense
Determine which of the following parameters would result in the most entry slice phenomenon (i.e. entry slice phenomenon would increase compared to the other options).
Slice 10 out of 20, 3000 TR, 1.2 mm slice thickness
Slice 10 out of 20, 400 TR, .7 mm slice thickness
Slice 1 of 20, 3000 TR, .7 mm slice thickness
Slice 1 out of 20, 400 TR, 1.2 mm slice thickness
Slice 1 of 20, 3000 TR, .7 mm slice thickness
What is T2 decay? (Select all that apply)
Spin-spin relaxation that results in decay or loss of coherent transverse magnetization.
Caused by the nuclei giving up their energy to the surrounding environment.
Spin lattice relaxation
The time it takes 63% of longitudianl magnetization to recover in the tissue.
Spin-spin relaxation that results in decay or loss of coherent transverse magnetization.
Which gradient performs slice selection for sagital slices?
Any combination of gradients
Z gradient
Y gradient
X gradient
X gradient
Gadolinium element is ________ and gadolinium chelate contrast media is ________.
Ferromagnetic/paramagnetic
Paramagnetic/paramagnetic
Ferromagnetic/ferromagnetic
Paramagnetic/ferromagnetic
Ferromagnetic/paramagnetic
What kind of information is contributed by data collected in the central lines of K space?
Contrast
Resolution
Signal
* weighting
Contrast
Signal
What is Vortex Flow?
Flow that is initially laminar, but then passes through a structure or stenosis in the vessel. Flow in the center of the Lumen has high velocity, but near the walls the flow spirals.
What is Laminar Flow?
Flow that occurs at different but consistent verlocities across a vessel. The flow at the center of the lumen of the vessel is faster than at the vessel wall where resistance slows down the flow. Velocity difference across the vessel is constant.
What is Spiral Flow?
The direction of the flow is spiral.
What is Turbulent Flow?
Flow at differnet velocities that fluctuates randomly. The velocity difference across the vessel changes erratically.
Once a ferromagnetic material is exposed to an externally applied magnetic field, it becomes magnetized (a permanent magnet). Permanent magnets are said to be:
Bipolar
Tripolar
Polar
Dipoles
Bipolar
T/F: Flow affects image quality.
True
Ohm’s law states:
B = H (1+x)
1 T = 10 kG
V = I (R)
B = k (l)
V = I (R)
Stationary nuclei always receive both excitation and rephasing pulses, but flowing nuclei present in the slice for the excitation may have exited the slice before rephasing. This is called ______________.
Entry Slice Phenomenon
Intra-Voxel Dephasing
Time of Flight Phenomenon
Turbulent Flow Effects
Time of Flight Phenomenon
What are the advantages of propeller K Space filling?
Rapid imaging, increased SNR and CNR, reduced motion artifact.
Better detail
Bright signal
Low SNR but high resolution
Rapid imaging, increased SNR and CNR, reduced motion artifact.
What is another name for a truncation artifact in a sagital cervical spine?
Faraday
Truncation
Gibbs
Gyromagnetic Artifact
Gibbs
What does the slope of the frequency encoding gradient determine?
The size of the anatomy covered along the frequency encoding axis
The 180 degree rephasing pulse
The size of the phase matrix
The FOV
The size of the anatomy covered along the frequency encoding axis
The FOV
What term is used to describe the net displacement of diffusion spins across a tissue?
fMRI
SWI
MRS
ADC
ADC
Which part of K space do shallow phase gradients fill?
Outer lines of K space, both positive and negative
Central lines of K space, both positive and negative
Central lines of K space, positive only
Outer lines of K space, positive only
Central lines of K space, both positive and negative
When is the slice select gradient switched on during a spin echo pulse sequence?
During the excitation pulse only
It is always on during the scan
During the 90 and 180 degree pulses
During the rephasing pulse only
During the 90 and 180 degree pulses
Which of the following are methods of reducing phase ghosting? (Choose all that apply)
Decrease the TE
Use “no phase wrap” softwareUse pre-saturation pulses
Swap phase and frequency
Carefully explain the procedure to the patient
Using respiratory compensation techniques
Use pre-saturation pulses
Swap phase and frequency
Carefully explain the procedure to the patient
Using respiratory compensation techniques
Which sequence would be used to best visualize metastatic lesions in the bone?
Fat saturation techniques with contrast
Non-contrast imaging
FLAIR with contrast
T2 weighted sequences
Fat saturation techniques with contrast
In spin echo sequences using a pre-saturation pulse, what would persistent bright signal within the vessel indicate?
Slow Flowing Blood
Blood Clot
Vascular Occlusion
Fast Flowing Blood
Slow Flowing Blood
Blood Clot
Vascular Occlusion
Which of the following best describe spin-lattice relaxation? (Choose all that apply)
T1 Recovery
T2 Decay
Nuclei give up energy to the surrounding environment, resulting in longitudinal recovery.
Time it takes 88% of the longitudinal magnetization to recover in tissue.
T1 Recovery
Nuclei give up energy to the surrounding environment, resulting in longitudinal recovery.
Which Fast Inversion Recovery sequence(s) do we often use?
SSFP
FLAIR
STIR
Incoherent Gradient Echo
FLAIR
STIR
Which of the following does NOT reduce flow motion artifact?
GMN
ECG gating
SAT
Subtraction
Subtraction
Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical process that is used to convert MR signal from a FID into a spectrum. FT occurs in the:
RF coil
Image processor
Array processor
Gradient amplifier
Array processor
T/F: The gyromagnetic ratio expresses the relationship between the angular momentum and the magnetic moment of each MR active nucleus.
True
In which direction does phase ghosting occur? (Choose all applicable)
Frequency Axis
Phase Axis
Slice Select Axis
Anterior to Posterior
Phase Axis
Which gradient locates signal along the LONG axis of the anatomy?
Slice select gradient
Isocenter gradient
Phase encoding gradient
Frequency encoding gradient
Frequency encoding gradient
What is the waiting period before each R wave called?
Available Imaging Time
Trigger Delay
R to R Interval
Trigger Window
Trigger Window
What MUST be done prior to anyone entering the scan room? (Select the BEST answer)
Pat the patient down for metal objects.
A screening sheet must be filled out and in the patient’s chart.
The patient must be scanned with the metal detector.
The completed screening sheet must be signed by a level II staff member and the patient must be scanned with the metal detector, prior to admittance to the MRI scan room.
The completed screening sheet must be signed by a level II staff member and the patient must be scanned with the metal detector, prior to admittance to the MRI scan room.
Which of the following best describes a T1 weighted image?
Bright fat
Bright water
Dark Fat
Dark Water
Bright fat
Dark Water
Select the three components of the magnetic field from those listed below.
Precessional Frequency Field
Faraday’s Field
Radiofrequency Fields
Time Varying Magnetic Fields
Static Magnetic Field
Radiofrequency Fields
Time Varying Magnetic Fields
Static Magnetic Field
Which of the following best describes Moire artifact?
Anatomy from outside the FOV are wrapped into the image.
Different chemical environments of fat and water produce a dark edge at the interface between fat and water.
Black and white banding artifact on the edge of the FOV
Fat and water are out of phase and their signals cancel each other out.
Black and white banding artifact on the edge of the FOV
The homogeneity of a magnetic field is expressed in units of:
G (gauss)
ppm (parts per million)
T (Tesla)
MHz (megaHertz)
ppm (parts per million)
What happens to the alignment of hydrogen protons when placed in an external magnetic field? (Check all that apply)
The magnetic moments of the nuclei align with or against the main magnetic field.
Nothing until an RF pulse is applied.
More nuclei oppose the main magnetic field than line up with the main magnetic field.
Slightly more nuclei line up with the main magnetic field than against it.
The magnetic moments of the nuclei align with or against the main magnetic field.
Slightly more nuclei line up with the main magnetic field than against it.
What is the approximate T1 relaxation time of CSF at 1T?
150 ms
500 ms
2000 ms
3000 ms
2000 ms
The magnetic field strength in superconducting magnets is maintained with cryogens at a temperature of:
450°C
70°F (+/- 2°F)
4 K
269°F
4 K
The vascular signal, produced on PC-MRA, relies on:
MOTA
Velocity-induced phase shifts
Flow related enhancement
PC
Velocity-induced phase shifts
Select all of the following that were discussed as possible MR contrast agents in the text.
Gadolinium
Blueberry juice
Mango juice
Dilute barium solutions
All of the above
In which direction does aliasing occur? (Choose all that apply)
Phase Axis
Frequency Axis
Slice Select Axis
Anterior to Posterior
Phase Axis
Frequency Axis
What type of echoes are sampled during SS-FSE?
Spin echoes
Gradient echoes
Incoherent Gradient echoes
Spin echoes
When using MRA to evaluate extracranial vascular flow, such as that within common carotid arteries, a recommended technique is:
3D phase contrast MRA
2D time of flight MRA
3D time of flight MRA
All of the above
2D time of flight MRA
What is Double IR prep used to accomplish?
Flips the NMV back to zero
Imaging large patients
Used to null blood for cardiac imaging
FSE sequences
Used to null blood for cardiac imaging
Which of the following are methods of reducing phase ghosting? (Choose all that apply)
Use pre-saturation pulses
Using respiratory compensation techniques
Decrease the TE
Swap phase and frequency
Use “no phase wrap” software
Carefully explain the procedure to the patient
Use pre-saturation pulses
Using respiratory compensation techniques
Swap phase and frequency
Swap phase and frequency
T/F: For resonance of hydrogen to occur, RF at EXACTLY the Larmor frequency of hydrogen must be applied.
True
What is the approximate T1 relaxation time of fat at 1T?
2000 ms
3000 ms
200 ms
500 ms
200 ms
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Mandibular condyle
Occipital Bone
Maxillary Sinus
EAM
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
E
Not Labeled

Lamina
Intervertebral Disc
Psoas Muscle
Intervertebral Foramina
Erector Spinae Muscle
Transverse Foramina
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Hamate
Triquetrum
Capitate
Ulna
Radius
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
E
Not Labeled

Superior Sagital Sinus
Tentorium
Parietal Lobe
Lateral Ventricle
Cerebellum
3rd Ventricle
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
E
Not Labeled

Trochlea
Radial Shaft
Humeral Shaft
Olecranon Processes
Corocoid Process
Ulnar Shaft
Identify the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Large Bowel
Common Iliac Artery
Small Bowel
Ilium
Appendix
What pathology is visible in this image?
Ovarian tumor
Ovarian cyst
Uterine fibroid
Prostate cancer
Uterine cancer

Uterine cancer
What pathology is seen in this image?
Spinal Metastasis
Spinal Meningioma
Spinal Ependymoma
Tethered cord

Spinal Meningioma
What pathology is seen in this image?
CAD
Pericardial Effusion
CHF
Myxoma

CHF
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Medulloblastom
Arachnoid Cyst
SDH
AVM
MS

AVM
What pathology is visible in the image below?
Arachnoid Cyst
Hydrocephalus
MS
Medulloblastoma
AVM

MS
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Pneumothorax
Hemothorax
Tuberculosis
Interstitial Lung Disease

Pneumothorax
Hemothorax
What pathology is visible in this image?
Horseshoe kidney
Renal Stone
RCC
Wilm’s tumor
PKD

PKD
What pathology is visible in the following image?
Spinal Stenosis
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Subluxation
Compression Fracture

Ankylosing Spondylitis
What pathology is seen in this image?
Spinal Metastasis
Spinal Meningioma
Tethered cord
Spinal Ependymoma

Spinal Metastasis
What pathology is visible in this image?
Liver cancer
Hemangiomas
Cirrhosis
Liver laceration

Liver cancer
What pathology is visible in this image?
Crohn’s disease
Colitis
Appendicitis
SBO
Colon cancer

Colitis
What pathology is visible in this image?
Renal Stone
TCC
RCC
BPH
Prostate cancer

TCC
What pathology is seen in this image?
Spinal Meningioma
Tethered cord
Bulging disc
Spinal Ependymoma

Bulging disc
What pathology is seen in this image?
Pericardial Effusion
PE
CAD
Myxoma

Myxoma
What pathology is visible in this image?
Adrenal mass
Renal Stone
Kidney laceration
Wilm’s tumor
RCC

Kidney laceration
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Medulloblastoma
EDH
ICB
Ischemic stroke
SDH

SDH
What pathology is seen in this image?
Compression Fracture
Tethered Cord
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Spondylolisthesis

Spondylolisthesis
Which of the following is a normal diastolic blood pressure?
115
89
75
125
75
Which of the following describes a severe reaction to iodinated contrast?
Hives
Hypotension
Itching
Diaphoresis
Hypotension
Which of the following terms are synonymous? (Choose all correct)
Cerebral Infarct
Ischemic Stroke
Transient Ischemic Attack
Cerebrovascular Accident
Cerebral Infarct
Ischemic Stroke
Cerebrovascular Accident
Which of the following lab values directly relate to renal performance? (choose all correct)
Creatinine
GFR
Hematocrit
PTT
Creatinine
GFR
Which of these medications would be especially valuable if a patient is having a respiratory reaction to ICM? (Choose all correct)
Oxygen
Epinephrine
Albuterol
Atropine
Oxygen
Epinephrine
Albuterol
Which of these cardiac conditions can cause inadequate ventricular filling in the presence of a healthy myocardium?
Myocardial Infarction
Cardiogenic Shock
Cardiac Tamponade
Congestive Heart Failure
Cardiac Tamponade
Define Vasoconstrictors?
A drug causing contraction and narrowing of blood vessels.
Define Antiarrythmics
These drugs function to reduce or prevent arrhythmias
Define Thrombolytics
A clot dissolbing drug specifically used to treat patients with acute symptoms of MI or stroke
Define Vasodilators
A drug causing relaxation and opening of blood vessels
Which of the following can cause respiratory arrest? (Choose all correct)
Decreased respiratory drive
Respiratory muscle weakness
Airway obstruction
Trauma
Decreased respiratory drive
Respiratory muscle weakness
Airway obstruction
Trauma
Tuberculosis requires what kind of isolation precaution?
Droplet Isolation
Airborne Isolation
Contact Isolation
Standard Precaution
Airborne Isolation
Define Pharmacology
The study of drug reactions with living organisms
Define Pharmacokinetics
Relates to the drugs process of absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion by the body (what the body does to the drug)
Define Pharmacodynamics
The study of mechanisms by which drug dosages produce physiological or biochemical changes in the body (what the drug does to the body)
C-Diff requires what kind of isolation precaution?
Airborne Isolation
Droplet Isolation
Standard Precaution
Contact Isolation
Contact Isolation
The formula for calculating a patient’s GFR includes which of the following? (choose all correct)
Creatinine level
Gender
Weight
Ethnicity
Age
Creatinine level
Gender
Age
What is the most common MRI contrast agent?
Hexabrix
Gadolinium
Iron
Omnipaque
Gadolinium
Which these conditions typically occurs secondary to myocardial infarction?
Congestive Heart Failure
Cardiac Tamponade
Cardiogenic Shock
Transient Ischemic Attack
Cardiogenic Shock
What are the chemical properties of Hypaque
Ionic, 300mgl/mL, Osmolality=1550
What are the chemical properties of Visipaque
Non-ionic, 320 mgl/mL, Osmolality=290
What are the chemical properties of Omnipaque
Non-ionic, 350mgl/mL, Osmolality=884
Which of these medications would be useful to a patient with an anxiety disorder?
Epinephrine
Valium
Reglan
Zofran
Valium
Internal and external protuberances are processes of what cranial bone?
Parietal
Sphenoid
Ethmoid
Occipital
Occipital
Which vertebral ligament attaches between the lamina of adjoining vertebrae?
Ligamentum flavum
Interspinous ligament
Anterior longitudinal ligament
Posterior longitudinal ligament
Ligamentum flavum
Which of the following describes the large opening on the inferior aspect of the sacrum?
Sacral Foramina
Sacral promontory
Lateral masses
Sacral hiatus
Sacral hiatus
The Dorsal cavity is partitioned into what two cavities? (mark all correct)
Spinal
Abdominal
Mediastinal
Pelvis
Cranial
Spinal
Cranial
Which of the following muscle groups extend from the cervical vertebrae through the upper thoracic spine?
Erector spinae muscles
Splenius muscles
Transversospinal muscles
Psoas muscles
Splenius muscles
Which of the paranasal sinuses is present at birth?
Maxillary
Sphenoid
Ethmoid
Frontal
Maxillary
The appendix is located within which quadrant of the abdomen?
RUQ
LUQ
LLQ
RLQ
RLQ
The whitish opaque portion of the eye is termed the:
Conjunctiva
Cornea
Lens
Sclera
Sclera
The terminal end of the spinal cord is described by which of the following?
Sella Turcica
Cauda equina
Medulla oblongata
Conus medullaris
Conus medullaris
An abnormal forward curvature of the thoracic spine is termed:
Prognosis
Lordosis
Hypnosis
Kyphosis
Kyphosis
Which aspect of the brainstem is continuous with the spinal cord?
Medulla oblongata
Mid brain
Pons
None of the above
Medulla oblongata
What fissure separates the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe?
Longitudinal Fissure
Central Fissure
Lateral Fissure
Rolandic Fissure
Lateral Fissure
The external walls of the EAM are formed by which portion of the temporal bone?
Squamous
Tympanic
Petrous
Mastoid
Tympanic
Which of the following is a direct extension of the ventricular system of the brain?
None of the above
Epidural space
Central canal
Subdural space
Central canal
What structure marks the beginning of the lower respiratory system?
Oropharynx
Larynx
None of the above
Nasopharynx
Larynx
During menstruation the walls of the uterus may appear thicker or thinner usual?
Thinner
Thicker
Thicker
A process of the malar bone joins with which bone of the cranium to form the zygomatic arch?
Temporal
Sphenoid
Frontal
Parietal
Temporal
Which of the following is not a retroperitoneal structure?
Transverse colon
Kidneys
Ureters
IVC
Transverse colon
The mandibular condyle articulates with which of the following cranial bones?
Frontal
Occipital
Parietal
Tempora
Tempora
The large projection on the posterior surface of the scapula dividing it into upper and lower fossae is termed the:
Acromion process
Scapular spine
Coracoid process
Glenoid fossa
Scapular spine
The perpendicular plate of what bone forms the superior portion of the nasal septum?
Ethmoid
Palatine
Vomer
Sphenoid
Ethmoid
The sigmoid colon is located within which quadrant of the abdomen?
LLQ
RUQ
RLQ
LUQ
LLQ
Which of the following lacks a typical vertebral body?
C2
C6
C7
C1
C1
The urethra in males passes through which of these organs?
Uterus
Iliac muscles
Rectum
Prostate
Prostate
Arterial blood to the liver is provided by a branch of what artery?
SMA
IMA
Celiac Trunk
Celiac Trunk
The pituitary gland is attached by the infundibulum to what other feature of the diencephalon?
Epithalamus
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
Hypothalamus
The lungs are located within which body cavity?
Dorsal
All of the above
Mediastinum
Pleural
Pleural
Which of the following describes potential characteristics of adrenal lesions (Choose all correct)
cystic
benign
malignant
metastatic
All of the above
Which of these conditions appears as inflammation in the bowel?
Cancer
Colitis
Abscess
Ascites
Colitis
T/F: Hemangiomas appear only in the liver.
False
Which of these lesions are most often malignant? (choose all correct)
Acoustic Neuromas
Pituitary adenoma
Medulloblastoma
Meningiomas
Astrocytoma
Medulloblastoma
Astrocytoma
Which of these fractures follows the “ring rule”?
Zygomaticomaxillary complex fractures
Nasal fractures
Blow-out fractures
Mandibular fractures
Mandibular fractures
From where do renal stones originate?
VUJ
Ureters
Bladder
Collecting system
Collecting system
What is the most common lesion of the brain?
Benign brain neoplasm
Gliomas
Metastatic brain cancer
Primary brain cancer
Metastatic brain cancer
Which of these fractures are most likely to result in CSF leakage? (choose all correct)
Depressed skull fracture
Basilar skull fracture
Diastatic fracture
Ping-pong fracture
Basilar skull fracture
Diastatic fracture
Which of the following statement concerning liver cancer are true? (choose all correct)
Primary liver cancer will enhance during the arterial phase of imaging
Metastatic liver cancer can be both singular or multi-focal
Primary liver cancer is more common than secondary liver cancer
Metastatic liver cancer will enhance during the venous phase of imaging
Primary liver cancer will enhance during the arterial phase of imaging
Metastatic liver cancer can be both singular or multi-focal\
Metastatic liver cancer will enhance during the venous phase of imaging
Which of these conditions is most likely to show contrast extravasation? Choose multiple if applicable.
Ruptured Aneurysm
Simple aneurysm
Dissecting aneurysm
Ruptured Aneurysm
What aspect of the kidney can be affected by renal cell carcinoma (RCC)? (Choose all correct)
cortex
Gerota’s fascia
collecting system
medulla
cortex
collecting system
medulla
Which of these conditions causes a permanent loss of neurologic function? (choose one or both)
Hemorrhagic stroke
Ischemic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke
Ischemic stroke
Traumatic contusions in the brain are one form of which of the following conditions?
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
Epidural Hemorrhage (EDH)
Subdural Hemorrhage (SDH)
Intracranial bleed (ICB)
Intracranial bleed (ICB)
Which of the following tumors are malignant? (Choose all correct)
Spinal Metastasis
Spinal Ependymoma
Spinal Meningioma
Astrocytoma
Spinal Metastasis
Astrocytoma
Which of the following describe imaging characteristics of pancreatitis? (Choose all correct)
Pancreatic pseudocysts
Ascites
Reactive fluid
Pancreas inflammation
Pancreatic pseudocysts
Ascites
Reactive fluid
Pancreas inflammation
Which of these fractures is most likely to be comminuted?
Basilar skull fracture
Ping-pong fracture
Diastatic fracture
Depressed skull fracture
Depressed skull fracture
Which of the following best describe contrast enhancement of pancreatic tumors?
Absence of venous enhancement
Highly vascular
Delayed enhancement
No contrast enhancement
Delayed enhancement
Which of these are common complications associated with zygomaticomaxillary complex fractures? (Choose all correct)
“Floating face”
Blood in the maxillary sinus
Ocular injuries
Dural tearing
Blood in the maxillary sinus
Ocular injuries
T/F: Malignant lesions identified in the spleen are most likely lymphoma.
True
Which of these conditions might be viewed as surface and parenchymal nodularity in the liver?
Laceration
Primary liver cancer
Secondary liver cancer
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Which of the following are common causes of pneumonia? (choose all correct)
Fungal infections
Aspiration
Chemical inhalation
Chest trauma
All of the above
What term describes a cancer in one organ/tissue but originated from a different organ/tissue?
Malignant neoplasm
Benign neoplasm
Primary cancer
Metastatic neoplasm
Metastatic neoplasm
T/F: Leiomyomas are benign tumors that arise from overgrowth of smooth muscle and connective tissue in the bladder.
False
Most deep vein blood clots occur in the _______.
Lungs
IVC
Lower leg or thigh
Foot
Lower leg or thigh
T/F: SNR is dependent on the quality of the coil
True
The American Cancer Society recommends screening breast MRI in addition to annual mammograms in which of the following?
Patients with less than a 15% lifetime risk of breast cancer.
To evaluate implant integrity.
In patients with greater than 20% lifetime risk of breast cancer.
In all women over the age of 40.
In patients with greater than 20% lifetime risk of breast cancer.
A patient presents with pain in the neck and shoulder, numbness and tingling in the fingers, and a weak grip. Which of the following is most likely the cause?
Herniated thoracic disc
Whiplash
Schwannoma
Thoracic outlet syndrome
Thoracic outlet syndrome
Which of the following best defines spatial resolution?
The ability to distinguish two between two points as separate and distinct
The difference in the SNR between two adjacent areas
The ratio of the amplitude of signal received by the coil to the amplitude of the noise
The time required to complete the acquisition of data
The ability to distinguish two between two points as separate and distinct
Which of the following is a malignant bone tumor that affects children and young adults? the tumor may start anywhere in the body, usually in the long bones of the arms and legs, the pelvis, or the chest.
Ewing Sarcoma
Chordoma
Transitional Cell Carcinoma
Teratoma
Ewing Sarcoma
Enlargement of the left lobe of the liver is most likely a sign of which of the following diseases processes?
Hepatic mets
Renal failure
Cirrhosis
Ascites
Cirrhosis
A/an _________ can break loose and cause a pulmonary embolism.
DVT
Arterial stenosis
Atherosclerosis
Lymph node
DVT
Adhesive capsulitis is also known as:
Trough lesion
Carpal tunnel
Tennis elbow
Frozen shoulder
Frozen shoulder
On sagital T-Spine images that demonstrate cord compression, the vertebral level can be determined by (think about how you determine this in clinicals when scanning):
Using lead markers to mark T12 and T1 on large FOV images
Using the sternal notch as a landmark and counting down from T1
Using the xyphoid as a landmark and counting up from T12
Using a large FOV localizer and counting down from C2
Using a large FOV localizer and counting down from C2
T/F: MRI is the most sensitive detection method for calcaneal stress fracture.
True
T/F: A SLAP tear occurs where the biceps tendon anchors to the labrum.
True
The “candy cane” view is best described by which of the following:
Long axis view of the heart
Axial view of the thoracic aorta
Sagital/oblique view of the pulmonary arteries
Sagital/oblique view of the thoracic aorta
Sagital/oblique view of the thoracic aorta
Indications for MRV of the lower extremities includes all but which of the following?
Leg swelling
Recent twisted ankle
Evaluation for free-floating thrombus
Recent orthopedic surgery
Recent twisted ankle
Which of the following sequences would be most helpful in diagnosing MS?
Open and closed views
Thin slices through the optic chiasm
Sagital STIR
Sagital FLAIR
Sagital FLAIR
Which of the following anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx?
Sacral hiatus
Conus medularis
Filum terminale
Cauda equina
Filum terminale
The coil usually preferred to image the shoulder for the maximization of SNR is the:
Surface or local coil
Body coil
Small extremity coil
Phased array coil
Surface or local coil
A patient who presents with numbness of the first three digits and nighttime pain from the wrist to the forearm most likely has:
Carpal tunnel syndrome
De Quervain Tenosynovitis
Sarchoidosis
Hamartoma
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Which diagnosis is considered most likely in a patient who presents with pain, swelling, and reddening over the olecranon. The MR images show bone marrow and soft tissue edema.
Triceps tendon tear
Rheumatoid arthritis
Osteomyelitis
SLAP tear
Osteomyelitis
To minimize pulsatile flow motion artifacts, cardiac images are acquired by:
Performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation
None of the above
Taking the patient’s pulse, calculating the heart rate in beats per minute, then entering this data into the imaging system
Attaching ECG leads, monitoring the cardiac cycle and triggering the pulse sequence from each R wave
Attaching ECG leads, monitoring the cardiac cycle and triggering the pulse sequence from each R wave
T/F: A common artifact seen when scanning the cervical spine region is the result of swallowing motion.
True
T/F: Contrast is routinely used in MRI of the hand
False
Cancer that begins in the plasma cells in bone marrow is known as:
Glioma
Metastatic disease
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple Myeloma
Which of the following is another word for bulging of one or both eyes?
Pseudotumor
Proptosis
COW
Sarcoid
Proptosis
T/F: Motion artifact can be problematic in 2D TOF imaging.
True
Which of the following is not in the distal row of carpal bones?
Trapezium
Hamate
Lunate
Capitate
Lunate
Common sources of artifact for an orbital MR exam include all of the following except:
flow motion in the Circle of Willis
zipper artifact
using a small FOV- aliasing
eye movement
zipper artifact
In spine imaging, to rule out metastatic lesions of the spinal cord, contrast enhancement can be used with T1 weighted images because:
CSF is bright and cord is dark
Normal cord enhances and metastatic lesions do not
Metastatic lesions enhance and normal cord does not
Scar enhances and disk does not
Metastatic lesions enhance and normal cord does not
T/F: Patients may be positioned feet first supine for an MRI of the lumbar spine.
True
T/F: When positioning a patient’s legs for a lower extremity vascular study, the legs should be placed as far apart as possible.
False
Which of the following sequence(s)/technique(s) can be used to make vessels appear bright?
All of the above
Gradient Moment Rephasing
Contrast Enhancement
Gradient Echo Imaging
All of the above
What rule determines the direction of current flow through a coil, and the direction of the magnetic field that the current produces?
Whether you are using an open or closed configuration
Right hand thumb rule
MRI Fringe Field Rule
The size of the magnetic field
Right hand thumb rule
MRA techniques include all of the following EXCEPT:
CT-MRA
CE-MRA
PC-MRA
TOF-MRA
CT-MRA
T/F: Perfusion is measured using MRI by tagging the fat in arterial blood during image acquisition.
False
T/F: Even echo rephasing reduces intra-voxel dephasing.
True
What is the extrinsic parameter that controls the amount of diffusion seen in an image?
flip angle
b factor
TR
TE
b factor
T/F: TR controls T2 weighting.
False
Which of the following is used to trigger each pulse sequence when using ECG gating?
R wave
S wave
P wave
Q wave
R wave
Choose extrinsic contrast parameters from the list below.
Flip Angle
T1 Recovery Time
Flow
TR
Proton Density
TE
b Value
Flip Angle
TR
TE
b Value
T/F: The TE is twice the TAU.
True
Which of the following effects does TOF depend on?
TE
TR
Slice Thickness
Velocity of flow
TE
Slice Thickness
Velocity of flow
T/F: TOF phenomenon results in a dark vessel.
True
T/F: To reduce chemical shift artifact, ALWAYS use the widest receive bandwidth in keeping with good SNR and the smallest FOV possible.
True
Which of the following is a remedy for aliasing?
Decreasing the slice thickness
Using “no phase wrap” software
Decreasing the TE
Decreasing the size of the FOV
Using “no phase wrap” software
Choose all of the following that enhancement agents can be useful in detecting.
Tumors
Infarction
Inflammation
Infection
All of the above
Which cryogen is commonly used to super cool wires in MRI?
Liquid helium
Niobium
Hydrogen
Alnico
Liquid helium
What do T2 images typically best demonstrate?
Bony anatomy
Anatomy
Pathology
Fat
Pathology
Determine which of the following parameters would result in the most entry slice phenomenon (i.e. entry slice phenomenon would increase compared to the other options).
Slice 10 out of 20, 3000 TR, 1.2 mm slice thickness
Slice 1 of 20, 3000 TR, .7 mm slice thickness
Slice 10 out of 20, 400 TR, .7 mm slice thickness
Slice 1 out of 20, 400 TR, 1.2 mm slice thickness
Slice 1 of 20, 3000 TR, .7 mm slice thickness
Magnetic field strength can be expressed in units of Tesla (T) or gauss (G), where:
3.0 T = 0.3 G
1 T = 1 G
1 T = 10 000 G
1.5 T = 1500 G
1 T = 10 000 G
The signal from flowing blood within vessels in MRI and MRA relies on:
Fourth order motion
Second order motion
Third order motion
First order motion
First order motion
T/F: ECG gating is prospective.
True
What are the two results of resonance? (Choose from the list below)
The NMV moves into a repeating pattern of +/- 100 MHZ.
The magnetic moments of hydrogen nuclei move into phase with each other.
The NMV moves out of alignment and away from B0.
The magnetic momements of hydrogen nuclei move out of phase with each other.
The magnetic moments of hydrogen nuclei move into phase with each other.
The NMV moves out of alignment and away from B0.
T/F: Intra-voxel dephasing results in an increase in total signal amplitude from the voxel.
False
T/F: All gadolinium contrast agents have the same ‘relaxivity’.
False
How often must we sample frequencies, according to the Nyquist Theorem?
Once per cycle
Twice per cycle
Less than once per cycle
Three times per cycle
Twice per cycle
What are the guidelines for pregnant employees? (Choose all that apply)
Pregnant employees MUST transfer to x-ray once they’ve announced their pregnancy to the MRI department.
Pregnant employees may enter the scan room, but should leave before scanning begins.
Pregnant employees are exempt from scanning and may only do paperwork.
No changes to pregnant employees work environment in MRI. Everyone knows that MRI doesn’t use radiation.
Pregnant employees may enter the scan room, but should leave before scanning begins.
What is the chemical shift at 1.5 T?
220 Hz
2.2 Hz
220 KHz
22 Hz
220 Hz
T/F: Another term for time of flight is inflow effect.
False
The anatomy of white matter tracts can be mapped using strong multi-directional gradients in which of the following?
SWI
diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
continuous arterial spin labeling (CASL)
CBV
diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
T/F: In some circumstances, magnetic susceptibility artifact can be useful in diagnosis.
True
Passive magnetic shielding can be accomplished by lining the scan room walls with:
Shim plates
Lead
Copper
Steel
Steel
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
Not labeled

Frontal
Temporal Bone
Occipital Bone
External Occipital Protuberance
Label the anatomy in this image
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Right Coronary Artery
Left Main Coronary Artery
LAD
Circumflex Artery
Coronary Sinus
Label the anatomy in this image.
A
B
C
D
Subclavian Artery
You Answered
Not Labeled

Esophagus
Brachiocephalic Vein
Sternoclavicular Joint
Subclavian Artery
Pulmonary Artery
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Vertebral Body
Transverse Process
Articular Facets
Spinous Process
Intervertebral Foramina
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
E
Not labeled

Pariental Bone
Choroid Plexus
Longitudical Fisure
Lateral Ventrical
Parietal Lobe
Lateral Fissure
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
E
Not Labeled

Abductor Digiti Muscles
Pisiform
Thenar Muscle
Trapezium
Flexor Muscles
Ulna
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
E
Not Labeled

Extensor Digitorum Muscle
Fibula
Tibia
Flexor Hallicus Longus Muscle
Achilles Tendon
Posterior Tibialis Tendon
Identify the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Uterus
Bowel
Urinary bladder
Rectum
Ovary
What pathology is visible in the image below?
Chiari Malformation
ICB
SDH
Medulloblastoma
EDH

Chiari Malformation
Which of the following pathologies is visualized in this image? (choose all correct)
Linear skull fracture
Depressed skull fracture
Epidural hematoma
Basilar skull fracture
Ping-pong skull fracture

Ping-pong skull fracture
What pathology is visible in this image? (Choose all correct)
Ascites
Neoplasm
Abscess
Cyst

Ascites
Neoplasm
What pathology is visible in this image?
Colitis
Crohn’s disease
Appendicitis
SBO
Colon cancer

Crohn’s disease
What pathology is visible in this image? (choose multiple)
Crohn’s disease
Colitis
SBO
Appendicitis
Colon cancer

SBO
Colon cancer
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
SDH
EDH
Ischemic stroke
Abscess
Neoplasm

Ischemic stroke
What pathology is visible in this image?
Pancreatic Cancer
Cholelithiasis
Pancreatitis
GB Cancer
Liver cancer

Pancreatitis
What pathology is visualized in the following image?
Dental abscess
Mandible Fracture
Blow-out fracture
LeFort fracture
Zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture

Mandible Fracture
What pathology is visible in this image?
Liver cancer
Hemangiomas
Cirrhosis
Liver laceration

Liver laceration
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
SDH
Ischemic stroke
Astrocytoma
Abscess
Medulloblastoma

Medulloblastoma
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Pneumonia
Tuberculosis
Pneumothorax
COPD

COPD
What pathology is visible in this image?
Liver cancer
Splenic Laceration
Lymphoma
Gastric cancer

Lymphoma
What pathology is visible in this image?
Laceration
Neoplasm
Hematoma
Infarct

Infarct
Which of the following best describes the anatomy indicated by number twelve on the image shown below:
Teres major muscle
Spine of the scapula
Scapula
Acromion

Scapula
Which of these medications should be administered prior the CT exam if the patient has had a prior reaction to iodinated contrast?
Zofran
Solu-medrol
Glucagon
Atropine
Solu-medrol
Which of these precautions is most relevant when a patient carries an infectious agent that may be spread through talking, sneezing, or coughing?
Droplet Isolation
Contact Isolation
Standard Precaution
Airborne Isolation
Droplet Isolation
BLS skills include recognition of which of the following conditions? (Choose all correct)
TIA/CVA
FBAO
MI
Anaphylaxis
TIA/CVA
FBAO
MI
Define Teratogenic
Adverse affects of drug use to a fetus that causes abnormal development.
Define Carcinogenic
Drugs that are indicated as cancer producing.
Define Nephrotoxic
Drugs that adversely affect the kidneys or their functions.
Correctly order the sequence through which a drug is delivered into systemic circulation.
Absorption through the small bowel
Metabolism in the liver
Systemic circulation
Passage through the portal hepatic system
First
Third
Fourth
Second
Which of these medications would be especially valuable to a patient experiencing bronchospasms during a contrast reaction?
Albuterol
Atropine
Epinephrine
Lasix
Albuterol
Which of the following describes a negative contrast agent?
Paramagnetic particles
Barium Sulfate
Microbubbles
Visipaque
Microbubbles
Which of the follow is a transmission-based infection precaution? (Choose all correct)
Contact Isolation
Airborne Isolation
Droplet Isolation
Standard Precaution
Contact Isolation
Airborne Isolation
Droplet Isolation
Creatinine level can fluctuate with which of the following? (choose all correct)
Muscle Mass
Gender
Age
Hydration
Muscle Mass
Gender
Age
Hydration
Meningitis requires what kind of isolation precaution?
Standard Precaution
Droplet Isolation
Contact Isolation
Airborne Isolation
Droplet Isolation
Which of the following can cause respiratory arrest? (Choose all correct)
Decreased respiratory drive
Trauma
Respiratory muscle weakness
Airway obstruction
Decreased respiratory drive
Trauma
Respiratory muscle weakness
Airway obstruction
What term describes an atom or molecule that dissociates into ions when placed in water?
Ionic
Non-ionic
Cation
Monomer
Ionic
Which of these lab tests may help to indicate if a patient has anemia? (choose all correct)
Hematocrit
Platelet count
PTT
Hemoglobin
Hematocrit
Hemoglobin
Which these conditions typically occurs secondary to myocardial infarction?
Cardiac Tamponade
Cardiogenic Shock
Congestive Heart Failure
Transient Ischemic Attack
Cardiogenic Shock
Which of these procedures include hand washing, routine equipment cleaning, and proper personal hygiene?
Medical Asepsis
Sterile Technique
Medical Asepsis
Which vertebral ligament covers the dorsal surface of the vertebral bodies of the spine?
Anterior longitudinal ligament
Ligamentum flavum
Posterior longitudinal ligament
Interspinous ligament
Posterior longitudinal ligament
Which of these medications would help to increase blood pressure in the event of a hypotensive reaction? (Choose all correct)
Epinephrine
Atropine
Valium
Zofran
Epinephrine
Atropine
Which of the following are clinical signs of anaphylaxis? (Choose all correct)
Vasoconstriction
Airway edema
Hypertension
Mucus secretions
Airway edema
Mucus secretions
Which of the following should be disclosed for the sake of “informed consent”? (choose all correct)
The risks and benefits of a proposed treatment or procedure
Alternatives
The risks and benefits of not receiving or undergoing a treatment or procedure
The patient’s diagnosis, if known
The risks and benefits of a proposed treatment or procedure
Alternatives
The risks and benefits of not receiving or undergoing a treatment or procedure
The patient’s diagnosis, if known
Which of the following describes a required characteristic of IV injectable contrast media? (choose all correct)
Isotonic
Low-density barium
Water-soluble
Non-ionic
Isotonic
Water-soluble
Non-ionic
The transparent anterior bulge of the bulbus oculi is termed the:
Conjunctiva
Sclera
Lens
Cornea
Cornea
Which of the following describes the large opening on the inferior aspect of the sacrum?
Sacral promontory
Sacral hiatus
Sacral Foramina
Lateral masses
Sacral hiatus
Widened areas of the subarachnoid space are referred to as:
Ventricles
Basal cisterns
Meninges
Choroid plexus
Basal cisterns
Posteriorly the trachea is in contact with which structure of the mediastinum?
Esophagus
Carotid arteries
Thyroid tissue
Larynx
Esophagus
The large projection on the posterior surface of the scapula dividing it into upper and lower fossae is termed the:
Coracoid process
Glenoid fossa
Scapular spine
Acromion process
Scapular spine
The perpendicular plate articulates with which bone to form the boney nasal septum?
Sphenoid
Ethmoid
Occipital
Vomer
Vomer
What term describes the s-shaped portion of the large bowl in the LLQ?
Descending colon
Sigmoid colon
Rectum
Anus
Sigmoid colon
Which aspect of the sternum is visualized on an axial image displaying the articulation of the clavicles with the sternum?
Any of the above
Body
Xiphoid process
Manubrium
Manubrium
Which of the following is not a retroperitoneal structure?
Kidneys
IVC
Ureters
Transverse colon
Transverse colon
The chin is also called the:
Acanthion
Ramus
Mentum
Gonion
Mentum
The Xiphoid process is at the level of:
T10
T12
T11
T9
T10
Which of the following is accessed during an epidural to inject anesthetic agents?
Subdural space
Subarachnoid space
None of the above
Central canal
None of the above
Which of the following terms refers to the most posterior aspect of the neural arch?
Lamina
Pedicle
Transverse process
Articular Facets
Lamina
Which of the following terms is also termed tertiary bronchi?
Alveolar ducts
Lobular bronchi
Secondary bronchi
Primary bronchi
none of the above (lobular are secondary)
Segmental is the correct answer but not an option
Which of the following is also known as the ala?
Lateral masses
Sacral Foramina
Sacral promontory
Sacral hiatus
Lateral masses
Define Proximal
Towards the origin
Define Deep
Away from the skin/surface
Define Cranial/Cephalic
Towards the head
Define Caudal
Towards the feet
Define Distal
Away from the origin
Define Superficial
Towards the skin/surface
Which of the following is a direct extension of the ventricular system of the brain?
Epidural space
None of the above
Central canal
Subdural space
Central canal
Which structure is positioned closest to the spine?
Trachea
Esophagus
Esophagus
The most posterior aspect of the cerebrum is the:
Diencephalon
Cerebellum
Occipital lobe
Brainstem
Occipital lobe
Which of the following is not composed of white brain matter?
Corpus Callosum
Cerebral cortex
None of the above
Myelinated Axons
Cerebral cortex
Which of these structures are contained within the pelvic cavity? (choose all correct)
Ovaries
Kidneys
Rectum
Gonads
Ovaries
Rectum
Gonads
Which of the following arteries circulate blood around the major vessels of the Circle of Willis?
Basilar artery
Cerebral arteries
Communicating arteries
Internal carotids
Communicating arteries
Which of the following is the most posterior structure in the male pelvis?
Uterus
Iliac muscles
Prostate
Rectum
Rectum
Which of the following continues as the sigmoid colon?
Ascending colon
Transverse colon
Cecum
Descending colon
Descending colon
In standard anatomic position, the hands and feet are:
Dorsaflexed
Forward
Internally Rotated
Pronated
Forward
The lobes of the cerebellum are connected medially by which of the following structures?
Midbrain
Insula
Corpus Callosum
Vermis
Vermis
Costo-vertebral joints are a feature unique to which aspect of the vertebral column?
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacral
Thoracic
Which of the following supplies arterial blood to the myocardium?
Pulmonary veins
Pulmonary arteries
Coronary arteries
Aorta
Coronary arteries
The coronary arteries extend from what large vessel of the heart?
Pulmonary arteries
Superior Vena Cava
Aorta
Azygos Vein
Aorta
T/F: The vertebral arteries pass through the vertebral foramina of the cervical spine on the way to the cranium.
False
During menstruation the walls of the uterus may appear thicker or thinner usual?
Thicker
Thinner
Thicker
Which of the following connects the ventricular system to the subarachnoid space?
Interventricular foramen
Cerebral aqueduct
Foramen of Luschka
Foramen of Magendie
Foramen of Luschka
The cochlea is found in which portion of the ear?
External
Tympanic portion
Middle
Inner
Inner
Which of the following is least likely to be identified in the pelvis?
Cecum
Jejunum
Duodenum
Ileum
Duodenum
Which of these fractures is comparable to a green stick fracture in long bones?
Depressed skull fracture
Diastatic fracture
Basilar skull fracture
Ping-pong fracture
Ping-pong fracture
Which of following describes the appearance of a brain abscess in sectional imaging? (Choose all correct)
May be associated with edema
Often rim-enhancing
May shows areas of necrosis
Often associated with hemorrhage
May be associated with edema
Often rim-enhancing
May shows areas of necrosis
Which of the following is the most common primary cancer?
Breast
Colorectal
Lung
Prostate
Prostate
Which of the following describe imaging characteristics of pancreatitis? (Choose all correct)
Ascites
Pancreas inflammation
Pancreatic pseudocysts
Reactive fluid
Ascites
Pancreas inflammation
Pancreatic pseudocysts
Reactive fluid
Which of these lesions grow primarily in the cerebellum/posterior fossa of the cranial cavity?
Medulloblastoma
Pituitary adenoma
Astrocytoma
Meningiomas
Acoustic Neuromas
Medulloblastoma
Which of the following is a form of lung cancer? (choose all correct)
Primary lung cancer
Interstitial Lung Disease
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
Metastatic Lung Cancer
Primary lung cancer
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
Metastatic Lung Cancer
Which of these conditions appear most similar on sectional imaging? (choose two)
Pleural Effusion
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
Tuberculosis
Hemothorax
Pleural Effusion
Hemothorax
What is the most common etiology of colon cancer?
Ulcerative colitis
Colic ulcer
Crohn’s disease
Polyp neoplasm
Polyp neoplasm
Which of these conditions appear most similar in sectional imaging? (choose two)
COPD
Pneumothorax
Hemothorax
Interstitial Lung Disease
COPD
Interstitial Lung Disease
Which of these conditions is caused by blood extravasation in the brain? (choose one or both)
Ischemic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke
Which of these brain lesions is most likely to appear in multiples?
Benign brain neoplasm
Metastatic brain cancer
Primary brain cancer
Gliomas
Metastatic brain cancer
Which of the following are imaging indications of organ laceration? (Choose all correct)
Limited or absence of contrast perfusion through the organ
Contrast extravasation in or around the organ
Atypical contrast perfusion through the organ
Hematoma in the area of the organ
Limited or absence of contrast perfusion through the organ
Contrast extravasation in or around the organ
Atypical contrast perfusion through the organ
Hematoma in the area of the organ
Which of these lesions are most likely to be associated with hormonal imbalances?
Medulloblastoma
Meningiomas
Pituitary adenoma
Astrocytoma
Acoustic Neuromas
Pituitary adenoma
Which of these pathologies is sometimes accompanied by meningocele formation?
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Spina Bifida
Spinal Meningioma
Tethered cord
Spina Bifida
Which of these conditions commonly exist secondary to primary or metastatic lung cancer? (choose all correct)
Abscess formations
Necrosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Pleural effusions
Abscess formations
Necrosis
Pleural effusions
Which of the following are common causes of renal stones? (Choose all correct)
low fluid intake
metabolic abnormalities
dehydration
recurrent yeast infections
low fluid intake
metabolic abnormalities
dehydration
Ischemic stroke may be a result of arterial interruption in which of these vessels? (choose all correct)
Basilar artery
Internal carotids
Descending aorta
Cerebral arteries
Basilar artery
Internal carotids
Cerebral arteries
Which of these fractures occur only along suture lines?
Depressed skull fracture
Basilar skull fracture
Ping-pong fracture
Diastatic fracture
Diastatic fracture
What term describes a cancer in one organ/tissue but originated from a different organ/tissue?
Metastatic neoplasm
Primary cancer
Malignant neoplasm
Benign neoplasm
Metastatic neoplasm
Which of these conditions might appear as a walled cavity filled with infected fluid, blood, and sometimes air?
Hematoma
Ascites
Abscess
Inflammation
Abscess
Where is a myxoma most likely to be imaged?
Left Atrium
Left Ventricle
Right Ventricle
Right Atrium
Left Atrium
Which of these conditions causes a permanent loss of neurologic function? (choose one or both)
Ischemic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke
Ischemic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke
T/F: SNR is dependent on the quality of the coil
True
T/F: When positioning a patient’s legs for a lower extremity vascular study, the legs should be placed as far apart as possible.
False
When imaging the wrist, the optimal plane in which to visualize the carpal tunnel is the:
Oblique
Sagital
Coronal
Axial
Axial
Which of the following is the most inferior portion of the spinal cord?
Sacral hiatus
Cauda equina
Conus medullaris
Filum terminale
Conus medullaris
T/F: When performing a MSK study, it is often helpful to place a marker over the ROI.
True
Adhesive capsulitis is also known as:
Tennis elbow
Carpal tunnel
Frozen shoulder
Trough lesion
Frozen shoulder
Indications for MRV of the lower extremities includes all but which of the following?
Recent twisted ankle
Recent orthopedic surgery
Leg swelling
Evaluation for free-floating thrombus
Recent twisted ankle
A patient who presents with numbness of the first three digits and nighttime pain from the wrist to the forearm most likely has:
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Sarchoidosis
Hamartoma
De Quervain Tenosynovitis
Carpal tunnel syndrome
To image the veins of the head:
a pre-saturation pulse is placed superior to the FOV
contrast must always be used
the COW is visualized
a pre-saturation pulse is placed inferior to the FOV
a pre-saturation pulse is placed inferior to the FOV
T/F: For an MRI of the hand or wrist, a patient may be positioned prone or supine, depending on the coil options available.
True
Enlargement of the left lobe of the liver is most likely a sign of which of the following diseases processes?
Cirrhosis
Renal failure
Hepatic mets
Ascites
Cirrhosis
T/F: Careful timing of post contrast pituitary scans is important because eventually the pituitary gland enhances itself, as well as a microadenoma, if present.
True
T/F: When positioning the patient for an MR examination of the shoulder, the humerus should be perpendicular to the scan table.
False
The “candy cane” view is best described by which of the following:
Long axis view of the heart
Sagital/oblique view of the pulmonary arteries
Axial view of the thoracic aorta
Sagital/oblique view of the thoracic aorta
Sagital/oblique view of the thoracic aorta
T/F: The most common site of aneurysms in the thoracic aorta is the ascending aorta.
True
When scanning a routine female pelvis exam, axials would be angled in which manner?
Perpendicular to the uterus
Perpendicular to the cervix
Parallel to the uterus
Parallel to the cervix
Perpendicular to the uterus
At which level does the spinal cord typically terminate?
L1-L2
L5-S1
L3-L4
L2-L3
L1-L2
CNR between pathology and other structures can best be demonstrated by which of the following?
Non-contrast studies
Lower field strength magnets
Utilizing T1 sequences
Suppression of normal tissues via sequences that null signal from certain tissues (i.e. FLAIR, STIR)
Suppression of normal tissues via sequences that null signal from certain tissues (i.e. FLAIR, STIR)
Which of the following is considered the most common cause of PAD?
Leg numbness or weakness
No pulse or weak pulse in the legs or feet
Shiny skin on legs
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis
T/F: The emotional well being of a patient is just as important as their physical condition.
True
T/F: MRI can assist in detecting the presence of osteomyelitis.
True
T/F: MRA and MRV can be performed either with contrast or without contrast, using different imaging techniques.
True
T/F: There are five ventricles in the brain.
False
Common sources of artifact for an orbital MR exam include all of the following except:
using a small FOV- aliasing
flow motion in the Circle of Willis
eye movement
zipper artifact
zipper artifact
The American Cancer Society recommends screening breast MRI in addition to annual mammograms in which of the following?
To evaluate implant integrity.
Patients with less than a 15% lifetime risk of breast cancer.
In patients with greater than 20% lifetime risk of breast cancer.
In all women over the age of 40.
In patients with greater than 20% lifetime risk of breast cancer.
Which of the following best represents a coarse matrix?
256 X 128
256 X 256
512 X 512
256 X 128
T/F: Teratomas are present at birth and may contain hair, teeth, and other tissues.
True
The coil usually preferred to image the shoulder for the maximization of SNR is the:
Phased array coil
Surface or local coil
Small extremity coil
Body coil
Surface or local coil
Which of the following is a malignant bone tumor that affects children and young adults? the tumor may start anywhere in the body, usually in the long bones of the arms and legs, the pelvis, or the chest.
Transitional Cell Carcinoma
Chordoma
Teratoma
Ewing Sarcoma
Ewing Sarcoma
T/F: There are four ventricles in the brain.
True
Which of the following best describes the ACL?
Extends from the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle to the posterior tibial spine
Extends from the medial aspect of the medial femoral condyle to the anterior tibial spine
Extends from the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle to the anterior tibial spine
Extends from the lateral aspect of the medial femoral condyle to the anterior tibial spine
Extends from the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle to the anterior tibial spine
T/F: Patients are positioned supine head first for run-off exams.
False
To minimize aliasing in axial slices of the thoracic spine, one would use:
Saturation pulses
Oversampling
Chemical presaturation
Breath holds
Oversampling
T/F: MRI is the most sensitive detection method for calcaneal stress fracture.
True
Which of the following would best demonstrate hemorrhage?
FSE
GRE
STIR
FLAIR
GRE
Scan time can be decreased by using which of the following?
A long TR
The most NEX allowable
A fine matrix
A short TR
A short TR
Which diagnosis is considered most likely in a patient who presents with pain, swelling, and reddening over the olecranon. The MR images show bone marrow and soft tissue edema.
Rheumatoid arthritis
SLAP tear
Osteomyelitis
Triceps tendon tear
Osteomyelitis
Which of the following sequences provides temporal resolution of enhancing lesions and indicates brain activity?
T1
Perfusion
STIR
FLAIR
Perfusion
T/F: Careful timing of post contrast pituitary scans is important because eventually the pituitary gland enhances itself, as well as a microadenoma, if present.
True
T/F: The optimal imaging window for evaluation of breast cancer is immediately following the start of the menstrual cycle.
False
Which of the following sequences fills all of K space in one repetition by using very long echo trains?
SE
STIR
EPI
GRE
EPI
A patient presents with pain in the neck and shoulder, numbness and tingling in the fingers, and a weak grip. Which of the following is most likely the cause?
Schwannoma
Whiplash
Thoracic outlet syndrome
Herniated thoracic disc
Thoracic outlet syndrome
T/F: Careful explanation of free breathing and breath holds is crucial to a good abdominal study.
True
For optimal imaging of the cervical spine, patient positioning and local coil placement are:
Supine/around the neck to include from C1 to C7
Prone/on top of the neck to include from C1 to C7
Supine/on top of the neck to include from C1 to C7
Supine/beside the neck to include from C1 to C7
Supine/around the neck to include from C1 to C7
T/F: Contrast is routinely used in the cervical spine for patients with a diagnosis of MS.
True
T/F: MRA is generally considered “non-invasive.”
True
Prior to an MRCP examination, patients should be NPO for __ hours.
three
four
two
one
four
T/F: Toe movement will not affect MR foot image quality.
False
Axial slices through the thoracic spine are angled parallel to:
Z joints
disc spaces
spinous processes
spinal cord
disc spaces
T/F: Any tissue can be nulled as long as an RF pulse matching its precessional frequency is applied to the imaging volume before excitation.
True
How often must we sample frequencies, according to the Nyquist Theorem?
Twice per cycle
Three times per cycle
Once per cycle
Less than once per cycle
Twice per cycle
SSFP sequences usually produce images that are ___ weighted.
T1
T2
T2*
T1 or T2*
T2
T/F: MR microscopy (MRM) is useful as a research tool when studying detail in a very small area of tissue.
True
Which of the following does NOT reduce flow motion artifact?
SAT
GMN
ECG gating
Subtraction
Subtraction
What unit is used to express the amount of chemical shift?
gyromagnetic ratio
ppm
MHz
Hz
ppm
The homogeneity of a magnetic field is expressed in units of:
MHz (megaHertz)
G (gauss)
ppm (parts per million)
T (Tesla)
ppm (parts per million)
To maintain the magnetic field of a resistive magnet, the following should be applied to the magnet coils:
Heat
Cooling
Water
Current
Current
What is another term for phase ghosting?
Phase mismapping
Phase wrap
Aliasing
Chemical misregistraion
Phase mismapping
Which of the following best describe spin-lattice relaxation? (Choose all that apply)
Nuclei give up energy to the surrounding environment, resulting in longitudinal recovery.
T2 Decay
T1 Recovery
Time it takes 88% of the longitudinal magnetization to recover in tissue.
Nuclei give up energy to the surrounding environment, resulting in longitudinal recovery.
T1 Recovery
In which direction does truncation occur? (Choose all that apply)
Slice Select Axis
Anterior to Posterior
Frequency Axis
Phase Axis
Phase Axis
Which part of K space do steep phase gradients fill?
Outer lines of K space, both positive and negative
Central lines of K space, positive only
Outer lines of K space, positive only
Central lines of K space, both positive and negative
Outer lines of K space, both positive and negative
Which gradient performs phase encoding for coronal slices?
Y gradient
Z gradient
X gradient
Any combination of gradients
X gradient
How is K space filled in Fast Gradient Echo Sequences? (choose all that apply)
Elliptical filling
Centric filling
Keyhole filling
Outside to inside
Centric filling
Keyhole filling
T/F: Parallel imaging is usually used to increase resolution or decrease scan time
True
What does the slope of the frequency encoding gradient determine?
The size of the phase matrix
The size of the anatomy covered along the frequency encoding axis
The FOV
The 180 degree rephasing pulse
The size of the anatomy covered along the frequency encoding axis
The FOV
When is the phase encoding gradient switched on in a pulse sequence?
Between TRs
During the spin echo
Usually just before the application of the 180 degree rephasing pulse
Before the 90 degree excitation pulse
Usually just before the application of the 180 degree rephasing pulse
Magnetic field strength can be expressed in units of Tesla (T) or gauss (G), where:
1 T = 1 G
- 5 T = 1500 G
- 0 T = 0.3 G
1 T = 10 000 G
1 T = 10 000 G
What are the advantages of propeller K Space filling?
Better detail
Bright signal
Rapid imaging, increased SNR and CNR, reduced motion artifact.
Low SNR but high resolution
Rapid imaging, increased SNR and CNR, reduced motion artifact.
What is the unit of K space?
Inches
Radians per centimeter
Degrees
Radians per meter
Radians per centimeter
Which of the following is a possible cause of shading artifact?
Inhomogeneities in the main magnetic field
A leak in the RF shielding of the scan room
Spin echo sequences
A hemorrhage
Inhomogeneities in the main magnetic field
Which cryogen is commonly used to super cool wires in MRI?
Hydrogen
Liquid helium
Niobium
Alnico
Liquid helium
T/F: During EPI all the lines of K space are filled during one repetition.
True
The anatomy of white matter tracts can be mapped using strong multi-directional gradients in which of the following?
diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
continuous arterial spin labeling (CASL)
CBV
SWI
diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
Contrast enhanced MRAs are acquired with all of the following EXCEPT:
Bolus tracking
Fluoro triggering
Test bolus
VENC settings
VENC settings
Determine which of the following parameters would result in the most entry slice phenomenon (i.e. entry slice phenomenon would increase compared to the other options).
Slice 10 out of 20, 400 TR, .7 mm slice thickness
Slice 1 of 20, 3000 TR, .7 mm slice thickness
Slice 1 out of 20, 400 TR, 1.2 mm slice thickness
Slice 10 out of 20, 3000 TR, 1.2 mm slice thickness
Slice 1 of 20, 3000 TR, .7 mm slice thickness
Is the following extrinsic or intrinsic?
Pulse sequence type
Extrinsic
Is the following extrinsic or intrinsic?
T1 recovery time
Intrinsic
Is the following extrinsic or intrinsic?
TR
Extrinsic
Is the following extrinsic or intrinsic?
Flip Angle
Extrinsic
Is the following extrinsic or intrinsic?
T2 decay time
Intrinsic
T/F: Gadolinium chelates are ferromagnetic.
False
T/F: The SNR is enhanced when using local coils.
True
Which of the following are methods of reducing phase ghosting? (Choose all that apply)
Using respiratory compensation techniques
Decrease the TE
Carefully explain the procedure to the patient
Use pre-saturation pulses
Swap phase and frequency
Use “no phase wrap” software
Using respiratory compensation techniques
Carefully explain the procedure to the patient
Use pre-saturation pulses
Swap phase and frequency
Which gradient performs slice selection for sagital slices?
Z gradient
X gradient
Any combination of gradients
Y gradient
X gradient
Which of the following sequence(s)/technique(s) can be used to make vessels appear bright?
Gradient Echo Imaging
Gradient Moment Rephasing
Contrast Enhancement
All of the above
All of the above
T2* decay is faster than T2 decay since it is a combination of which of the following effects?
T2 decay itself
* weighting
Dephasing due to magnetic field inhomogeneities
T1 decay with spin echo
T2 decay itself
Dephasing due to magnetic field inhomogeneities
T/F: Intra-voxel dephasing results in an increase in total signal amplitude from the voxel.
False
Which of the following best describes a use for MR Spectroscopy (MRS)?
To demonstrate perfusion
To aid in brain tumor staging
To show ankle anatomy
To aid in brain tumor staging
Enhanced MR images are evaluated for sensitivity and specificity, where sensitivity is ________ and specificity is ________.
The ability to detect the lesion/the ability to classify the lesion
TR used to evaluate the lesion/TE used to evaluate the lesion
The ability to classify the lesion/the ability to detect the lesion
TE used to evaluate the lesion/TR used to evaluate the lesion
The ability to detect the lesion/the ability to classify the lesion
What are the guidelines for pregnant employees? (Choose all that apply)
Pregnant employees MUST transfer to x-ray once they’ve announced their pregnancy to the MRI department.
No changes to pregnant employees work environment in MRI. Everyone knows that MRI doesn’t use radiation.
Pregnant employees may enter the scan room, but should leave before scanning begins.
Pregnant employees are exempt from scanning and may only do paperwork.
Pregnant employees may enter the scan room, but should leave before scanning begins.
What is the available imaging time using these parameters? R to R 800 ms, trigger window 10%, delay after trigger 4 ms.
800 ms
700 ms
716 ms
688 ms
716 ms
What happens to the alignment of hydrogen protons when placed in an external magnetic field? (Check all that apply)
Slightly more nuclei line up with the main magnetic field than against it.
Nothing until an RF pulse is applied.
The magnetic moments of the nuclei align with or against the main magnetic field.
More nuclei oppose the main magnetic field than line up with the main magnetic field.
Slightly more nuclei line up with the main magnetic field than against it.
The magnetic moments of the nuclei align with or against the main magnetic field.
T/F: Intrinsic parameters are those that cannot be changed because they are inherent to the body’s tissues.
True
Which of the following best describes a remedy for cross excitation?
Excite alternate slices during the acquisition
Use a long tE
Use spin echo sequences
Call the service engineer
Excite alternate slices during the acquisition
Ohm’s law states:
1 T = 10 kG
V = I (R)
B = k (l)
B = H (1+x)
V = I (R)
In which direction does truncation occur? (Choose all that apply)
Phase Axis
Frequency Axis
Anterior to Posterior
Slice Select Axis
Phase Axis
What controls the polarity of a gradient?
The steepness of the slice select gradient
The strength of the main magnetic field
The sharpness of the frequency readout
The direction of the current through the gradient coil
The direction of the current through the gradient coil
Which gradient performs slice selection for coronal slices?
Y gradient
Any combination of gradients
X gradient
Z gradient
Y gradient
The signal from flowing blood within vessels in MRI and MRA relies on:
Third order motion
Fourth order motion
First order motion
Second order motion
First order motion
The following image is displayed in what plane?
Oblique
Axial
Coronal
Sagittal

Axial
Identify the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Large Bowel
Common iliac artery
Small bowel
Ilium
Appendix
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
E
Not Labeled

Deltoid muscle
Humeral Head
Infraspinatus Muscle
Clavicle Bone
Scapular Spine
Supraspinatus Muscle
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
E
Not Labeled

Extensor Digitorum Brevis Muscle
Calcaneus
Navicular
Talus
Abductor Hallicus Muscle
Cuboid
Label vessels in the image below.
1
2
3
4
5

Aorta
Right Coronary Artery
Left Anterior Descending Artery
Circumflex Artery
Left Coronary Artery
What pathology is visible in this image?
Prostate cancer
Ovarian cyst
Uterine cancer
Uterine fibroid
Ovarian tumor

Uterine fibroid
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Neoplasm
EDH
Abscess
SDH
Ischemic stroke

Ischemic stroke
What pathology is seen in this image?
CAD
Myxoma
Pericardial Effusion
CHF

Pericardial Effusion
Which of the following pathologies is visualized in this image? (choose all correct)
Linear skull fracture
Basilar skull fracture
Ping-pong skull fracture
Epidural hematoma
Depressed skull fracture

Epidural hematoma
Depressed skull fracture
What pathology is seen in this image?
Aortic Aneurysm
CAD
Pericardial Effusion
PE

PE
What pathology is visualized in the following image?
Blow-out fracture
Nasal fracture
Zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture
Dental abscess
LeFort fracture

Zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture
What pathology is visible in this image?
Lymphoma
Liver cancer
Splenic Laceration
Gastric cancer

Lymphoma
What pathology is visible in this image?
Gastric cancer
Splenic Laceration
Lymphoma
Cirrhosis
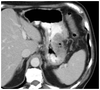
Gastric cancer
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below? (choose all correct)
Edema
Ischemic stroke
ICB
SDH

Edema
ICB
What pathology is seen in this image?
PE
CAD
Pericardial Effusion
Myxoma

Myxoma
What pathology is visible in this image?
Liver cancer
Lymphoma
Splenic Laceration
Gastric cancer

Splenic Laceration
What pathology is seen in this image?
Spina bifida occulta
Meningocele
Myelomeningocele

Meningocele
Which of the following pathologies is visualized in this image? (choose all correct)
Depressed skull fracture
Epidural hematoma
Linear skull fracture
Basilar skull fracture
Ping-pong skull fracture

Depressed skull fracture
What pathology is seen in this image?
Spinal Meningioma
Spina bifida
Spinal Ependymoma
Tethered cord

Spina bifida
What pathology is visualized in the following image?
Dental abscess
Nasal fracture
LeFort fracture
Blow-out fracture
Zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture

LeFort fracture
What pathology is visible in this image?
RCC
Wilm’s tumor
Kidney laceration
Adrenal mass
Renal Stone

Wilm’s tumor
Which of the following best describes the anatomy indicated by number twelve on the image shown below:
Teres major muscle
Scapula
Acromion
Spine of the scapula

Scapula
What type of isolation precaution is most relevant when infectious agents can be suspended in air for long periods of time over long distances?
Standard Precaution
Airborne Isolation
Droplet Isolation
Contact Isolation
Airborne Isolation
Which of these precautions is most relevant when infectious agents may be spread through contaminated medical instruments?
Contact Isolation
Droplet Isolation
Standard Precaution
Airborne Isolation
Contact Isolation
Which of the following may be caused by feelings of apprehension or pain? (Choose all correct)
Syncope
Bradycardia
Hypotension
Vasovagal Response
Syncope
Bradycardia
Hypotension
Vasovagal Response
Which of these procedures is required during IV catheter insertion?
Sterile Technique
Medical Asepsis
Sterile Technique
Which of the follow is a transmission-based infection precaution? (Choose all correct)
Airborne Isolation
Droplet Isolation
Contact Isolation
Standard Precaution
Airborne Isolation
Droplet Isolation
Contact Isolation
How long do the symptoms of a TIA typically last?
<1 hour
<1 minute
>24 hours
Permanently
<1 hour
What is the minimum amount of iodinated contrast that may induce an allergic reaction?
50
1% of the patient’s total blood volume
10 ml
>1 ml
>1 ml
Which of the following medications should be adminstered to a patient with a known iodine allergy prior to IV infusion of iodinated contrast media? (choose all correct)
Antibiotics
Benedryl
NSAIDS
Steroids
Benedryl
Steroids
Which of these medications function as an immunosuppressant to counteract hives and/or itching? (Choose all correct)
Solu-medrol
Benedryl
Atropine
Epinephrine
Solu-medrol
Benedryl
Which of the following represents a normal creatinine value?
.8
18
1.8
.08
.8
Which of these procedures is also referred to as aseptic technique?
Sterile Technique
Medical Asepsis
Sterile Technique
Which of the following risk factors require a renal function test prior to administrattion of iodinated contrast? (choose all correct)
STD/AIDS
Prior contrast reaction
Renal failure
Liver disease
STD/AIDS
Renal failure
Liver disease
Which of the following are considered common vasovagal responses? (Choose all correct)
Syncope
Fainting
Spontaneous arrhythmias
Death
Syncope
Fainting
Which of these factors potential affect the pharmacokinetics of a drug? (choose all correct)
Patient immune status
Patient age
Patient gender
Patient weight
Patient immune status
Patient age
Patient gender
Patient weight
Hypertonic solution refers to:
Solution with a changing solute concentration
Solution with a lower solute concentration
Solution with an equal amount of concentration
Solution with a higher solute concentration
Solution with a higher solute concentration
Which of the following represents a normal BUN?
3,000+
3
13
303
13
Which of these lab tests may indicate a patients potential for bleeding? (choose all correct)
Hematocrit
Platelet count
WBC count
Hemoglobin
Platelet count
Which of these medications might be administered if a patient is having only hives and itching? (Choose all correct)
Benedryl
Solu-medrol
Zofran
Epinephrine
Benedryl
Solu-medrol
Which of the following describes a required characteristic of IV injectable contrast media? (choose all correct)
Low-density barium
Isotonic
Water-soluble
Non-ionic
Isotonic
Water-soluble
Non-ionic
The SVC is formed by the joining of which of the following vessels? (choose all correct)
IVC
Azygos vein
Right brachiocephalic vein
Left brachiocephalic vein
Right brachiocephalic vein
Left brachiocephalic vein
The cerebellum communicates with other aspects of the brain by way of which of the following?
Peduncles
Tentorium
All of the above
Vermis
Peduncles
Which of the following vessels is visualized on the posterior surface of the pancreas?
Hepatic artery
Left gastric artery
Splenic artery
SMA
Splenic artery
T/F: The kidneys are oriented deep to the muscles of the abdominal wall.
True
Much of the SB is located within which quadrant of the abdomen?
LUQ
LLQ
RUQ
RLQ
LLQ
The descending colon is visualized in what portion of the abdomen?
Central
Left
Right
None of the above
Left
Which of the following is the visceral layer of the heart’s serous membrane?
Myocardium
Pericardium
Epicardium
Endocardium
Epicardium
Each common carotid artery bifurcates into internal and external carotid arteries at the level of the:
Foramen magnum
Thyroid cartilage
Jugular notch
EAM
Thyroid cartilage
T/F:The anterior and external jugular veins usually drain superficial areas such as the face and scalp.
True
Which vertebral ligament can be seen on sagittal imaging extending between the spinous processes of adjacent vertebrae?
Posterior longitudinal ligament
Interspinous ligament
Ligamentum flavum
Anterior longitudinal ligamen
Interspinous ligament
The left lung has how many fissures?
One
Two
Three
One
Which of the following is formed within the transverse processes of the sacral vertebrae?
Sacral hiatus
Sacral promontory
Lateral masses
SI Joint
Lateral masses
Which of the following is a fibrous tissue lining the inner walls of the hearts chambers?
Myocardium
Epicardium
Pericardium
Endocardium
Endocardium
Which of the following is not a salivary gland?
Parathyroid
Submandibular
Sublingual
Parotid
Parathyroid
Which of the following forms the wings attaching to the sacrum?
Ilium
Pubis
Ischium
Ilium
Which of the following supplies blood to the majority of the body?
Pulmonary arteries
Coronary arteries
Aorta
Pulmonary veins
Aorta
Which of the following is accessed during an epidural to inject anesthetic agents?
Subarachnoid space
None of the above
Central canal
Subdural space
None of the above
Which primary bronchus has a greater diameter?
Left
Right
Right
The omentum attaches to which of the following structures?
Stomach
Large bowel
Small bowel
Liver
Stomach
Which of the following in not a branch of the celiac truck?
Hepatic artery
SMA
Left gastric artery
Splenic artery
SMA
The peritoneum is a:
Serous Membrane
Muscle
Vessel
Organ
Serous Membrane
Which of the following is also known as the ala?
Lateral masses
Sacral Foramina
Sacral promontory
Sacral hiatus
Lateral masses
Which of the following describes the most anterior structure of the female pelvis?
Rectum
Uterus
Prostate
Bladder
Bladder
T/F: The large nerve exiting the eye is termed the ophthalmic nerve.
False
Which of these is the only portion of the colon that is peritoneal?
Cecum
Transverse colon
Descending colon
Ascending colon
Transverse colon
Which primary bronchus is directed more inferiorly than laterally?
Right
Left
Right
The mesentery is primary attached to which of the following structures?
Small bowel
Liver
Stomach
Large bowel
Small bowel
An exaggerated curve of the lumbar spine is termed:
Kyphosis
Hunchback
Scoliosis
Lordosis
Lordosis
The external and middle ear are separated by the:
Eustachian tube
EAM
Auricle
Tympanic membrane
Tympanic membrane
Which aspect of the scapula articulates with the humeral head?
Acromion process
Coracoid process
Scapular spine
Glenoid fossa
Glenoid fossa
Which of the following refers to the heart muscle?
Myocardium
Epicardium
Endocardium
Myocardium
Which of these pathologies is sometimes accompanied by meningocele formation?
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Tethered cord
Spina Bifida
Spinal Meningioma
Spina Bifida
What is the most common etiology of colon cancer?
Ulcerative colitis
Polyp neoplasm
Colic ulcer
Crohn’s disease
Polyp neoplasm
hich of the following describes the appearance of lung cancer in specialty imaging? (choose all correct)
Rim-enhancing
Poorly defined neoplasm
Single lesions only
Most common in the mediastinum
Rim-enhancing
Most common in the mediastinum
Which of these pathologies have the most similar presentation in diagnostic imaging? (choose two)
Primary lung cancer
Pneumonia
Pleural effusion
Tuberculosis
Pneumonia
Tuberculosis
Which of these conditions is also called an “intracranial bleed”? (choose one or both)
Ischemic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke
Which of these conditions commonly exist secondary to primary or metastatic lung cancer? (choose all correct)
Abscess formations
Pulmonary Embolism
Necrosis
Pleural effusions
Abscess formations
Necrosis
Pleural effusions
Which of these conditions appears in sectional imaging as an enlarged artery? Choose multiple if applicable.
Simple aneurysm
Ruptured Aneurysm
Dissecting aneurysm
Simple aneurysm
Ruptured Aneurysm
Dissecting aneurysm
T/F: Pneumonia can infect the entire lung.
True
Which of these conditions appear most similar on sectional imaging? (choose two)
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
Hemothorax
Pleural Effusion
Tuberculosis
Hemothorax
Pleural Effusion
Which of the following statement concerning liver cancer are true? (choose all correct)
Primary liver cancer is more common than secondary liver cancer
Metastatic liver cancer will enhance during the venous phase of imaging
Primary liver cancer will enhance during the arterial phase of imaging
Metastatic liver cancer can be both singular or multi-focal
Metastatic liver cancer will enhance during the venous phase of imaging
Primary liver cancer will enhance during the arterial phase of imaging
Metastatic liver cancer can be both singular or multi-focal
Which of these fractures is associated with a floating face?
LeFort fractures
Nasal fractures
Blow-out fractures
Zygomaticomaxillary complex fractures
LeFort fractures
Which of these lesions grows from the Schwann cell’s of the 8th cranial nerve?
Pituitary adenoma
Meningiomas
Medulloblastoma
Acoustic Neuromas
Astrocytoma
Acoustic Neuromas
Which of the following imaging characteristics indicate prostate cancer as opposed to BPH? (Choose all correct)
urine outflow obstructions
General enlargement
lymphadenopathy
asymmetry
lymphadenopathy
asymmetry
Which of the following are likely indicators of bladder cancer? (Choose all correct)
focal mass lesion
renal stone
hydronephrosis
asymmetrical wall thickening
focal mass lesion
asymmetrical wall thickening
Which of these brain neoplasms is potentially fatal? (choose all correct)
Metastatic brain cancer
Primary brain cancer
Secondary brain cancer
Benign brain neoplasm
Metastatic brain cancer
Primary brain cancer
Secondary brain cancer
Benign brain neoplasm
Define Spina bifida occulta
incomplete closure of the spinal column
Define Meningocele
a collection of CSF formed by herniation of the meninges through an opening in the vertebral canal
Define Myelomeningocele
herniation of the spinal cord through an opening in the vertebral canal
Which of these fractures is least likely to cause boney protrusion into the cranium?
None of these fractures intrude into the cranium.
Depressed skull fracture
Linear skull fracture
Ping-pong fracture
Linear skull fracture
When imaging the wrist, the optimal plane in which to visualize the carpal tunnel is the:
Sagital
Oblique
Coronal
Axial
Axial
Which of the following sequences is known for its sensitivity to magnetic susceptibility?
Perfusion
FLAIR
GRE
SE
GRE
T/F: Leiomyomas are benign tumors that arise from overgrowth of smooth muscle and connective tissue in the bladder.
False
Which cranial nerve has receptors for the sense of smell?
CN VI
CN III
CN II
CN I
CN I
Which of the following is thought to be due to chronic entrapment of the nerve by the intermetatarsal ligament?
Synovial sarcoma
Morton’s Neuroma
Calcaneal fatigue fracture
PVNS
Morton’s Neuroma
T/F: The main source of artifact in the brain is from flow motion of the popliteal artery.
False
To tighten the tendons of the rotator cuff, positioning for shoulder imaging may require:
Flexion
Neutral Position
Slight external rotation
Slight internal rotation
Extension
Slight external rotation
Which of the following would best demonstrate hemorrhage?
FSE
STIR
GRE
FLAIR
GRE
Which of the following sequences uses a 90 degree flip angle followed by several 180 degree rephasing pulses?
IR
GRE
SE
FSE
FSE
Which of the following describes a typical injury pattern observed after a posterior glenohumeral dislocation?
Adhesive capulitis
Hill-Sachs lesion
Paralabral joint cyst
Trough lesion
Trough lesion
The optimal plane to use when evaluating patients for cruciate ligament tears of the knee is the:
Sagital
Axial
Coronal
Axial and coronal
Sagital
Which of the following best describes the appearance of acute stroke on an axial DWI?
Dark
Bright
Bright
T/F: MRA is generally considered “non-invasive.”
True
T/F: For an MRI of the hand or wrist, a patient may be positioned prone or supine, depending on the coil options available.
True
T/F: Coverage for axial slices includes the foramen magnum to the superior surface of the brain.
True
T/F: Patients are positioned supine head first for run-off exams.
False
T/F: Patient motion is a concern in hand imaging. The patient should be immobilized as much as possible.
True
T/F: A bursa is a fat filled sac that allows smooth motion between two uneven surfaces.
Fasle
T/F: Closed and open mouth views are performed for TMJs.
True
Enlargement of the left lobe of the liver is most likely a sign of which of the following diseases processes?
Cirrhosis
Hepatic mets
Renal failure
Ascites
Cirrhosis
Which of the following best describes the ACL?
Extends from the medial aspect of the medial femoral condyle to the anterior tibial spine
Extends from the lateral aspect of the medial femoral condyle to the anterior tibial spine
Extends from the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle to the anterior tibial spine
Extends from the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle to the posterior tibial spine
Extends from the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle to the anterior tibial spine
Patients fast prior to an MRCP to do all but which of the following?
Promote gallbladder distension
Decrease fluid secretions in the stomach and duodenum
Increase the incidence of gallstones
Decrease bowl peristalsis
Increase the incidence of gallstones
Which of the following is the most common mass in the popliteal fossa?
Synovial sarcoma
Baker cyst
Popliteal aneurysm
Ganglion cyst
Baker cyst
Which of the following is considered the most common cause of PAD?
Shiny skin on legs
No pulse or weak pulse in the legs or feet
Atherosclerosis
Leg numbness or weakness
Atherosclerosis
Which of the following best defines spatial resolution?
The ratio of the amplitude of signal received by the coil to the amplitude of the noise
The time required to complete the acquisition of data
The difference in the SNR between two adjacent areas
The ability to distinguish two between two points as separate and distinct
The ability to distinguish two between two points as separate and distinct
Which of the following sequences provides temporal resolution of enhancing lesions and indicates brain activity?
STIR
FLAIR
Perfusion
T1
Perfusion
T/F: FOV boundaries for sagital thoracic spine images include from T2 to L1.
False
To minimize pulsatile flow motion artifacts, cardiac images are acquired by:
Taking the patient’s pulse, calculating the heart rate in beats per minute, then entering this data into the imaging system
Attaching ECG leads, monitoring the cardiac cycle and triggering the pulse sequence from each R wave
Performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation
None of the above
Attaching ECG leads, monitoring the cardiac cycle and triggering the pulse sequence from each R wave
To minimize aliasing in axial slices of the thoracic spine, one would use:
Oversampling
Chemical presaturation
Breath holds
Saturation pulses
Oversampling
When using MRA to evaluate peripheral vascular flow, such as that within the arteries of the legs, saturation pulses are placed:
Placed in the acquired slices
Placed superior to the acquired slices
Not necessary
Placed inferior to the acquired slices
Placed inferior to the acquired slices
Axial slices through the thoracic spine are angled parallel to:
Z joints
spinous processes
disc spaces
spinal cord
disc spaces
T/F: A Chiari Malformation can be see on a cervical spine image.
True
T/F: Contrast is routinely used in the cervical spine for patients with a diagnosis of MS.
True
Spatial resolution may be increased by selecting which of the following?
Coarse matrices
Thin Slices
Thick slices
A large FOV
Thin Slices
Which of the following best describes ascites?
The accumulation of excess fluid in the abdominal cavity
A type of kidney failure
An infection of the spleen
A disease in which the liver becomes permanently damaged
The accumulation of excess fluid in the abdominal cavity
The hip is one of the most frequent sites for which of the following:
ACL tears
Baker cysts
Avascular necrosis
Ganglion cysts
Avascular necrosis
To image the veins of the head:
contrast must always be used
the COW is visualized
a pre-saturation pulse is placed inferior to the FOV
a pre-saturation pulse is placed superior to the FOV
a pre-saturation pulse is placed inferior to the FOV
Which of the following marks the upper boundary of breast tissue?
Clavicle
Third rib
Sternum
Chest muscles
Clavicle
T/F: When positioning a patient for a head MRI exam, the horizontal alignment light should pass through the nasion.
True
Which of the following is another word for bulging of one or both eyes?
Proptosis
COW
Pseudotumor
Sarcoid
Proptosis
A patient presents with pain in the neck and shoulder, numbness and tingling in the fingers, and a weak grip. Which of the following is most likely the cause?
Thoracic outlet syndrome
Schwannoma
Herniated thoracic disc
Whiplash
Thoracic outlet syndrome
T/F: When positioning the patient for an MR examination of the shoulder, the humerus should be perpendicular to the scan table.
False
For optimal imaging of the cervical spine, patient positioning and local coil placement are:
Prone/on top of the neck to include from C1 to C7
Supine/on top of the neck to include from C1 to C7
Supine/beside the neck to include from C1 to C7
Supine/around the neck to include from C1 to C7
Supine/around the neck to include from C1 to C7
Adhesive capsulitis is also known as:
Frozen shoulder
Tennis elbow
Trough lesion
Carpal tunnel
Frozen shoulder
The coil usually preferred to image the shoulder for the maximization of SNR is the:
Small extremity coil
Phased array coil
Body coil
Surface or local coil
Surface or local coil
T/F: All halos are MRI safe.
False
T/F: Wrist imaging requires a small dedicated surface coil.
True
To minimize magnetic susceptibility artifact from a hip prosthesis, a technologist should:
Use GRE sequences
Use as small a FOV as possible
Use SE or FSE sequences with a broad receive bandwidth
Increase the SNR
Use SE or FSE sequences with a broad receive bandwidth
T/F: Contrast is routinely used for disc disease in the cervical spine.
False
In which direction does aliasing occur? (Choose all that apply)
Frequency Axis
Anterior to Posterior
Phase Axis
Slice Select Axis
Frequency Axis
Phase Axis
What is the maximum field strength allowed for clinical imaging of adults in the USA?
3 T
4 T
8 T
10 T
8 T
What MUST be done prior to anyone entering the scan room? (Select the BEST answer)
The completed screening sheet must be signed by a level II staff member and the patient must be scanned with the metal detector, prior to admittance to the MRI scan room.
Pat the patient down for metal objects.
The patient must be scanned with the metal detector.
A screening sheet must be filled out and in the patient’s chart.
The completed screening sheet must be signed by a level II staff member and the patient must be scanned with the metal detector, prior to admittance to the MRI scan room.
T/F: Flow affects image quality.
True
What is T2 decay? (Select all that apply)
Caused by the nuclei giving up their energy to the surrounding environment.
The time it takes 63% of longitudianl magnetization to recover in the tissue.
Spin lattice relaxation
Spin-spin relaxation that results in decay or loss of coherent transverse magnetization.
Spin-spin relaxation that results in decay or loss of coherent transverse magnetization.
When is the slice select gradient switched on during a spin echo pulse sequence?
It is always on during the scan
During the excitation pulse only
During the rephasing pulse only
During the 90 and 180 degree pulses
During the 90 and 180 degree pulses
Which of the following does NOT reduce flow motion artifact?
SAT
Subtraction
GMN
ECG gating
Subtraction
T/F: The purpose of magnetic field shimming is to reduce the size of the fringe field.
False
What unit is used to express the amount of chemical shift?
Hz
ppm
MHz
gyromagnetic ratio
ppm
T/F: Even echo rephasing reduces intra-voxel dephasing.
True
In which direction does truncation occur? (Choose all that apply)
Slice Select Axis
Phase Axis
Frequency Axis
Anterior to Posterior
Phase Axis
What are the two results of resonance? (Choose from the list below)
The NMV moves out of alignment and away from B0.
The magnetic moments of hydrogen nuclei move into phase with each other.
The NMV moves into a repeating pattern of +/- 100 MHZ.
The magnetic momements of hydrogen nuclei move out of phase with each other.
The NMV moves out of alignment and away from B0.
The magnetic moments of hydrogen nuclei move into phase with each other.
Which gradient performs slice selection for coronal slices?
Z gradient
Any combination of gradients
X gradient
Y gradient
Y gradient
Which of the following is a remedy for aliasing?
Decreasing the TE
Using “no phase wrap” software
Decreasing the size of the FOV
Decreasing the slice thickness
Using “no phase wrap” software
In which direction does phase ghosting occur? (Choose all applicable)
Slice Select Axis
Anterior to Posterior
Phase Axis
Frequency Axis
Phase Axis
Is the following extrinsic or intrinsic: Pulse sequence type
Extrisic
Is the following extrinsic or intrinsic: T1 recovery time
Intrinsic
Is the following extrinsic or intrinsic: TR
Extrinsic
Is the following extrinsic or intrinsic: Flip Angle
Extrinsic
Is the following extrinsic or intrinsic: T2 decay time
Intrinsic
The vascular signal, produced on time of flight MRA (TOF-MRA), relies on:
PC
Velocity-induced phase shifts
Flow related enhancement
MOTA
Flow related enhancement
T/F: Parallel imaging is usually used to increase resolution or decrease scan time.
True
Which of the following is a possible cause of shading artifact?
A hemorrhage
A leak in the RF shielding of the scan room
Inhomogeneities in the main magnetic field
Spin echo sequences
Inhomogeneities in the main magnetic field
What is the approximate T1 relaxation time of fat at 1T?
500 ms
200 ms
2000 ms
3000 ms
200 ms
In spin echo sequences using a pre-saturation pulse, what would persistent bright signal within the vessel indicate?
Slow Flowing Blood
Fast Flowing Blood
Vascular Occlusion
Blood Clot
Slow Flowing Blood
Vascular Occlusion
Blood Clot
Enhanced MR images are evaluated for sensitivity and specificity, where sensitivity is ________ and specificity is ________.
The ability to classify the lesion/the ability to detect the lesion
TE used to evaluate the lesion/TR used to evaluate the lesion
TR used to evaluate the lesion/TE used to evaluate the lesion
The ability to detect the lesion/the ability to classify the lesion
The ability to detect the lesion/the ability to classify the lesion
What is the approximate T1 relaxation time of water at 1T?
2500 ms
200 ms
2000 ms
500 ms
2500 ms
Which of the following can be used to improve coverage and at the same time maintain the signal from blood flowing within the larger volume?
MC-TOF
PC-MRA
MOTSA
Phase images
MOTSA
What is the gyromagnetic ratio of hydrogen?
- 28 MHz/T
- 8 MHz/T
- 57 MHz/T
- 57 MHz/G
42.57 MHz/T
Which of the following best describes a T1 weighted image?
Bright fat
Dark Water
Dark Fat
Bright water
Bright fat
Dark Water
T/F: TOF phenomenon results in a dark vessel.
True
T/F: Perfusion is measured using MRI by tagging the fat in arterial blood during image acquisition.
False
Contrast enhanced MRAs are acquired with all of the following EXCEPT:
VENC settings
Bolus tracking
Fluoro triggering
Test bolus
VENC settings
T/F: The gyromagnetic ratio expresses the relationship between the angular momentum and the magnetic moment of each MR active nucleus.
True
When is the phase encoding gradient switched on in a pulse sequence?
Before the 90 degree excitation pulse
Between TRs
Usually just before the application of the 180 degree rephasing pulse
During the spin echo
Usually just before the application of the 180 degree rephasing pulse
T/F: There are no known contraindications to gadolinium contrast.
False
T/F: Scar tissue enhances in the lumbar spine shortly after the injection of contrast.
True
Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical process that is used to convert MR signal from a FID into a spectrum. FT occurs in the:
RF coil
Array processor
Image processor
Gradient amplifier
Array processor
What is another term for phase ghosting?
Chemical misregistraion
Phase wrap
Phase mismapping
Aliasing
Phase mismapping
When using MRA to evaluate extracranial vascular flow, such as that within common carotid arteries, a recommended technique is:
3D time of flight MRA
3D phase contrast MRA
All of the above
2D time of flight MRA
2D time of flight MRA
In which direction does aliasing occur? (Choose all that apply)
Phase Axis
Anterior to Posterior
Slice Select Axis
Frequency Axis
Phase Axis
Frequency Axis
What is the unit of K space?
Degrees
Radians per meter
Inches
Radians per centimeter
Radians per centimeter
Select the three components of the magnetic field from those listed below.
Precessional Frequency Field
Time Varying Magnetic Fields
Static Magnetic Field
Faraday’s Field
Radiofrequency Fields
Time Varying Magnetic Fields
Static Magnetic Field
Radiofrequency Fields
Which sequence would be used to best visualize metastatic lesions in the bone?
T2 weighted sequences
Non-contrast imaging
Fat saturation techniques with contrast
FLAIR with contrast
Fat saturation techniques with contrast
What type of echoes are sampled during SS-FSE?
Spin echoes
Incoherent Gradient echoes
Gradient echoes
Spin echoes
Which of the following best describe spin-lattice relaxation? (Choose all that apply)
Time it takes 88% of the longitudinal magnetization to recover in tissue.
Nuclei give up energy to the surrounding environment, resulting in longitudinal recovery.
T1 Recovery
T2 Decay
Nuclei give up energy to the surrounding environment, resulting in longitudinal recovery.
T1 Recovery
What is another name for a truncation artifact in a sagital cervical spine?
Gyromagnetic Artifact
Truncation
Faraday
Gibbs
Gibbs
The magnetic field strength in superconducting magnets is maintained with cryogens at a temperature of:
4 K
70°F (+/- 2°F)
269°F
450°C
4 K
In which direction does phase ghosting occur? (Choose all applicable)
Anterior to Posterior
Frequency Axis
Phase Axis
Slice Select Axis
Phase Axis
Which of the following is used to trigger each pulse sequence when using ECG gating?
P wave
R wave
Q wave
S wave
R wave
After gadolinium administration, it is recommended that which images are acquired?
One T1 weighted image
Multiple T2 weighted images
Multiple T1 weighted images
One T2 weighted image
Multiple T1 weighted images
Which of the following is/are result(s) of time of flight?
Entry slice phenomenon
High velocity signal void
Flow-related enhancement
Zipper effect
High velocity signal void
Flow-related enhancement
What rule determines the direction of current flow through a coil, and the direction of the magnetic field that the current produces?
MRI Fringe Field Rule
Right hand thumb rule
The size of the magnetic field
Whether you are using an open or closed configuration
Right hand thumb rule
What do T2 images typically best demonstrate?
Bony anatomy
Pathology
Fat
Anatomy
Pathology
What EKG rhythm is represented by the graph?
Ventricular Tachycardia
A-fib
Normal Sinus Rhythm
Myocardial Infarction

Myocardial Infarction
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
E
Not labled

Abductor Digiti Muscles
Pisiform
Thenar muscles
Trapezium
Flexor Muscles
Ulna
Label the anatomy in this image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Main Stem Bronchi
Ascending Aorta
Pulmonary Trunk
Descending Aorta
IVC
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Mandibular condyle
Occipital bone
Maxillary sinus
EAM
Sphenoid bone
Identify the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Large bowel
Common iliac artery
Small bowel
Ilium
Appendix
Identify the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not labeled

Thyroid cartilage
Common carotid artery
SCM muscle
Internal jugluar vein
Intrernal carotid artery
Identify the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
E
Not labeled

Lamina
Intervertebral disc
Psoas muscle
Intervertebral foramina
Erector spinae muscle
Transverse foramina
Identify the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not labeled

Mastoid air cells
C1
C2
Transverse process
Sphenoid sinuses
Identify the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not labeled

Ischium
Pubis
Pubis symphysis
Femur
Ilium
Label the anatomy in this image.
A
B
C
D
E
Not labeled

SVC
Aorta
Common Carotid
Subclavian Artery
Pulmonary Artery
Subclavian vein
What pathology is visible in this image? (Choose all correct)
Hematoma
Laceration
Neoplasm
Inflammation

Hematoma
Laceration
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Arachnoid Cyst
SDH
Meningitis
Medulloblastoma
Abscess

Abscess
What pathology is seen in this image?
Aortic Aneurysm
CHF
Pulmonary Embolism
Pericardial Effusion

Pulmonary Embolism
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Medulloblastoma
EDH
SDH
Ischemic stroke
ICB

SDH
What pathology is visible in the image below?
Arachnoid Cyst
MS
Hydrocephalus
AVM
Medulloblastoma

MS
What pathology is visualized in the following image?
Nasal fracture
Blow-out fracture
Zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture
Dental abscess
Mandible Fracture

Dental abscess
What pathology is seen in this image?
PE
Pericardial Effusion
Aortic Aneurysm
CAD

PE
What pathology is seen in this image?
Spinal Ependymoma
Tethered cord
Spinal Metastasis
Spinal Meningioma

Spinal Ependymoma
What pathology is visible in this image?
Hemangiomas
Liver cancer
Cirrhosis
Liver laceration

Liver cancer
Which of the following pathologies is visualized in this image? (choose all correct)
Depressed skull fracture
Basilar skull fracture
Epidural hematoma
Linear skull fracture
Ping-pong skull fracture

Basilar skull fracture
Linear skull fracture
What pathology is visible in this image?
Horseshoe kidney
Renal Stone
Wilm’s tumor
RCC

RCC
What pathology is visible in this image?
Kidney laceration
RCC
Adrenal mass
Renal Stone
Wilm’s tumor

Adrenal mass
What pathology is visible in the image below?
AVM
MS
Hydrocephalus
Arachnoid Cyst
Medulloblastoma

Hydrocephalus
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below? (choose all correct)
ICB
Ischemic stroke
Medulloblastoma
Edema
SDH

ICB
Edema
What pathology is seen in this image?
Aortic Aneurysm
Pericardial Effusion
PE
CAD

Aortic Aneurysm
What pathology is seen in this image?
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Spondylolisthesis
Tethered Cord
Compression Fracture

Spondylolisthesis
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Acoustic Neuroma
Astrocytoma
Metastatic brain cancer
Medulloblastoma
Pituitary Adenoma

Metastatic brain cancer
What pathology is seen in this image?
PE
Myxoma
CAD
Pericardial Effusion

Myxoma
What pathology is visualized in the following image?
Blow-out fracture
Nasal fracture
Dental abscess
LeFort fracture
Zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture

LeFort fracture
Which of the following pathologies is visualized in this image? (choose all correct)
Epidural hematoma
Basilar skull fracture
Linear skull fracture
Ping-pong skull fracture
Depressed skull fracture

Ping-pong skull fracture
What pathology is visible in this image? (Choose multiple)
GB Cancer
Pancreatitis
Cholelithiasis
Liver cancer
Pancreatic Cancer

GB Cancer
Liver cancer
What pathology is seen in this image?
CAD
Myxoma
CHF
Pericardial Effusion

CHF
What pathology is visible in this image?
Cholelithiasis
Pancreatic Cancer
Liver cancer
GB Cancer
Pancreatitis

Pancreatitis
Which of the following best describes the anatomy indicated by number twelve on the image shown below:
Acromion
Scapula
Teres major muscle
Spine of the scapula

Scapula
MRSA requires what kind of isolation precaution?
Standard Precaution
Contact Isolation
Droplet Isolation
Airborne Isolation
Contact Isolation
What is the first step a technologist should take in responding to an ICM reaction?
Discontinue ICM administration
Acquire vital signs
Call for nursing and Physician/Radiologist on staff
Assess patient’s ABC’s (airways, breathing, and circulation)
Discontinue ICM administration
Define Antiplatelets
A substance that inhibits or destroys the effects of platelets
Define Antibiotics
A soluble substance derived from a mold or bacterium that kills or inhibits the growth of other microorganisms
Define Anxiolytics
An anti-anxiety medication
Define Antiemetics
A drug that prevents or minimizes nausea and vomitting
Define Anticoagulants
A drug that prevents or reduces the coagulation (clotting) of blood
Which of the following could potential cause a vasovagal response? (Choose all correct)
Fear
Anxiety
Pain
Medications
Fear
Anxiety
Pain
Medications
Which of the following represents a desirable TI?
2: 1
1: 2
1: 30,000
30,000:1
30,000:1
Which of these medications would be especially valuable to a patient experiencing bronchospasms during a contrast reaction?
Lasix
Albuterol
Epinephrine
Atropine
Albuterol
Which of these procedures should be followed any time the patient’s skin is intentionally perforated?
Medical Asepsis
Sterile Technique
Sterile Technique
Which of the follow is a critical cardiac arrhythmia? (Choose all correct)
Ventricular Fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation
Asystole
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular Fibrillation
Asystole
Ventricular Tachycardia
Which of the following is a process of the sphenoid bone? (choose all correct)
Greater wings
Tuberculum Sellae
Lesser wings
Sella Turcica
Greater wings
Tuberculum Sellae
Lesser wings
Sella Turcica
The foramen spinosum provides passage for which of the following?
Maxillary Nerve
Middle meningeal artery
Mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve
Optic Nerve
Middle meningeal artery
Which of the following drains blood from the posterior thorax and abdomen?
Right brachiocephalic vein
Left brachiocephalic vein
IVC
Azygos vein
Azygos vein
What single cranial bone articulated with all other cranial bones?
Sphenoid
Ethmoid
Occipital
Parietal
Sphenoid
The largest immovable bones of the face are which of the following?
Zygoma
Palatine
Mandible
Maxillae
Maxillae
The most lateral aspect of the lung base may be described as which of the following?
Costal surface
Hilum
Costo-phrenic angles
Lung root
Costo-phrenic angles
T/F: The lateral masses of C1 bear the weight of the head.
True
The cecum is located within which quadrant of the abdomen?
RUQ
LUQ
LLQ
RLQ
RLQ
Which vertebral ligament runs along the ventral surface of the vertebral column?
Interspinous ligament
Ligamentum flavum
Anterior longitudinal ligament
Posterior longitudinal ligament
Anterior longitudinal ligament
Deoxygenated blood leaves the heart via what chamber?
Left Atrium
Right Ventricle
Left Ventricle
Right Atrium
Right Ventricle
The first _______ ribs are considered true ribs.
Seven
Five
Eight
Six
Seven
Which of these structures describes the junction of the stomach and the esophagus?
Antrum
Cardia
Fundus
Pylorus
Cardia
T/F: The appendix is always found directly behind the cecum at the level of S1.
False
The right sided branch of the celiac trunk is which of the following?
Hepatic artery
Left gastric
Splenic artery
SMA
Hepatic artery
Generally, the most superior structure of the renal hilum is the:
Ureter
Any of the above
Renal vein
Renal artery
Renal artery
What fissure separates the frontal and parietal lobes of the brain?
Central Fissure
Interhemispheric Fissure
Lateral Fissure
Longitudinal Fissure
Central Fissure
Which of the following does not form the rami of the obturator foramen?
Ischium
Pubis
Ilium
Ilium
The subarachnoid space is between which meninges?
Dura and arachnoid
Arachnoid and pia
Pia and dura
Arachnoid and pia
Which of the following is a feature characteristic of only cervical vertebrae?
Large vertebral bodies
Fused transverse processes
Transverse foramina
Facets and demi-facets
Transverse foramina
Which of the sinuses is the largest?
Maxillary
Ethmoid
Frontal
Sphenoid
Maxillary
Which of the following muscle groups are the chief extends of the entire spine?
Psoas muscles
Transversospinal muscles
Splenius muscles
Erector spinae muscles
Erector spinae muscles
Which of the following structures is sometime situated above and behind the bladder?
Prostate
Uterus
Iliac muscles
Rectum
Uterus
Which portion of the temporal bone is considered the thickest boney aspect of the cranium?
Tympanic
Squamous
Mastoid
Petrous
Petrous
T/F: The 2nd cervical vertebra has both an anterior arch and a posterior arch.
False
Which of the following is an insertion site for the transversospinal muscles of the vertebral column?
Transverse process
Pedicle
Articular Facets
Lamina
Transverse process
Which of the following describes the anatomical unit of the lungs?
Secondary lobules
Lobes
Alveoli
Primary lobules
Primary lobules
Which of these conditions results in abnormal stiffening of the vertebral column?
Tethered cord
Spinal Meningioma
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Spina Bifida
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Which of these conditions is sometimes accompanied by an intradural lipoma?
Spinal Meningioma
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Spina Bifida
Tethered cord
Tethered cord
What is the most common primary neoplasm of the spinal cord?
Astrocytoma
Spinal Ependymoma
Spinal Meningioma
Spinal Metastasis
Spinal Ependymoma
Wilm’s tumor is most likely to affect which of the following demographics?
Children
Smokers
Elderly
Males
Children
T/F: The terms inflammation and infection are synonymous.
False
T/F: A patient diagnosed with CAD will invariably exhibit symptoms characteristic of MI.
False
Which of these conditions may result in or contribute to dental abscess formation? (Choose all correct)
autoimmune disorders
diabetes
tooth infection
radiation/chemotherapy
autoimmune disorders
diabetes
tooth infection
radiation/chemotherapy
T/F: Lymphoma primarily affects the spleen.
False
Which of these conditions is most likely to be associated with an aneurysm? (Choose all correct)
Intracranial bleed (ICB)
Epidural Hemorrhage (EDH)
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
Subdural Hemorrhage (SDH)
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
Define Ascites
abnormal fluid collections in the abdominal cavity
Define Abscess
an infected fluid collection
Define Hematoma
an abnormal collection of blood outside of a vascular structure
Define Colitis
inflammation of the colon
Which of these conditions may be secondary to cerebral atrophy?
ICB
Brain abscess
Meningitis
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus
Uterine fibroids are also known as:
Leiomyoma
endometrial cancer
BPH
TCC
Leiomyoma
Which of the following are common causes of pneumonia? (choose all correct)
Fungal infections
Chemical inhalation
Chest trauma
Aspiration
Fungal infections
Chemical inhalation
Chest trauma
Aspiration
What is the most common primary brain tumor?
Medulloblastoma
Acoustic Neuroma
Meningiomas
Astrocytoma
Pituitary adenoma
Astrocytoma
Which of these conditions are idiopathic? (Choose all correct)
Crohn’s disease
Cirrhosis
Ulcerative Colitis
SBO
Crohn’s disease
Ulcerative Colitis
Describe Cardiomegaly
enlarged heart
Describe CHF
insufficient caridac output
Decsribe Myxoma
benign tumor of the heart
Describe CAD
chronic obstruction of the coronary vessels
Describe Pericardial Effusion
excessaive fluid in the pericardium
T/F: Myeloma is the medical term for a tumor that begins in the brain or spinal cord.
False
The “candy cane” view is best described by which of the following:
Sagital/oblique view of the thoracic aorta
Sagital/oblique view of the pulmonary arteries
Long axis view of the heart
Axial view of the thoracic aorta
Sagital/oblique view of the thoracic aorta
Which of the following is a demyelinating disease of the CNS?
Graves disease
Multiple sclerosis
CCF
COW
Multiple sclerosis
Positioning for an abdominal MRI would include centering the horizontal alignment light on the patient’s:
Belly button
Iliac crest
Xyphoid process
Lower costal margin- L3
Lower costal margin- L3
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs as a result of compression of which nerve?
Median
Radial
Ulnar
Transverse carpal
Median
Which of the following best defines CNR?
The ratio of the amplitude of signal received by the coil to the amplitude of the noise
The time required to complete the acquisition of data
The difference in the SNR between two adjacent areas
The ability to distinguish between two points as separate and distinct
The difference in the SNR between two adjacent areas
Indications for and MRA of the Head include which of the following?
Proptosis
Suspected internal meniscal derangement
Intracranial vascular assessment of aneurysms and infarcts
Graves disease
Intracranial vascular assessment of aneurysms and infarcts
Which of the following best describes the ACL?
Extends from the lateral aspect of the medial femoral condyle to the anterior tibial spine
Extends from the medial aspect of the medial femoral condyle to the anterior tibial spine
Extends from the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle to the anterior tibial spine
Extends from the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle to the posterior tibial spine
Extends from the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle to the anterior tibial spine
To better evaluate the ACL, positioning for knee imaging may require:
Extension
15 degree external rotation
Flexion
15 degree internal rotation
15 degree external rotation
Coronal oblique images of the shoulder are angled parallel with which anatomy?
Supraspinatus muscle
AC joint
Bicipital groove
Glenoid cavity
Supraspinatus muscle
Which of the following best describes what the “QRS” complex represents?
Ventricular Diastole (Relaxation)
Atrial Systole (Contraction)
Ventricular Systole
None of the above
Ventricular Systole
T/F: Data in K space are symmetrical.
True
To achieve T1 weighting in gradient echo sequences, the flip angle should be ______.
Small
No flip angle should be used
Large
Large
T/F: Spin echo pulse sequences are classified according to whether the residual transverse magnetization is in phase (coherent) or out of phase (incoherent).
False
What artifact occurs if we sample frequencies less than once per cycle?
Cross talk
Cross excitation
Aliasing
Zipper
Aliasing
When using MRA to evaluate intracranial vascularity, flow within smaller vessels can best be demonstrated by:
2D Time of Flight MRA
All of the Above
3D Time of Flight MRA
3D Phase Contrast MRA
3D Time of Flight MRA
Which of the following best describes what the “T” wave represents?
Atrial Systole (Contraction)
Ventricular Diastole (Relaxation)
None of the above
Ventricular Systole
Ventricular Diastole (Relaxation)
On a T1 weighted pre-contrast image, fat appears _____ and water appears _____.
Bright, Bright
Dark, Dark
Bright, Dark
Dark, Bright
Bright, Dark
Which of the following best describes the appearance of chemical shift artifact on an image?
Extra information wraps into the image
Produces a dark edge at the interface between fat and water.
The cancellation of fat and water signals when they are out of phase.
Banding artifact at the interfaces of high and low signal.
Produces a dark edge at the interface between fat and water.
What artifact can occur as a result of using long echo trains?
Cross talk
Truncation
Image Blurring
Aliasing
Image Blurring
T/F:Perfusion is the regional blood flow in tissues and is defined as the volume of blood that flows into one gram of tissue.
True
What is the waiting period after each R wave called?
Available Imaging Time
Trigger Window
Trigger Delay
R to R Interval
Trigger Delay
In a dual echo sequence, which of the following combinations would result in reduced flow artifact in the second echo?
TE 40 and 80 ms
TE 20 and 50 ms
TE 40 and 95 ms
TE 20 and 70 ms
TE 40 and 80 ms
T/F: STIR sequences should NOT be used in conjunction with contrast enhancement.
True
How is time reduced in fast spin echo? (Choose all that apply)
Use an echo train
Use thinner slices
Use a turbo factor
The operator must prescribe fewer slices
Use an echo train
Use a turbo factor
T/F: STIR is most useful in post contrast imaging.
False
Identify which of the following describe a “fringe field.” (Select all that apply)
Active or passive shielding is used to reduce the size of the fringe field.
The stray magnetic field outside the bore of the magnet.
The fringe field is not confined by walls, floors, or ceilings.
An area on the outskirts of the magnet– generally two feet long by three feet wide.
Active or passive shielding is used to reduce the size of the fringe field.
The stray magnetic field outside the bore of the magnet.
The fringe field is not confined by walls, floors, or ceilings.
T/F: Gadolinium cannot cross the intact blood-brain barrier (BBB).
True
The following image is displayed in what plane?
Sagittal
Oblique
Coronal
Axial

Sagittal
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
E
Not labeled

Brachioradialis Muscle
Olecranon Process
Cephalic Vein
Pronator Teres Muscle
Capitulum (Trochlea is the right answer, but not an option)
Radial Head
Identify the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not labeled

External iliac artery
Prostate gland
Urinary bladder
Rectum
Uterus
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not labeled

Hepatic Artery
IVC
Splenic Artery
Celiac Trunk
SMA
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
Not labeled

Radial Head
ulna
Cephalic vein
Ulnar nerve
Radial Artery
What pathology is visible in the image below?
SDH
ICB
Medulloblastoma
EDH
Chiari Malformation

Chiari Malformation
What pathology is visible in this image?
Uterine cancer
Ovarian cyst
Prostate cancer
Uterine fibroid
Ovarian tumor

Uterine cancer
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Medulloblastoma
Abscess
Meningitis
SDH
Arachnoid Cyst

Abscess
What pathology is visible in this image?
SBO
Appendicitis
Crohn’s disease
Colon cancer
Colitis
Appendicitis
What pathology is seen in this image?
CHF
Aortic Aneurysm
Pulmonary Embolism
Pericardial Effusion

Pulmonary Embolism
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Tuberculosis
Lung Cancer
Pneumonia
Pleural Effusion
Tuberculosis
Pneumonia
What pathology is visible in the image below?
Medulloblastoma
AVM
Arachnoid Cyst
Hydrocephalus
MS

Hydrocephalus
What pathology is seen in this image?
Spina bifida
Spinal Meningioma
Tethered cord
Spinal Ependymoma
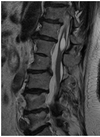
Tethered cord
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
ICB
EDH
SDH
AVM
Astrocytoma

EDH
What pathology is seen int his image?
Spinal Metastasis
Spinal Ependymoma
Tethered cord
Spinal Meningioma

Spinal Meningioma
What pathology is seen in this image?
CAD
Myxoma
PE
Pericardial Effusion

Myxoma
What pathology is visible in this image?
Laceration
Hematoma
Infarct
Neoplasm

Hematoma
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
SDH
ICB
Medulloblastoma
EDH
Ischemic stroke

SDH
What pathology is seen in this image?
Pericardial Effusion
PE
Aortic Aneurysm
CAD

PE
What pathology is seen in this image?
Pericardial Effusion
Myxoma
CAD
CHF

Pericardial Effusion
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Acoustic Neuroma
Medulloblastoma
Metastatic brain cancer
Pituitary Adenoma
Astrocytoma

Medulloblastoma
Which of these isolation precautions is applicable to a patient with an infectious condition that may be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact?
Contact Isolation
Airborne Isolation
Droplet Isolation
Standard Precaution
Contact Isolation
Which of the following describes why a drug might be classified as “by prescription only”? (choose all correct)
Habit-forming
Unsafe for self-medication
New drug
Rapid onset of action
Habit-forming
Unsafe for self-medication
New drug
What medication classification is Calcium-Channel Blocker
Antiarrythmics
What medication classification is Epinephrine
Vasoconstrictors
What medication classification is Xanax
Anxiolytics
What medication classification is tPA
Thrombolytic
What medication classification is Zofran
Anitemetics
What druge classification is Fentanyl
drug classification not provided
Which of the following describe non-idiosyncratic contrast reactions? (Choose all correct)
Minor Nausea and vomiting
Hives
Itching
Feeling of warmth
Minor Nausea and vomiting
Feeling of warmth
Systolic blood pressure corresponds with the contraction of which chamber of the heart?
Right ventricle relaxation
Left ventricle contraction
Left ventricle relaxation
Right atrial relaxation
Left ventricle contraction
The superior sagittal sinus continues as what venous pathway in the brain?
Straight sinus
Inferior sagittal sinus
Sigmoid sinus
Transverse sinus
Transverse sinus
The cerebral aqueduct of the ventricular system is a passage way for: which of the following?
Venous blood
Myelinated axon bodies
Arterial blood
CSF
CSF
Which of the following statements describes the 8th, 9th, and 10th ribs?
All of the above
They do not attach to the sternum
They are fused together by costal cartilage
They are considered floating ribs
They are fused together by costal cartilage
Which of these continues as the duodenum?
Antrum
Pylorus
Fundus
Cardia
Pylorus
The thymus is located within which body cavity?
Pleural
Dorsal
Mediastinum
All of the above
Mediastinum
The bones of the cranium are joined together at immovable joints called:
Spines
Sphenoid
Sutures
Sinuses
Sutures
The dens is a feature of which cervical vertebra?
C6
C1
C2
C7
C2
The spinal cord continues from what other feature of the CNS?
Conus medullaris
Sella Turcica
Medulla oblongata
Cauda equina
Medulla oblongata
Which of the following cavities is not filled by CSF?
Subarachnoid space
Central canal
None of the above
Subdural space
Subdural space
Which of the following is the largest aperture connection the 4th ventricle to the basal cisterns and central canal of the spinal cord?
Cerebral aqueduct
Foramen of Luschka
Interventricular foramen
Foramen of Magendie
Foramen of Magendie
The ph of the fluid secreted by the prostate is acidic or alkaline?
Alkaline
Acidic
Alkaline
Which of the following is a branch of the left main coronary artery?
Right main
Right anterior descending
None of the above
Circumflex
Circumflex
The ureters joint to the bladder on which of its surfaces?
Anterior
Superior
Posterior
Inferior
Posterior
The most medial aspect of the lungs’ surface is termed the: (choose all correct)
Costal surface
Lung root
Hilum
Costo-phrenic angles
Lung root
Hilum
The mastoid air cells are found in which of the following cranial bones?
Occipital
Sphenoid
Temporal
Ethmoid
Temporal
Costo-vertebral joints are a feature unique to which aspect of the vertebral column?
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacral
Thoracic
The trachea begins at what level of the spine?
C6
T6
T12
T1
C6
Which primary bronchus divides into three braches?
Right
Left
Right
Which aspect of the larynx covers the trachea during swallowing?
Cricoid cartilage
Epiglottis
Thyroid cartilage
Soft palate
Epiglottis
The semispinalis muscles belong to which of the following muscle groups?
Psoas muscles
Erector spinae muscles
Splenius muscles
Transversospinal muscles
Splenius muscles
The trigone is a feature of which CSF reservoir?
Fourth ventricle
Third ventricle
Superior Sagittal Sinus
Lateral ventricles
Lateral ventricles
Which of the following describes the early-stage appearance of endometrial cancer?
loculations
wall thickening
necrosis
hemorrhage
wall thickening
Which of these fractures are most likely to result in CSF leakage? (choose all correct)
Basilar skull fracture
Depressed skull fracture
Diastatic fracture
Ping-pong fracture
Basilar skull fracture
Diastatic fracture
Which of the following may be an underlying cause of SBO? (Choose all correct)
Pregnancy
Lesion
Crohn’s disease
Volvulus
Pregnancy
Lesion
Crohn’s disease
Volvulus
Which of these conditions is almost always the result of trauma to the brain? (Choose all correct)
Epidural Hemorrhage (EDH)
Intracranial bleed (ICB)
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
Subdural Hemorrhage (SDH)
Epidural Hemorrhage (EDH)
Subdural Hemorrhage (SDH)
Which of these conditions appear most similar in sectional imaging? (choose two)
Pneumothorax
Interstitial Lung Disease
Hemothorax
COPD
Interstitial Lung Disease
COPD
Which of the following is a common cause of cancer? (choose all correct)
Chemicals
Radiation
Immune conditions
Inherited mutations
Chemicals
Radiation
Immune conditions
Inherited mutations
Which of the following describes the appearance of uterine fibroids in sectional imaging? (Choose all correct)
Calcified
Cystic
Solid
Variable size
Calcified
Solid
Variable size
What is the most significant complication often associated with a depressed skull fracture?
CSF leaking
Dural tearing
All of the above
Epidural hemorrhage
Epidural hemorrhage
Which of these conditions causes blood accumulation on the periphery of the brain? (Choose all correct)
Subdural Hemorrhage (SDH)
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
Epidural Hemorrhage (EDH)
Intracranial bleed (ICB)
Subdural Hemorrhage (SDH)
Epidural Hemorrhage (EDH)
Which of these pathologic processes is most likely to be associated with hepatitis or malignancy?
Hematoma
Abscess
Cysts
Ascites
Ascites
Which of the following occurs because nuclei that move through the slice may receive only one of the RF pulses applied?
MRA
Intra-voxel dephasing
Time of flight
Entry slice phenomenon
Time of flight
Axial slices for an MR hip protocol are prescribed:
Posterior to anterior
Anterior to posterior
Superior to inferior
Inferior to superior
Superior to inferior
T/F: It is crucial that technologists obtain pertinent patient history and document the information for the interpreting radiologist.
True
SNR may be increased by using which of the following?
A small FOV
A fine matrix
A coarse matrix
Gradient echo sequences
A coarse matrix
T/F: Additional thinner axial slices are often prescribed through areas of pathology.
True
Flow from CSF in the thoracic spine can be minimized by utilizing:
Breath holds
Oversampling
Saturation Pulses
Chemical Presaturation
Saturation Pulses
T/F: False aneurysms are usually the result of knee trauma, surgery/intervention or infection.
True
T/F: Thoracic aortic aneurysms may cause no symptoms at all.
True
T/F: FLAIR stands for Fluid Low Attenuation Inversion Recovery
False
T/F: Counter current flow occurs when flowing nuclei are traveling in the same direction as slice selection.
False
What does the phase encoding gradient do?
Encode data along the SHORT axis of the anatomy
Encode data along the DIAGONAL axis of the anatomy
Both the DIAGONAL and SHORT axes
Encode data along the LONG axis of the anatomy
Encode data along the SHORT axis of the anatomy
T/F: Spin echo sequences do not compensate for magnetic field inhomogeneities, while gradient echo sequences do compensate for magnetic field inhomogeneities.
False
Select all of the following that determine the strength of an electromagnet:
The diameter of the wire used in the windings
The number of windings in the coil
The amount of current passed through the windings
The distance or spacing between the windings
The diameter of the wire used in the windings
The number of windings in the coil
The amount of current passed through the windings
The distance or spacing between the windings
Gradient strength is expressed in units of all of the following EXCEPT:
mT/m
G/cm
T/m/s
w/kg
w/kg
An inversion recovery pulse sequence begins with which of the following?
180 rephasing pulse
Gradient pulse (variable flip angle)
180 degree inverting pulse
90 degree RF pulse
180 degree inverting pulse
T/F: The scan time is the time to fill K space.
True
Where do we look up the safety of an implanted device? (Check all that apply)
www.MRISafety.com
If we remember that it is a safe implant, there is no need to look it up again.
The manufacturer’s website
Shellock’s reference manual
www.MRISafety.com
The manufacturer’s website
Shellock’s reference manual
Which of the following best describes a remedy for cross excitation?
Use a long tE
Call the service engineer
Excite alternate slices during the acquisition
Use spin echo sequences
Excite alternate slices during the acquisition
What makes a nucleus an MR active nucleus? (Select all that apply)
Atoms with a balanced mass number
Nuclei with a net spin or angular momentum
None of the above
Odd mass numbers
Nuclei with a net spin or angular momentum
Odd mass numbers
Which gradient performs slice selection for coronal slices?
X gradient
Any combination of gradients
Z gradient
Y gradient
Y gradient
What kind of information is contributed by data collected in the outer lines of K space?
Contrast
Resolution
* Weighting
Signal
Resolution
What would you do in the event of a CODE BLUE in MRI? (Select all that apply)
Activate the Code Blue response process (push the Code Blue button).
Get the patient out of the scanner and into Zone III; locking the scan room door and monitoring it when other Code Team members arrive.
Stay with the patient in the scan room until help arrives.
Begin CPR.
Activate the Code Blue response process (push the Code Blue button).
Get the patient out of the scanner and into Zone III; locking the scan room door and monitoring it when other Code Team members arrive.
Begin CPR.
T/F: Phase encoding gradient positive fills the bottom half of K space.
Fasle
What are the two extremes of contrast in MRI?
Air
T1 Recovery
Fat
Water
Fat
Water
Which of the following best describes Moire artifact?
Different chemical environments of fat and water produce a dark edge at the interface between fat and water.
Black and white banding artifact on the edge of the FOV
Fat and water are out of phase and their signals cancel each other out.
Anatomy from outside the FOV are wrapped into the image
Black and white banding artifact on the edge of the FOV
Define Contrast
The differance in optical density between adjacent structures
Define Contrast Media
Any substance introduced into the body that increases radiographic contrast or enhacnes visibility
Define Ion
A charged atomic particle
Define Ionic
Describes and atom or molecule thgat dissociates into ions when placed into water
Define Non-ionic
Describes an atom or moelcule that does not dissociate into ions when placed in water
Define Cation
Positively charged ion (Na+)
Define Anion
Negatively charged ion (Cl-)
Define Enteral
In the GI tract
Define Parenteral
Not int he GI tract
Define Monomer
A single independant molecule
Define Dimer
One or more monomers chemically joined
Define Ankylosing Spondylitis
an autoimmune condition
Define Tethered cord
visualized by an abnormally low conus medullaris
Define Spina Bifida
characterized by incomplete closure of the vertebral canal
Define Compression Fracture
caused by axial loading
Which of these rhythms is considered critical and requires immediate attention? (choose all correct)
D
B
C
A

C
A
What EKG rhythm is represented by the graph?
Bradycardia
Tachycardia
Normal Sinus Rhythm
A-fib

Tachycardia
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Perpendicular plate
Zygomatic arch
Thmoid Sinus
Maxillary sinus
Mandible
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
E
Not Labeled

Capitulum
Radial Head
Humerous
Trochlea
Corocoid process
Label the anatomy in this image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Scapular Spine
Clavicle
Sternum
Rib
Coracoid process
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not labeled

Frontal bone
Nasal bone
Frontal sinus
Maxillary bone
Zygoma
Label the antomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
E

C2
Vertebral Foramen
Mandible
Transverse Foramen
C1
Identify the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Urinary bladder
Uterus
Vagina
pubis symphysis
Ovary
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Acoustic Neuroma
Astrocytoma
Pituitary Adenoma
Metastatic brain cancer
Medulloblastoma

Metastatic brain cancer
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
COPD
Pneumonia
Tuberculosis
Pneumothorax

COPD
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Lung Cancer
Pneumonia
Interstitial lung disease
Pneumothorax

Pneumonia
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Pleural Effusion
Interstitial lung disease
Tuberculosis
Lung Cancer

Pleural Effusion
What pathology is visualized in the following image?
Zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture
Dental abscess
Nasal fracture
LeFort fracture
Blow-out fracture

Nasal fracture
What pathology is visible in the following image?
Subluxation
Compression Fracture
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Spinal Stenosis

Subluxation
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
SDH
Ischemic stroke
Medulloblastoma
EDH
ICB

SDH
What pathology is seen in this image?
Pericardial Effusion
CAD
PE
Aortic Aneurysm

Aortic Aneurysm
What pathology is visible in this image?
RCC
Renal Stone
Horseshoe kidney
Wilm’s tumor

RCC
What pathology is visible in the following image?
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Subluxation
Spinal Stenosis
Compression Fracture

Ankylosing Spondylitis
Which of the following pathologies is visualized in this image? (choose all correct)
Depressed skull fracture
Epidural hematoma
Ping-pong skull fracture
Linear skull fracture
Basilar skull fracture

Linear skull fracture
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Neoplasm
EDH
Abscess
Ischemic stroke
SDH

Ischemic stroke
What pathology is visible in this image?
RCC
TCC
BPH
Renal Stone
Prostate cancer

TCC
What pathology is visible in this image?
Kidney laceration
Wilm’s tumor
Adrenal mass
Renal Stone
RCC

Renal Stone
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Pleural Effusion
Interstitial lung disease
Lung Cancer
Tuberculosis

Tuberculosis
What pathology is visible in this image?
Liver cancer
Liver laceration
Cirrhosis
Hemangiomas

Cirrhosis
What pathology is seen in this image?
CHF
CAD
Pericardial Effusion
Myxoma

Pericardial Effusion
What pathology is visible in this image?
Appendicitis
Colitis
SBO
Crohn’s disease
Colon cancer

Crohn’s disease
Which of the following pathologies is visualized in this image? (choose all correct)
Ping-pong skull fracture
Basilar skull fracture
Linear skull fracture
Epidural hematoma
Depressed skull fracture

Epidural hematoma
Depressed skull fracture
Which of the following best describes the anatomy indicated by number twelve on the image shown below:
Scapula
Teres major muscle
Acromion
Spine of the scapula

Scapula
Which of the following indicate a severe contrast reaction? (Choose all correct)
Syncope
Hypotension
Feeling of warmth
Bronchospasm
Hives
Syncope
Hypotension
Bronchospasm
Define Antagonist
A drug or natural substance that is attractied to and blocks certain receptor sites
Define Therapeutic Index (TI)
A measure of the relative safety of a drug
Define Drug receptors
Specific biological sites located on a cell surface or within the cell
Define Agonist
A drug or natural substance withg an attraction to a specific receptor site that produces a physisiological response
Which type of isolation precaution is used for all patients at all times?
Droplet Isolation
Standard Precaution
Contact Isolation
Airborne Isolation
Standard Precaution
T/F: Hypotension and hypertension are always secondary to other clinical conditions.
False
Which boney process within the cranium contains the pituitary gland?
Foramen magnum
Sphenoid sinus
Dorsum Sellae
Sella Turcica
Sella Turcica
The thoracic cavity is further subdivided into what other body cavities? (choose all correct)
Pleural
Mediastinal
Cranial
Pelvis
Spinal
Pleural
Mediastinal
Which lobe of the left lung comprises most of that lungs anterior surface?
Any of the above
Inferior
Middle
Superior
Superior
The space outside of the dura mater is termed the:
Subdural space
Subarachnoid space
Cisterna magna
Epidural space
Epidural space
Which of the following is a retroperitoneal structure? (choose all correct)
Spleen
Aorta
Small bowel
Ascending colon
Aorta
Ascending colon
Which portion of the brainstem is identifiable as a prominent bulge near the center of the brain?
Mid brain
None of the above
Pons
Medulla oblongata
Pons
Which of these is found between the hepatic and splenic flextures?
Transverse colon
Descending colon
Cecum
Ascending colon
Transverse colon
The anterior projections of the gray matter within the spinal cord continue outside of the cord as which of the following?
Dorsal nerve roots
White matter
Ganglia
Ventral nerve roots
Ventral nerve roots
Which of these muscles marks the division between the chest and abdominal cavities?
Diaphragm
Iliac
Quadratus lumborum
Psoas
Diaphragm
Which of the following is formed at the carina?
Alveolar ducts
Secondary bronchi
Lobular bronchi
Primary bronchi
Primary bronchi
Which lobe of the left lung constitutes almost the entire lung base?
Any of the above
Superior
Inferior
Middle
Inferior
Which of the following bones joint at the acetabulum? (select all correct)
Ischium
Pubis
Ilium
Ischium
Pubis
Ilium
Spinal nerves exit the vertebral column via what feature of the spine?
Intervertebral foramina
Transverse foramina
Spinal canal
Vertebral canal
Intervertebral foramina
Which of the following is the largest cavity of the body?
Mediastinum
Cranial
Dorsal
Ventral
Ventral
Which of the following describes an organ with thin muscular walls located on the anterior abdominal wall?
Prostate
Rectum
Bladder
Uterus
Bladder
T/F: The large nerve exiting the eye is termed the ophthalmic nerve.
False
Which of the following is the largest lobe of the liver?
Right
Quadrate
Left
Caudate
Right
The primary pulmonary veins are how many in number?
Four
Two
Three
Four
The transverse foramina are a pathway for which of the following?
Spinal nerves
Vertebral arteries
Jugular veins
Spinal cord
Vertebral arteries
The mandible and maxillary bones each have which of the following processes?
Alveolar
Zygomatic
Condylar
Palatine
Alveolar
The Xiphoid process is at the level of:
T10
T11
T12
T9
T10
What is the most significant indication of hemangioma in sectional imaging?
No contrast enhancement
Delayed contrast enhancement
Absence of venous enhancement
Rim-enhancement
Delayed contrast enhancement
Which of these conditions will present with an intimal flap? Choose multiple if applicable.
Simple aneurysm
Ruptured Aneurysm
Dissecting aneurysm
Dissecting aneurysm
What is the typical presentation of GB cancer? (Choose all correct)
Notable GB atrophy
Mass completely replacing the gallbladder
Intraluminal mass
Wall thickening
Mass completely replacing the gallbladder
Intraluminal mass
Wall thickening
Which of the following statements are true concerning RCC? (Choose all correct)
unifocal or multifocal
general kidney atrophy
calcification in 30% of lesions
necrosis in large lesions
unifocal or multifocal
calcification in 30% of lesions
necrosis in large lesions
T/F: Pneumonia can infect the entire lung
True
Which of these conditions is related to vascular insufficiency?
Infectious colitis
Crohn’s disease
Ischemic colitis
Ulcerative colitis
Ischemic colitis
Which of these conditions are most likely to co-exist with a hemothorax? (choose all correct)
Pneumothorax
Fractures
Interstitial Lung Disease
Atelectasis
Pneumothorax
Fractures
Atelectasis
Which of these conditions is most likely to be associated with compensatory mechanism such as increased blood volume and increased myocardium muscle mass?
CHF
Pericardial Effusion
Myxoma
CAD
CHF
Which of these conditions results in bleeding focused in the suprasellar cistern?
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
Intracranial bleed (ICB)
Epidural Hemorrhage (EDH)
Subdural Hemorrhage (SDH)
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
Which of the lesions may grow from the spinal cord itself? (Choose all correct)
Spinal Ependymoma
Spinal Metastasis
Spinal Meningioma
Spinal Ependymoma
Spinal Metastasis
In dynamic breast imaging, lesions that ___________ are suspicious for malignancy.
show no enhancement
wash in and out quickly
wash in and out slowly
display plateau enhancement
wash in and out quickly
T/F: Patients are positioned supine head first for run-off exams.
False
Which of the following best describes ascites?
A disease in which the liver becomes permanently damaged
An infection of the spleen
The accumulation of excess fluid in the abdominal cavity
A type of kidney failure
The accumulation of excess fluid in the abdominal cavity
Which of the following best describes the ACL?
Extends from the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle to the posterior tibial spine
Extends from the medial aspect of the medial femoral condyle to the anterior tibial spine
Extends from the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle to the anterior tibial spine
Extends from the lateral aspect of the medial femoral condyle to the anterior tibial spine
Extends from the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle to the anterior tibial spine
At standard does, gadolinium has the most apparent effect on the ___ relaxation time and therefore is used as an enhancement agent on ___.
T1/T1 weighted images
T1/T2 weighted images
T2/T2 weighted images
T2/T1 weighted images
T1/T1 weighted images
T/F: A popliteal artery aneurysm is the most 2nd most common type of aneurysm in the body.
True
Which of the following is a malignant bone tumor that affects children and young adults? the tumor may start anywhere in the body, usually in the long bones of the arms and legs, the pelvis, or the chest.
Teratoma
Ewing Sarcoma
Transitional Cell Carcinoma
Chordoma
Ewing Sarcoma
T/F: Fat saturation techniques are valuable when imaging the orbits post contrast due to the presence of orbital fat.
True
The vascular signal, produced on time of flight MRA (TOF-MRA), relies on:
Velocity-induced phase shifts
Flow related enhancement
PC
MOTA
Flow related enhancement
When would we be most likely to use a STIR sequence?
MSK studies (i.e. knee, wrist)
All studies must include a STIR sequence
Head or Spine studies (to look for periventricular lesions)
CSF flow studies
MSK studies (i.e. knee, wrist)
T/F: As velocity of flow decreases, the time of flight effect decreases.
True
Which of the following best describes a remedy for cross excitation?
Use spin echo sequences
Use a long tE
Call the service engineer
Excite alternate slices during the acquisition
Excite alternate slices during the acquisition
Which of the following best describes what the “QRS” complex represents?
Atrial Systole (Contraction)
Ventricular Diastole (Relaxation)
None of the above
Ventricular Systole
Ventricular Systole
Which of the following best describes what the “P” wave represents?
Ventricular Systole
Ventricular Diastole
None of the above
Atrial Systole (Contraction)
Atrial Systole (Contraction)
T/F: Pre-saturation techniques increase the RF deposition to the patient.
True
Choose the two main uses of spatial pre-saturation from the list below.
FLAIR
SPIR
Chemical Pre-saturation
STIR
SPIR
Chemical Pre-saturation
Chemical shift is measured in which of the following units?
mm/s
ppm
G/cm
T/m
ppm
What is the most common material used to make permanent magnets?
Alnico
Titanium
Helium
Iron
Alnico
Which of the following best describes Moire artifact?
Fat and water are out of phase and their signals cancel each other out.
Anatomy from outside the FOV are wrapped into the image.
Black and white banding artifact on the edge of the FOV
Different chemical environments of fat and water produce a dark edge at the interface between fat and water.
Black and white banding artifact on the edge of the FOV
What is the approximate T1 relaxation time of fat at 1T?
200 ms
500 ms
3000 ms
2000 ms
200 ms
Which best describes the appearance of a zipper artifact?
Tissues return a high signal intensity
Anatomy folded into the FOV
A dense line on the image at a specific point.
Distortion of the image together with large signal voids.
A dense line on the image at a specific point.
Label the anatomy in this image.
A
B
C
D
E
Not labeled

SVC
Aorta
Common Carotid
Subclavian Artery
Pulmonary Arytery
Subclavian Vein
Label the anatomy in this image.
A
B
C
D
E
Not labeled

Pulmonary Vein
Right Atrium
Right Ventricle
Left Ventricle
Left Atrium
Pulmonary Artery
Label vessels in the image below.
1
2
3
4
5

Aorta
Right Coronary Artery
Left Anterior Descending Artery
Circumflex Artery
Left Coronary Artery
Label the anatomy in this image.
A
B
C
D

Basilar Artery
Brachiocephalic
Vertebral Artery
Common Carotid Artery
Internal Carotid Artery
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
E
Not labeled

Pariental Bone
Choroid plexus
Longidutical Fissures
Lateral ventrical
Parietal Lobe
Lateral Fissure
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
E

IVS
Portal vein
Stomach
Large bowel
Spleen
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
E
Not labeled

Hamate
Abductor digiti minimi muscle
Trapezoid
Trapezium
Thenar muscle
Pisiform
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
ICB
Medulloblastoma
EDH
SDH
Ischemic stroke

SDH
What pathology is seen in this image?
Spinal Meningioma
Spinal Metastasis
Spinal Ependymoma
Tethered cord

Spinal Metastasis
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Tuberculosis
Pleural Effusion
Lung Cancer
Interstitial lung disease

Pleural Effusion
What pathology is visible in this image?
Horseshoe kidney
Wilm’s tumor
Renal Stone
PKD
RCC

Wilm’s tumor
What pathology is visible in this image? (Choose all correct)
Cyst
Abscess
Neoplasm
Ascites

Neoplasm
Ascites
What pathology is visible in this image?
Uterine cancer
Uterine fibroid
Ovarian tumor
Prostate cancer
Ovarian cyst
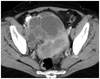
Uterine cancer
What pathology is visible in the following image?
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Compression Fracture
Subluxation
Spinal Stenosis
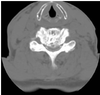
Spinal Stenosis
What pathology is visible in this image? (Choose multiple)
GB Cancer
Cholelithiasis
Pancreatitis
Pancreatic Cancer
Liver cancer

GB Cancer
What pathology is visible in the image below?
Arachnoid Cyst
Medulloblastoma
Hydrocephalus
AVM
MS

Arachnoid Cyst
What pathology is visible in this image?
Adrenal mass
Kidney laceration
RCC
Renal Stone
Wilm’s tumor

Kidney laceration
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Abscess
Astrocytoma
Medulloblastoma
SDH
Ischemic stroke

Medulloblastoma
What pathology is seen in this image?
CHF
CAD
Myxoma
Pericardial Effusion

CHF
What pathology is visible in this image?
Renal Stone
TCC
RCC
BPH
Prostate cancer

TCC
What pathology is visualized in the following image?
Nasal fracture
LeFort fracture
Zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture
Blow-out fracture
Dental abscess

Zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Medulloblastoma
Metastatic brain cancer
Astrocytoma
Acoustic Neuroma
Pituitary Adenoma

Astrocytoma
What pathology is visible in this image?
Pancreatitis
Pancreatic Cancer
GB Cancer
Liver cancer
Cholelithiasis

Pancreatic Cancer
What pathology is visible in this image?
Gastric cancer
Splenic Laceration
Cirrhosis
Lymphoma

Gastric cancer
Which of the following best describes the anatomy indicated by number twelve on the image shown below:
Acromion
Spine of the scapula
Scapula
Teres major muscle

Scapula
Define Embolism
Clotting within a blood vessel
Define Thrombus
Anything blocking a blood vessel
Define Thrombotic Embolism
Condition in which the formation or movement of a thrombus occludes a vessel causing infractions of the tissue being supplied by the vessel
Define CVA
A criticval condition in which a thrombus in the brain causes damage to the brain cells (infraction)
Define TIA
An acute episode of temporary neurological dysfunction resulting from focal cerebral ischmeia not associated with permanent cerebral infraction
Which of these medications would help to minimize nausea and vomiting?
Epinephrine
Atropine
Valium
Zofran
Zofran
The jugular foramen is formed at the junctions of what two bones?
Temporal and parietal
Sphenoid and temporal
Temporal and sphenoid
Occipital and temporal
Occipital and temporal
Most venous blood from the lower abdomen travel back to the heart via what vessel?
SVC
Aorta
Portal vein
IVC
IVC
Which of the following is the most inferior aspect of the brainstem?
Pons
Medulla oblongata
None of the above
Mid brain
Medulla oblongata
The hepatic flexture of the colon is located within which quadrant of the abdomen?
LUQ
LLQ
RUQ
RLQ
RUQ
Define Anterior/Ventral
Towards the front
Define Superior
Above
Define Posterior/Dorsal
Towards the back
Define Medial
Towards the midline
Define Inferior
Below
Define Lateral
Away from midline
The fold of the dura mater extending into the longitudinal fissure is termed the:
Superior Sagittal Sinus
Inferior Sagittal Sinus
Falx Cerebri
Falx Cerebelli
Falx Cerebri
The cranium is comprised of how many bones?
None of the above
8
22
14
8
The basilar artery is formed at the level of which of the following structure?
EAM
Jugular notch
Thyroid cartilage
Foramen magnum
Foramen magnum
Define Ipsilateral
on the same side
Define Plantar
bottom of foot
Define Contralateral
on the opposite side
Define Palmar
the anterior hand
Which fold of the dura mater covers the pituitary gland?
Tentorium
Diaphragma sellae
Falx cerebelli
Falx cerebrum
Diaphragma sellae
The spine is nearest what surface of the body?
Anterior
Rostral
Dorsal
Ventral
Dorsal
T/F: During ovulation the ovaries decrease in size.
False
Which of the major braches of the aorta feed the stomach?
IMA
SMA
All of the above
Celiac Trunk
Celiac Trunk
The ophthalmic artery is a direct branch of which of the following vessels?
Common carotid
Internal jugular
Internal carotid
External carotid
Internal carotid
Which of the meninges attaches directly to the surface of the brain?
Arachnoid
All of the above
Pia mater
Dura mater
Pia mater
Which primary bronchus is longer?
Left
Right
Left
Which of the following is a retroperitoneal structure?
Jejunum
All of the above
Duodenum
Ileum
Duodenum
Which of these conditions can be further defined with angiographic/contrast enhanced imaging? (Choose all correct)
Subdural Hemorrhage (SDH)
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
Intracranial bleed (ICB)
Ischemic stroke
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
Ischemic stroke
Which of these skull fractures is least likely to require intervention?
Linear skull fracture
Basilar skull fracture
Depressed skull fracture
Ping-pong fracture
Linear skull fracture
Which of the following describes the appearance of lung cancer in specialty imaging? (choose all correct)
Rim-enhancing
Poorly defined neoplasm
Most common in the mediastinum
Single lesions only
Rim-enhancing
Most common in the mediastinum
Which of these pathologies is sometimes accompanied by meningocele formation?
Spina Bifida
Tethered cord
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Spinal Meningioma
Spina Bifida
Which of these conditions will be accompanied by hematoma formation? Choose multiple if applicable.
Simple aneurysm
Ruptured Aneurysm
Dissecting aneurysm
Ruptured Aneurysm
Which of these conditions appears in imaging as tissue ischemia and/or areas of poor contrast perfusion?
Infarct
Aneurysm
Abscess
Malignancy
Infarct
What may be responsible for the formation of a pneumothorax? (choose all correct)
Trauma
Hemothorax
Spontaneous
Surgery
Trauma
Spontaneous
Surgery
Which of the following best describes ascites?
A disease in which the liver becomes permanently damaged
An infection of the spleen
A type of kidney failure
The accumulation of excess fluid in the abdominal cavity
The accumulation of excess fluid in the abdominal cavity
What effect does the magneto-hemodynamic effect have? Is this a permanent effect? (Check all that apply)
Increase in the amplitude of the “T” wave on EKG gating.
Increase in the amplitude of the “R” wave on EKG gating.
Permanent effect– EKG tracing continues to show an elevated wave form after the patient has had an MRI exam.
Reversible effect– EKG tracing returns to normal when the patient is removed from the static magnetic field.
Increase in the amplitude of the “T” wave on EKG gating.
Reversible effect– EKG tracing returns to normal when the patient is removed from the static magnetic field.
T/F: As velocity of flow decreases, the time of flight effect decreases.
True
Identify the two factors that determine which hydrogen nuclei align parallel and which align anti-parallel with the main magnetic field.
The strength of the external magnetic field
The thermal energy level of the nuclei
The orientation of the patient in the scanner (head first vs. feet first)
How many nuclei there are in each patient’s body
The strength of the external magnetic field
The thermal energy level of the nuclei
What is the chemical shift at 1.5 T?
22 Hz
2.2 Hz
220 KHz
220 Hz
220 Hz
Which of the following best describe spin-lattice relaxation? (Choose all that apply)
T2 Decay
Time it takes 88% of the longitudinal magnetization to recover in tissue.
Nuclei give up energy to the surrounding environment, resulting in longitudinal recovery.
T1 Recovery
Nuclei give up energy to the surrounding environment, resulting in longitudinal recovery.
T1 Recovery
Which of the following is known as the basic MRI contrast?
Proton density weighting
T2 weighting
T1 weighting
Gray imaging
Proton density weighting
Why do we use shimming?
To make the magnetic field smaller
To make the field even or homogenous
To induce a current
To apply a magnetic field
To make the field even or homogenous
What does BOLD stand for?
Type of CT scanning
Blood oxygen line developed
Body oriented level dependent
Blood oxygenation level dependent
Blood oxygenation level dependent
Which of the following statements is true in an incoherent gradient echo sequence?
The flip angle is always 10°
The system discriminates between residual and the most recently created transverse magnetization because it has a different phase value
It is not a steady state sequence
Residual transverse magnetization has the same phase as the magnetization most recently created
The system discriminates between residual and the most recently created transverse magnetization because it has a different phase value
Which of the following best describes Moire artifact?
Black and white banding artifact on the edge of the FOV
Different chemical environments of fat and water produce a dark edge at the interface between fat and water.
Fat and water are out of phase and their signals cancel each other out.
Anatomy from outside the FOV are wrapped into the image.
Black and white banding artifact on the edge of the FOV
T/F: T2 shine through occurs when lesions or areas with a very long T1 decay time remain bright on the DW or trace image.
False
Identify the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not labeled

Urinary bladder
Uterus
Vagina
Pubis symphysis
Ovary
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
Not labeled

Ulna
Flexor Tendons
Radius
Extensor Tendons
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not labeled

Stomach
Ascending Colon
Splenic fixture
Descending colon
Small bowel
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below? (choose all correct)
Astrocytoma
MS
Brain contusions
EDH
SDH

Brain contusions
EDH
What pathology is seen in this image?
Spinal Meningioma
Tethered cord
Spinal Ependymoma
Spinal Metastasis

Spinal Ependymoma
What pathology is seen in this image?
Spinal Stenosis
Compression Fracture
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Subluxation

Spinal Stenosis
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Pituitary Adenoma
Meningioma
Medulloblastoma
Astrocytoma
Metastatic brain cancer

Meningioma
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below? (choose all correct)
Ischemic stroke
SDH
ICB
Edema
Medulloblastoma

ICB
Edema
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple only if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Hemothorax
Tuberculosis
Lung Cancer
Pleural Effusion

Lung Cancer
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Acoustic Neuroma
Metastatic brain cancer
Pituitary Adenoma
Astrocytoma
Medulloblastoma

Acoustic Neuroma
What pathology is visible in this image? (choose multiple)
Crohn’s disease
Colon cancer
SBO
Appendicitis
Colitis

Colon cancer
SBO
What pathology is visible in this image?
PKD
Horseshoe kidney
Wilm’s tumor
RCC
Renal Stone

RCC
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Medulloblastoma
Astrocytoma
Pituitary Adenoma
Acoustic Neuroma
Metastatic brain cancer

Astrocytoma
What pathology is visible in this image?
Hemangiomas
Liver cancer
Liver laceration
Cirrhosis

Liver cancer
What pathology is visible in this image?
Gastric cancer
Liver cancer
Splenic Laceration
Lymphoma

Splenic Laceration
What pathology is seen in this image?
Meningocele
Myelomeningocele
Spina bifida occulta

Meningocele
What pathology is seen in this image?
Pulmonary Embolism
Aortic Aneurysm
Pericardial Effusion
CHF

Pulmonary Embolism
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Pneumothorax
Interstitial lung disease
Lung Cancer
Pneumonia

Pneumonia
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Arachnoid Cyst
Cerebral Atrophy
Meningitis
Chiari Malformation
Hydrocephalus

Meningitis
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Tuberculosis
Pneumonia
Pneumothorax
COPD

COPD
What pathology is visualized in the following image?
Blow-out fracture
Nasal fracture
Dental abscess
LeFort fracture
Zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture

Zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Tuberculosis
Pleural Effusion
Lung Cancer
Pneumonia

Tuberculosis
Pneumonia
What pathology is visible in this image?
Splenic Laceration
Lymphoma
Liver cancer
Gastric cancer

Lymphoma
Which of the following pathologies is visualized in this image? (choose all correct)
Basilar skull fracture
Depressed skull fracture
Linear skull fracture
Epidural hematoma
Ping-pong skull fracture

Ping-pong skull fracture
What pathology is visible in this image?
Ovarian tumor
Ovarian cyst
Uterine fibroid
Uterine cancer
Prostate cancer

Uterine cancer
Which of the following represents a normal oral temperature? (in degrees F)
97
94
101
100
97
The spleen is located within which quadrant of the abdomen?
RLQ
RUQ
LUQ
LLQ
LUQ
The longitudinal fissure separates which aspects of the brain?
Right and Left Cerebral Lobes
Cerebral and Cerebellar
Frontal and Parietal
Temporal and Parietal Lobes
Right and Left Cerebral Lobes
The aorta bifurcates into which of the following at the level of L4?
Internal iliac arteries
IVC
Common iliac arteries
Common femoral arteries
Common iliac arteries
Which aspect of the ventricular system is positioned between the lobes of the thalamus?
Third ventricle
Fourth ventricle
Superior Sagittal Sinus
Lateral ventricles
Third ventricle
All of the venous pathways in the brain ultimately drain into which major vessels of the neck?
Vertebral arteries
Common carotid arteries
Internal carotid arteries
Internal jugular veins
Internal jugular veins
The neck is ________ to the chest.
Inferior
Caudal
Posterior
Cephalic
Cephalic
Which aspect of the diencephalon helps to form the lateral walls of the third ventricles?
Pituitary gland
Thalamus
Epithalamus
Hypothalamus
Thalamus
Which fold of the dura mater separates the cerebrum and cerebellum?
Tentorium
Falx cerebelli
Falx cerebrum
Diaphragma sellae
Tentorium
Which of the following is the largest aspect of the brain?
Diencephalon
Cerebrum
Brainstem
Cerebellum
Cerebrum
The foramen rotundum provides passage for which of the following?
Optic Nerve
Mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve
Middle meningeal artery
Maxillary Nerve
Maxillary Nerve
Which of the following is a feature characteristic of only thoracic vertebrae?
Transverse foramina
Fused transverse processes
Large vertebral bodies
Facets and demi-facets
Facets and demi-facets
Which of the following arises from the right ventricle?
Pulmonary arteries
Aorta
Pulmonary veins
Coronary arteries
Pulmonary arteries
Which aspect of the diencephalon is considered the master endocrine gland?
Hypothalamus
Epithalamus
Pituitary gland
Thalamus
Pituitary gland
Which of these conditions is the most likely to be lethal?
Ischemic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke
Which of these conditions is most likely to present as standing and abscess formation in the RLQ?
Appendicitis
SBO
Colon cancer
Ulcerative colitis
Appendicitis
What is the most common location to visualize Crohn’s disease?
Terminal Ileum
Vesicular-Ureteral Junction
Jejunum
Duodenum
Terminal Ileum
Which of these areas are usually affected in a zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture? (choose all correct)
Maxillary sinus
Zygomatic arch
Orbital wall
Nasal bones
Maxillary sinus
Zygomatic arch
Orbital wall
Gallstones can be related to which of the following conditions? (Choose all correct)
Cirrhosis
Cholecystitis
Pancreatitis
Gall bladder cancer
Cholecystitis
Pancreatitis
Gall bladder cancer
Which of the following pathologies is imaged as filling a defect(s) in the coronary circulatory system?
CAD
CHF
Myxoma
Pericardial Effusion
CAD
With of these conditions can be identified as bowel wall thickening? (Choose all correct)
SBO
Ischemic colitis
Crohn’s disease
Ulcerative colitis
Ischemic colitis
Crohn’s disease
Ulcerative colitis
Which of the following is commonly known as washerwoman’s sprain?
De Quervain Tenosynovitis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Hamartoma
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
De Quervain Tenosynovitis
Which of the following best describes a remedy for cross excitation?
Call the service engineer
Use a long tE
Use spin echo sequences
Excite alternate slices during the acquisition
Excite alternate slices during the acquisition
How do gradients affect the main magnetic field?
They add to the main magnetic field
They give the image its shades of gray
They subtract from the main magnetic field
They alter the main magnetic field in a linear fashion
They add to the main magnetic field
They subtract from the main magnetic field
They alter the main magnetic field in a linear fashion
In a typical superconducting magnet, the direction of the magnetic field is:
Horizontal
Vertical
Hard to measure
Around the flux lines
Horizontal
T/F: The phase axis of K space is vertical and is centered in the middle of K space perpendicular to the frequency axis.
True
Multiphase images, acquired with additional modulation of magnetization, are known as:
TOF-MRA
SPAMM
PC-MRA
VENC
SPAMM
T/F: Functional imaging techniques allow MRI to be used to assess function and physiology as opposed to merely conventional structural imaging.
True
T/F: Interventional MRI includes performing biopsies in the MR suite.
True
T/F: K space is not the image.
True
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
Not labeled

Frontal
Temporal Bone
Occipital Bone
External Occipital Protuberance
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
E
Not labeled

Extensor Digitorum Brevis Muscle
Calcaneus
Navicular
Talus
Abductor Hallicus Muscle
Cuboid
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not labeled

Hepatic Artery
IVC
Splenic Artery
Celiac Trunk
SMA
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
E

Gallbladder
Kidney
Stomach
Pancreas
Splenic Vein
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Metastatic brain cancer
Astrocytoma
Medulloblastoma
Pituitary Adenoma
Acoustic Neuroma

Pituitary Adenoma
What pathology is visible in this image?
Ovarian cyst
Uterine fibroid
Uterine cancer
Ovarian tumor
Prostate cancer

Ovarian cyst
What pathology is visualized in the following image?
Dental abscess
Zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture
LeFort fracture
Nasal fracture
Blow-out fracture

Nasal fracture
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Abscess
Arachnoid Cyst
Medulloblastoma
Meningitis
SDH

Abscess
What pathology is visible in this image?
Lymphoma
Gastric cancer
Liver cancer
Splenic Laceration

Lymphoma
What pathology is visible in this image?
Wilm’s tumor
RCC
PKD
Renal Stone
Horseshoe kidney

Horseshoe kidney
What pathology is visible in this image? (Choose all correct)
Neoplasm
Hematoma
Inflammation
Laceration

Hematoma
Laceration
What pathology is seen in this image?
Tethered cord
Spina bifida
Spinal Meningioma
Spinal Ependymoma

Tethered cord
What pathology is visible in this image?
Liver cancer
Lymphoma
Splenic Laceration
Gastric cancer

Splenic Laceration
What pathology is visible in this image?
Malignant Neoplasm
Abscess
Cyst
Ascites

Cyst
What pathology is visible in this image?
Colitis
Cyst
Abscess
Neoplasm

Colitis
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
SDH
Neoplasm
EDH
Abscess
Ischemic stroke

Ischemic stroke
What pathology is visible in the image below?
EDH
ICB
Medulloblastoma
SDH
Chiari Malformation

Chiari Malformation
What pathology is visible in this image?
Hemangiomas
Liver laceration
Cirrhosis
Liver cancer

Hemangiomas
What pathology is seen in this image?
Myxoma
CHF
CAD
Pericardial Effusion

Pericardial Effusion
What pathology is visible in the image below?
Medulloblastoma
MS
Arachnoid Cyst
AVM
Hydrocephalus

MS
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Tuberculosis
Lung Cancer
Interstitial lung disease
Pleural Effusion

Tuberculosis
What pathology is visible in this image?
Pancreatic Cancer
Liver cancer
Pancreatitis
GB Cancer
Cholelithiasis

Pancreatitis
What pathology is seen in this image?
Spinal Meningioma
Spina bifida
Tethered cord
Spinal Ependymoma

Spinal Meningioma
Which of the following is a potential complication to IV therapy? (Choose all correct)
Hypothermia
Infection
Fluid-overload
Embolism
Hypothermia
Infection
Fluid-overload
Embolism
Which of these conditions is caused by a thrombus in the coronary arteries?
Cardiogenic Shock
Myocardial Infarction
Cardiac Tamponade
Congestive Heart Failure
Myocardial Infarction
Iodinated contrast for IV infusion should have an osmolarity that is:
Isotonic
Hypotonic
Hypertonic
None of the above
Isotonic
Which of these lab tests may help to indicate whether or not a patient has an infection? (choose all correct)
Hemoglobin
WBC count
Hematocrit
Platelet count
WBC count
Disrupting the body’s electrolyte balance is one risk associated with using which of the following contrast types for IV infusion?
Non-ionic
High osmolar
Ionic
Hypertonic
Ionic
The hepatic artery shares a common trunk with which of the following vessels?
Renal arteries
IMA
Splenic artery
SMA
Splenic artery
The angle of the mandible is also known as the:
Ramus
Alveolar Process
Body
Gonion
Gonion
Which of the following vessel pairs ultimately merge and form the basilar artery?
Vertebrals
External Carotids
Internal Carotids
Internal Jugulars
Vertebrals
The pre-central and post-central gyri are adjacent to which fissure of the brain?
Interhemispheric Fissure
Lateral Fissure
Longitudinal Fissure
Central Fissure
Central Fissure
As it passes behind the inguinal ligament, the external iliac artery becomes which of the following?
IVC
Common femoral arteries
Internal iliac arteries
Common iliac arteries
Common femoral arteries
Which of the follow list in order from superior to inferior the major branches of the abdominal aorta:
Celiac Trunk, SMA, Renal Arteries, IMA
Celiac Trunk, Renal Arteries, SMA, IMA
Celiac Trunk, SMA, IMA, Renal Arteries
SMA, IMA, Celiac Trunk, Renal Arteries
Celiac Trunk, SMA, Renal Arteries, IMA
Which of the following vessels supply blood to the face and scalp?
Internal Jugulars
Vertebrals
External Carotids
Internal Carotids
External Carotids
Which of the following muscle groups attach between the spinous processes and transverse processes of different vertebrae?
Erector spinae muscles
Psoas muscles
Transversospinal muscles
Splenius muscles
Transversospinal muscles
Renal pyramids are apparent in which aspect of the kidney?
Collecting system
Ureters
Cortex
Medulla
Medulla
What is most common area of the spine to identify spinal metastasis?
Sacral Spine
Thoracic Spine
Lumbar Spine
Cervical spine
Thoracic Spine
Which of these pathologies are defined as an abnormal fluid accumulation in the thoracic cavity? (choose all correct)
Pleural effusion
Pneumothorax
Pericardial Effusion
Pneumonia
Pleural effusion
Pericardial Effusion
Pneumonia
Which of the following describes the imaging characteristics of pneumonia? (choose all correct)
small to large accumulations
Common near the fissures of the lower lobes
rim-enhancing
Well-defined borders
small to large accumulations
Common near the fissures of the lower lobes
Which of these conditions appears as excessive fluid inside the abdomen but outside of the GI tract?
Colitis
Inflammation
Ascites
Abscess
Ascites
Which of these conditions is likely to be accompanied by ascites? (Choose all correct)
SBO
Appendicitis
Ulcerative colitis
Cirrhosis
Ulcerative colitis
Cirrhosis
Label the anatomy in this image.
A
B
C
Not Labeled

Mandible
Internal Jugular
Parotid Gland
Common Carotid
Label the anatomy in this image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Coracoid Process
Rib
Glenoid Process
Scapular Spine
Acromion Process
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
E
Not Labeled

Brachioradialis Muscle
Olecranon Process
Cephalic Vein
Pronator Tree Muscle
Capitulum
Radial Head
Identify the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Uterus
Bowel
Urinary bladder
Rectum
Ovary
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Radial Head
Ulna
Cephalic Vein
Ulnar Nerve
Radial Artery
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not labeled

Frontal Bone
Nasal Bone
Frontal Sinus
Maxillary Bone
Zygoma
Identify the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Ischium
Pubis
Pubis Symphysis
Femur
Ilium
Which of the following pathologies is visualized in this image? (choose all correct)
Ping-pong skull fracture
Epidural hematoma
Basilar skull fracture
Linear skull fracture
Depressed skull fracture

Basilar skull fracture
Linear skull fracture
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Tuberculosis
Pleural Effusion
Lung Cancer
Pneumonia

Tuberculosis
Pneumonia
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
SDH
Medulloblastoma
Ischemic stroke
ICB
EDH

SDH
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Medulloblastoma
Pituitary Adenoma
Metastatic brain cancer
Astrocytoma
Acoustic Neuroma

Astrocytoma
What pathology is visible in the following image?
Spinal Stenosis
Compression Fracture
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Subluxation

Ankylosing Spondylitis
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below? (choose all correct)
EDH
SDH
Brain contusions
Astrocytoma
MS

EDH
Brain contusions
What pathology is visible in this image?
Hemangiomas
Cirrhosis
Liver cancer
Liver laceration

Liver cancer
What pathology is visualized in the following image?
Dental abscess
Nasal fracture
Zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture
Blow-out fracture
Mandible Fracture

Dental abscess
Which type of isolation precaution requires special air handling units?
Airborne Isolation
Standard Precaution
Droplet Isolation
Contact Isolation
Airborne Isolation
Which of these medications would help to minimize nausea and vomiting?
Zofran
Atropine
Epinephrine
Valium
Zofran
Which of these lab tests may indicate a patients potential for bleeding? (choose all correct)
Hematocrit
Platelet count
Hemoglobin
WBC count
Platelet count
An axial plane divides the body into _______ and ________ portions.
Upper and lower
Front and back
Dorsal and ventral
Right and left
Upper and lower
The submandibular glands are located medially to what aspect of the mandible?
Body
None of the above
Ramus
Mentum
Body
Which of the following is not composed of white brain matter?
Corpus Callosum
Myelinated Axons
Cerebral cortex
None of the above
Cerebral cortex
Through which aspect of the brainstem does the cerebral aqueduct transverse?
Mid brain
None of the above
Medulla oblongata
Pons
Mid brain
What is the distinguishing feature of ovarian cancer?
Cystic changes
General enlargement
Wall thickening
Rim-enhancement
General enlargement
Which of these conditions may be further categorized as infectious, ulcerative, or ischemic?
Cysts
Colitis
Cancer
Abscess
Colitis
What is the most aggressive brain tumor?
Medulloblastoma
Pituitary adenoma
Astrocytoma
Meningiomas
Acoustic Neuroma
Medulloblastoma
Which of these conditions may account for the formation of a PE? (choose all correct)
pregnancy
Recent respiratory infection
immobility
recent surgery
pregnancy
immobility
recent surgery
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Vertebral Foramen
Sphenoid Sinus
Anterior Arch of C1
Odontoid Process
Transverse Foramina
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
E
Not Labeled

Infraspinatus Muscle
Pectoralis Major Muscle
Pectoralis Minor Muscle
Biceps Brachii Muscle
Subscapularis Muscle
Teres Minor Muscle
Label the anatomy in this image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Hyoid Bone
Internal Jugular Vein
SCM Muscle
Vertebral Artery
Parotid Gland
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
E
Not Labeled

Vastus Madialis Muscle
Sartorius Muscle
Semimembransis Muscle
Femoral Shaft
Biceps Femoris Muscle
Tibial Shaft
Label the anatomy in this image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Scapular Spine
Clavivle
Sternum
Rib
Coracoid Process
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
E
Not Labeled

Extensor Digitorium Brevis Muscle
Calcaneus
Navicular
Talus
Abducto Hallicus Muscle
Cuboid
What pathology is visible in the following image?
Spinal Stenosis
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Subluxation
Compression Fracture

Spinal Stenosis
What pathology is visible in this image?
Gastric cancer
Cirrhosis
Lymphoma
Splenic Laceration

Gastric cancer
What pathology is visible in this image?
Colitis
Colon cancer
Appendicitis
SBO
Crohn’s disease

Appendicitis
What pathology is visible in this image?
PKD
Horseshoe kidney
Wilm’s tumor
RCC
Renal Stone

Wilm’s tumor
What pathology is visible in this image? (Choose all correct)
Ascites
Hematoma
Infarct
Neoplasm

Infarct
What pathology is seen in this image?
Spinal Metastasis
Tethered cord
Spinal Meningioma
Spinal Ependymoma

Spinal Metastasis
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Pneumonia
Lung Cancer
Pneumothorax
Interstitial lung disease

Pneumonia
What pathology is visible in this image?
Neoplasm
Hematoma
Laceration
Infarct

Infarct
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Interstitial Lung Disease
Hemothorax
Pneumothorax
Tuberculosis

Hemothorax
Pneumothorax
What pathology is seen in this image?
CAD
PE
Pericardial Effusion
Aortic Aneurysm

PE
What pathology is visible in the following image?
Compression Fracture
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Spinal Stenosis
Subluxation

Ankylosing Spondylitis
What pathology is visible in this image?
Splenic Laceration
Lymphoma
Gastric cancer
Liver cancer

Lymphoma
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
E
Not Labeled

Navicular
Cuneiform
Tibia
Talus
Calcaneus
Fibula
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Vertebral Foramen
Sphenoid Sinus
Anterior Arch of C1
Odontoid Process
Transverse Foramina
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Uterus
Bowel
Urinary bladder
Rectum Ovary
Urinary bladder
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Urinary Bladder
Vagina
Psoas Muscle
Uterus
Sigmoid Colon
Identify the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Urinary Bladder
Uterus
Vagina
Pubis Symphysis
Ovary
Which of the following pathologies is visualized in this image? (choose all correct)
Ping-pong skull fracture
Basilar skull fracture
Epidural hematoma
Depressed skull fracture
Linear skull fracture

Ping-pong skull fracture
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
ICB
AVM
Astrocytoma
SDH
EDH

EDH
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Pneumothorax
Hemothorax
Interstitial lung disease
Pleural Effusion
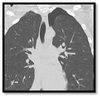
Pneumothorax
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below? (choose all correct)
SDH
Ischemic stroke
Medulloblastoma
ICB
Edema

ICB
Edema
What pathology is seen in this image?
Pericardial Effusion
Myxoma
CAD
CHF

CHF
What pathology is visible in this image? (Choose all correct)
Ascites
Cyst
Neoplasm
Abscess

Ascites
Neoplasm
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Metastatic brain cancer
Pituitary Adenoma
Medulloblastoma
Acoustic Neuroma
Astrocytoma

Astrocytoma
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple only if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Lung Cancer
Pleural Effusion
Hemothorax
Tuberculosis

Lung Cancer
What pathology is visible in the image below?
MS
AVM
Arachnoid Cyst
Hydrocephalus
Medulloblastoma

MS
What pathology is visible in this image?
RCC
TCC
Prostate cancer
BPH
Renal Stone
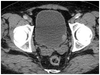
TCC
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below? (choose all correct)
Astrocytoma
Brain contusions
MS
EDH
SDH

Brain contusions
EDH
What pathology is visible in the following image?
Subluxation
Compression Fracture
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Spinal Stenosis
Subluxation
What pathology is seen in this image?
PE
Pericardial Effusion
CAD
Myxoma

Myxoma
What pathology is visible in this image?
Splenic Laceration
Lymphoma
Gastric cancer
Liver cancer
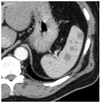
Lymphoma
What pathology is seen in this image?
Spondylolisthesis
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Compression Fracture
Tethered Cord

Spondylolisthesis
What pathology is visible in this image? (choose multiple)
SBO
Colitis
Appendicitis
Crohn’s disease
Colon cancer

SBO
Colon cancer
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Medulloblastoma
Pituitary Adenoma
Metastatic brain cancer
Acoustic Neuroma
Astrocytoma

Pituitary Adenoma
Define Narcotic
Opium-based or opium-like analgesics. These drugs are potent pain-releivers with mood-altering side effects
Define Analgesic
Pain releivers
Define Sedatives
A drug that quiets nervous excitement
Define Cardiogenic Shock
a psychologic state in which inadequate tissuer pefussion results from cardiac dysfunction
Define Myocardial Infarction
Irreversible necrosis of heart muscle secondary to prolonged ischemia
Define Congestive Heart Failure
a clinical syndrome in which the heart fails to pump blood at the rate required by the metabolizing tissues
Define Cardiac Tamponade
a clinical syndrome caused by the accumulation of fluid in the pericardial space
Label the anatomy in this image.
A
B
C
D
Not labeled

Hyoid bone
Internal jugular vein
SCM Muscle
Vertebral Artery
Parotid Gland
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not labeled

Transverse colon
Liver
Descending colon
Renal cortex
Renal Medulla
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
D
E
Not labeled

Trachea
Radial Shaft
humeral Shaft
Olecranon Process
Corocoid Process
Ulnar Shaft
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
E

IVC
Portal vein
stomach
large bowel
spleen
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
Not labeled

frontal
temporal bone
occipital bone
external occipital protuberance
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Medulloblastoma
Pituitary Adenoma
Astrocytoma
Metastatic brain cancer
Acoustic Neuroma

Metastatic brain cancer
What pathology is visible in this image?
Abscess
Ascites
Cyst
Malignant Neoplasm

Cyst
What pathology is visible in this image?
Infarct
Laceration
Hematoma
Neoplasm

Infarct
What pathology is visible in this image?
Liver cancer
Liver laceration
Hemangiomas
Cirrhosis

Liver cancer
What pathology is visible in this image? (Choose multiple)
Cholelithiasis
Pancreatic Cancer
Liver cancer
GB Cancer
Pancreatitis

Liver cancer
GB Cancer
What pathology is seen in this image?
Pericardial Effusion
Aortic Aneurysm
PE
CAD

Aortic Aneurysm
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
EDH
ICB
Astrocytoma
AVM
SDH

EDH
What pathology is visible in this image? (choose multiple)
Colon cancer
SBO
Crohn’s disease
Colitis
Appendicitis

Colon cancer
SBO
What pathology is seen in this image?
Tethered cord
Spinal Meningioma
Spinal Metastasis
Spinal Ependymoma

Spinal Metastasis
What pathology is visible in this image?
Colon cancer
Appendicitis
SBO
Crohn’s disease
Colitis

Colitis
What pathology is seen in this image?
Myxoma
Pericardial Effusion
CAD
CHF

CHF
What pathology is seen in this image?
PE
CAD
Myxoma
Pericardial Effusion

CAD
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Acoustic Neuroma
Astrocytoma
Medulloblastoma
Metastatic brain cancer
Pituitary Adenoma

Acoustic Neuroma
What pathology is visible in this image?
RCC
Renal Stone
Wilm’s tumor
Horseshoe kidney
PKD

PKD
What pathology is visible in this image?
Pancreatic Cancer
GB Cancer
Cholelithiasis
Liver cancer
Pancreatitis

Pancreatitis
Which of these procedures is focused on the absence of pathogenic organisms but does not require items to be sterile?
Medical Asepsis
Sterile Technique
Medical Asepsis
Define Non-toxic
elicits minimal adverse affects in the body
Define Stable
Does not break down in the body
Define Inert
Doe snot readily react woth other chemicals or medications
Define High Carrier Efficiency
small doses maximize contrst enhancement
Define Osmotically appropriate
Osmolarity of contrast agent matches that of surrouding tissue
Define Specificity
Contrast agewnt engages only the organs/tissues it is intended to effect
Define Non-flocculating
Does no cluster or clump together (especially Barium Sulfate suspensions)
Define Rapid Elimination
IS not retained or stored in the body
Label the anatomy in the following image
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Temporal Lobe
Cerebellum
Sella Turcica
Tentorium
Occipital Lobe
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Lung
Trachea
Aorta
Esophagus
SVC
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
E
F
Not Labeled

ALL
Intervertebral Disc
PLL
Spinous Process
Interspinous Ligament
Supraspinous Ligament
Ligimentum Flavum
The lungs are connected to the mediastinum via what structure?
Interlobular fissures
Mediastinal pleura
Lung roots
Visceral pleura
Lung roots
What pathology is visible in the following image?
Spinal Stenosis
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Subluxation
Compression Fracture

Spinal Stenosis
What pathology is visible in this image?
Gastric cancer
Cirrhosis
Lymphoma
Splenic Laceration

Gastric cancer
What pathology is visible in this image? (Choose all correct)
Ascites
Hematoma
Infarct
Neoplasm

Infarct
What pathology is visible in this image? Mark multiple if more than one pathology is visible or if clinical correlation is needed to distinguish between pathologies with similar imaging characteristics.
Interstitial Lung Disease
Hemothorax
Pneumothorax
Tuberculosis

Hemothorax
Pneumothorax
Which of these lesions will only be seen growing near the periphery of the spinal cord?
Spinal Metastasis
Spinal Ependymoma
Spinal Meningioma
Spinal Meningioma
What pathology is visible in the following image?
Compression Fracture
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Spinal Stenosis
Subluxation

Ankylosing Spondylitis
If a patient will not fit in the spine coil with the anterior aspect snapped down, which of the following would be the next best option to obtain the best possible SNR?
Use the anterior piece of the head coil
Use a c-collar
Use a flex coil
Use a halo
Use a flex coil
The linguine sign is:
indicative of breast cancer
indicative of thoracic aortic aneurysm
indicative of intracapsular implant rupture
a slice imaging plane for cardiac MRI
indicative of intracapsular implant rupture
If the R to R interval is 500 ms, the trigger window is 10%, and the trigger delay is 50 ms, what is the time available to acquire data?
500 ms
400 ms
460 ms
310 ms
400 ms
T/F: When using gadolinium, the T1 relaxation time of the water is reduced so enhancing lesions (such as tumors associated with free water) appear bright on a T1 weighted image.
True
Which artifact is produced as a result of motion of flowing nuclei?
Phase ghosting
Zipper effect
Aliasing
Truncation
Phase ghosting
How much does a typical patient’s heart rate vary during an exam?
10- 20 %
40- 50%
20- 30%
60- 70%
10- 20 %
Which sequence is considered the gold standard for MR imaging?
SSFP
Gradient Echo
Spin Echo
Coherent Gradient Echo
Spin Echo
Which of these lab values may indicate a patient’s potential for bleeding (choose all correct)
INR
Platelets
PTT
Hematocrit
INR
Platelets
PTT
How many vertebra of the spine are movable?
30
33
23
24
24
Which of the following describes a sac-like organ with variable appearance and orientation located in the center of the pelvic floor?
Prostate
Uterus
Bladder
Rectum
Uterus
A thoracic vertebra may be identified as it has which of the following?
Costal facets
Large vertebral body
Transverse foramina
All of the above
Costal facets
T/F: The external borders of the spinal cord are composes of white matter.
True
The gallbladder is located within which quadrant of the abdomen?
LLQ
RLQ
RUQ
LUQ
RUQ
The most superior bone of the pelvic bone is the:
Ischium
Ilium
Pubis
Ilium
Which of the following does not help supply blood to the Circle of Willis?
External Carotids
None of the above
Internal Carotids
Vertebrals
External Carotids
The sphenoid sinus is located below which aspect of the sphenoid bone?
Lesser wing
Optic Canal
Greater wing
Sella turcica
Sella turcica
What pathology is visible in this image?
Abscess
Ascites
Cyst
Malignant Neoplasm

Cyst
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Acoustic Neuroma
Pituitary Adenoma
Metastatic brain cancer
Astrocytoma
Medulloblastoma

Medulloblastoma
What pathology is visible in this image?
Liver cancer
Liver laceration
Hemangiomas
Cirrhosis

Liver cancer
What pathology is visible in this image? (Choose multiple)
Cholelithiasis
Pancreatic Cancer
Liver cancer
GB Cancer
Pancreatitis

Liver cancer
GB Cancer
Which of these conditions might demonstrate necrosis and cavity formation in specialty imaging?
Pleural effusion
Pneumonia
Tuberculosis
Pericardial Effusion
Tuberculosis
What pathology is seen in this image?
Tethered cord
Spinal Metastasis
Spinal Meningioma
Spinal Ependymoma

Tethered cord
What is the most common cause of kidney laceration?
Hemorrhage
Thrombus
Infarct
Trauma
Trauma
What pathology is visible in this image?
Colon cancer
Appendicitis
SBO
Crohn’s disease
Colitis

Colitis
Which of these conditions is almost always associated with a skull fracture? (Choose all correct)
Epidural Hemorrhage (EDH)
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
Intracranial bleed (ICB)
Subdural Hemorrhage (SDH)
Epidural Hemorrhage (EDH)
What pathology is seen in this image?
PE
CAD
Myxoma
Pericardial Effusion

CAD
Which of these neoplasms is most likely to be associated with cystic developments in the intramedullary canal?
Spinal Ependymoma
Spinal Meningioma
Spinal Metastasis
Spinal Ependymoma
Which of the following items are T1 and T2 relaxation times dependent on (hint: there are three)?
How well the molecular tumbling rate matches the Larmor frequency of hydrogen
The inherent energy of the tissue
The number of electrons orbiting the nucleus
How closely packed the molecules are
Spin-spin interactions of oxygen atoms
How well the molecular tumbling rate matches the Larmor frequency of hydrogen
The inherent energy of the tissue
How closely packed the molecules are
What do T1 images typically best demonstrate?
Anatomy
Everything
Bright fluid
Pathology
Anatomy
T/F: Generally speaking, gradient echo sequences are faster than spin echo sequences.
True
What are the three types of motion present in an atom? (Select all that apply)
Electrons spinning on their own axis.
Electrons orbiting the nucleus.
Nuclei spinning around each other.
The nucleus itself spinning about its own axis.
Electrons spinning on their own axis.
Electrons orbiting the nucleus.
The nucleus itself spinning about its own axis.
In which direction does chemical shift artifact occur? (Choose all that apply)
Anterior to Posterior
Frequency Axis
Phase Axis
Slice Select Axis
Frequency Axis
T/F: The “warm zone” in MRI is the scan room itself.
False
Which of these procedures should be used during procedures that involve entry into a sterile body cavity?
Medical Asepsis
Sterile Technique
Sterile Technique
Which of the following could potential cause a vasovagal response? (Choose all correct)
Pain
Fear
Anxiety
Medications
Pain
Fear
Anxiety
Medications
Which of the following applies to a patient with standard precautions? (Choose all correct)
Hand hygiene
Safe injection practices
Respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette
Use of personal protective equipment
Hand hygiene
Safe injection practices
Respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette
Use of personal protective equipment
Which of the following is a feature characteristic of only sacral vertebrae?
Transverse foramina
Large vertebral bodies
Fused transverse processes
Facets and demi-facets
Fused transverse processes
Which aspect of the ear contains the auditory ausicles?
Middle
External
Auricular portion
Inner
Middle
he spinal cord ends at the level of which vertebra?
C1
L1
T1
S1
L1
Which of the following vessels do not enter the skull?
Vertebrals
External Carotid
Internal Carotid
None of the above
External Carotid
Label the anatomy in this image.
A
B
C
D
E
F

Internal jugular vein
SVC
Parotid Gland
SCM
Common Carotid
Trachea
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

MAstoid Air Cells
C1
C2
Transverse Process
Sphenoid Sinuses
Which of the following is not an aspect of the cerebrum?
Vermis
Corpus Callosum
Cerebral Cortex
Insula
Vermis
The most superior point of the junction of what two bones is referred to as the vertex of the skull?
Temporal
Frontal
Sphenoid
Parietal
Parietal
Label the anatomy in the image below.
A
B
C
Not Labeled

Ulna
Flexor Tendons
Radius
Extensor Tendons
The folds of the brain’s surface may be referred to as:
Sulci
Fissures
Sinuses
Gyri
Gyri
Label the antomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
E

C2
Vertebral Foramen
Mandible
Transverse Foramen
C1
What is the most important indication of SBO?
Bowel distention
Bowel inflammation
Hemorrhage
Abscess
Bowel distention
Which of these fractures are most likely to affect children? (choose all correct)
Diastatic fracture
Ping-pong fracture
Basilar skull fracture
Depressed skull fracture
Diastatic fracture
Ping-pong fracture
What pathology is responsible for the appearance of this image?
GB Cancer
Cholelithiasis
Pancreatitis
Pancreatic Cancer
Liver cancer

Cholelithiasis
Which of these conditions will always present in imaging as an area of infarct in the brain? (choose one or both)
Hemorrhagic stroke
Ischemic stroke
Ischemic stroke
What pathology is visible in the image below?
EDH
Medulloblastoma
SDH
Chiari Malformation
ICB

Chiari Malformation
Typical spin echo sequences produce images known as:
Bright blood imaging
Subtraction images
Black blood imaging
Phase imaging
Black blood imaging
Which of the following sequence(s)/techniques(s) can be used to produce images where vessels appear dark?
GMN
The Application of Pre-Sat Pulses
Contrast Enhancement
Gradient Echo Sequences
Spin Echo Acquisitions
The Application of Pre-Sat Pulses
Spin Echo Acquisitions
T/F: Using a long echo train decreases the SAR.
False
Which type of motion can we compensate for in MRI?
Second order motion acceleration
All of those listed can be compensated for
First order laminar flow
Third order motion jerk
First order laminar flow
How can we reduce truncation?
Increase the number of phase encoding steps
Increase the TE
Increase the number of frequency encoding steps
Increase the TR
Increase the number of phase encoding steps
T/F: The appendix extends from the cecum
True
Which of the following terms refers to the lateral aspects of the vertebral arch to which the vertebral body attaches?
Articular Facets
Pedicle
Lamina
Transverse process
Pedicle
The right lung has how many lobes?
Three
Two
One
Three
The portal vein is formed by the confluence of which of the following vessels? (Choose all correct)
SMV
Renal veins
IMV
Splenic vein
SMV
IMV
Splenic vein
Structures within which portion of the ear also control equilibrium and balance?
Inner
Middle
External
Tympanic portion
Inner
Label the anatomy in the following image.
A
B
C
D
Not Labeled

Liver
Large Bowel
Small Bowel
Aorta
IVC
Match the following external landmarks with the corresponding vertrebal level:
Costal Margin
Symphysis Pubis
Mastoid Tip
Umbilicus
Iliac Crest
ASIS
Vertabra Prominens
Jugular Notch
Sternal Angle
L3
Coccyx
C1
L3/4
L4
S1
C7
T2/3
T4/5
The superior aspect of the lungs are grossly termed the:
Mediastinal surface
Diaphragmatic surface
Apex
Base
Apex
Which of the following is a feature characteristic of only lumbar vertebrae?
Transverse foramina
Large vertebral bodies
Fused transverse processes
Facets and demi-facets
Large vertebral bodies
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Astrocytoma
Metastatic brain cancer
Pituitary Adenoma
Acoustic Neuroma
Medulloblastoma

Astrocytoma
What pathology is seen in this image?
CAD
Pericardial Effusion
CHF
Myxoma

CHF
Adrenal mass
Renal Stone
Kidney laceration
RCC
Wilm’s tumor

Wilm’s tumor
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
Abscess
Astrocytoma
Medulloblastoma
MS
Arachnoid Cyst

Abscess
What pathology is visible in this image? (Choose all correct)
Ascites
Cyst
Abscess
Neoplasm

Ascites
Neoplasm
What pathology is visible in this image?
Wilm’s tumor
Adrenal mass
Kidney laceration
Renal Stone
RCC

Renal Stone
What pathology is visible in this image?
Neoplasm
Abscess
Colitis
Cyst

Colitis
Which of these pathologies is visualized in the image below?
EDH
ICB
SDH
AVM
Astrocytoma

EDH
What pathology is visible in the following image?
Compression Fracture
Spondylolisthesis
Spinal Stenosis
Ankylosing Spondylitis

Spondylolisthesis
What pathology is visible in this image?
Abscess
Cyst
Neoplasm
Ascites

Abscess
Lesions in the brain may be associated with which of these intracranial conditions? (choose all correct)
Ischemia
Mass effect
Bleeding
Edema
Ischemia
Mass effect
Bleeding
Edema
What pathology is visible in this image?
Colon cancer
Appendicitis
Crohn’s disease
Colitis
SBO

SBO
What pathology is visible in this image?
SBO
Appendicitis
Colon cancer
Crohn’s disease
Colitis

Colon cancer
What pathology is visible in this image? (Choose all correct)
Laceration
Hematoma
Inflammation
Neoplasm

Laceration
Hematoma
Functional imaging techniques include which of the following (check all that apply)?
fMRI
Perfusion imaging
DWI
Spectroscopy
fMRI
Perfusion imaging
DWI
Spectroscopy
What is VENC?
Velocity encodin - a parameter that must be specified before performing a phase-contrast (PC) MRI orMRA study.
How do you set VENC correctly?
VENC, measured in cm/sec, should be chosen to encompass the highest velocities likely to be encountered within the vessel of interest.
What does MOTSA stand for?
Multiple Overlapping Thin Slab Acquisitions


